Discover the majesty that soars through the Connecticut skies with the remarkable birds of prey. From the majestic ospreys to the agile hawks, these aerial predators leave us in awe. Join us on a journey as we explore their world, learn about their incredible adaptations, and witness their hunting prowess. Prepare to be captivated by the beauty and grace of Connecticut’s avian rulers of the sky.
List of Birds of Prey in Connecticut:
Red-tailed Hawk – As the most common hawk species in Connecticut, Red-tailed Hawks are often observed soaring above open fields, highways, and woodlands throughout the state.
Broad-winged Hawk – This medium-sized hawk is relatively common, especially during spring and autumn migration periods. Prime sightings occur in areas like Litchfield County.
Cooper’s Hawk – Known for their agile hunting in wooded areas, Cooper’s Hawks can be found across Connecticut, especially in suburban regions.
Red-Shouldered Hawk – These hawks are common in forests and woodlands across the state, including the Mashamoquet Brook State Park.
Sharp-shinned Hawk – While elusive due to their preference for dense forests, these birds can be spotted during migration seasons in areas like the Audubon Center in Greenwich.
Northern Harrier – Often seen in open habitats like marshes and grasslands, the Northern Harrier can be found in areas such as the Hammonasset Beach State Park.
Northern Goshawk – These powerful birds are less common, preferring remote forests in areas like the Shenipsit State Forest.
Rough-legged Hawk – A winter visitor, these hawks are the least common and can occasionally be spotted in open areas during colder months.
American Kestrel – The most common falcon in Connecticut, they are often seen hovering over fields or perched on telephone wires along country roads.
Peregrine Falcon – Having made a successful recovery, these fast raptors nest on tall structures and can often be seen in urban areas like Bridgeport and Hartford.
Merlin – Less common than the other falcons, these birds are mainly seen during their migration seasons, particularly in coastal regions.
Bald Eagle – These majestic birds have made a strong recovery and are now regularly sighted near large bodies of water, particularly along the Connecticut River.
Golden Eagle – These eagles are quite rare in Connecticut, with occasional sightings mainly during late autumn in areas like the Quinebaug Hills.
Great Horned Owl – As the most common owl species in Connecticut, these can be found in forests and large parks, including the Sleeping Giant State Park.
Eastern Screech-Owl – These small owls can be found in woods and suburbs across Connecticut, often heard more than seen due to their nocturnal nature.
Barred Owl – A frequent resident of Connecticut’s forests, they can be spotted in wooded areas across the state, including in areas like the Naugatuck State Forest.
Barn Owl – More common in open farmlands and marshes, Barn Owls can be found in areas like the Stewart B. McKinney National Wildlife Refuge.
Long-eared Owl – These owls are secretive and more challenging to spot, but can occasionally be found in dense woodlands.
Northern Saw-whet Owl – These tiny owls can be found in forested habitats, particularly during migration seasons.
Short-eared Owl – These owls are mostly winter visitors and can occasionally be spotted in open areas such as the grasslands of Fairfield County.
Osprey – As common summer residents, Osprey can be found near water bodies throughout Connecticut, with notable nesting sites along the coast and the Connecticut River.
The snowy owl and turkey vultures are very rare visitors to Connecticut.
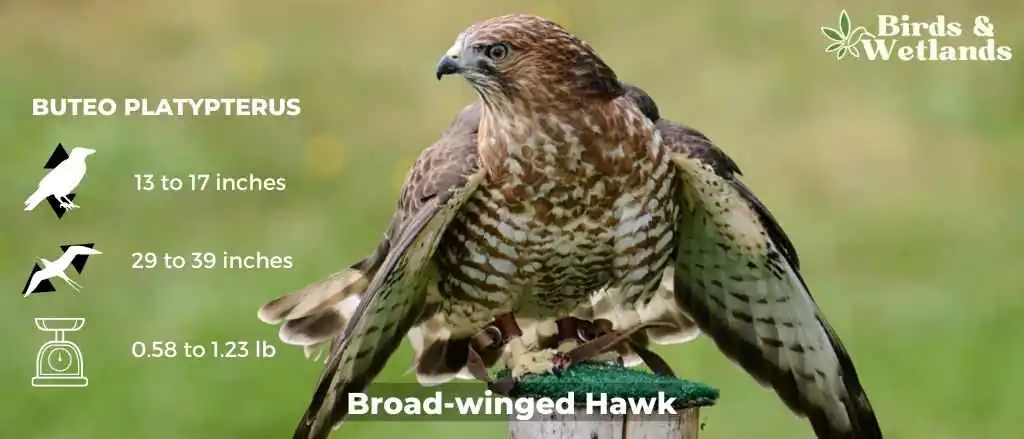
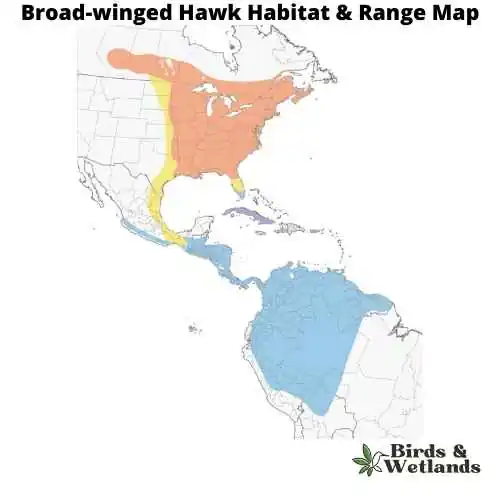
Broad-winged Hawk (Buteo platypterus)

Broad-winged Hawk Sound
The Broad-winged Hawk holds a commanding presence as one of the largest hawks in the world, known for its broad wings. Its formidable size is a testament to its prowess as a bird of prey, effortlessly navigating the open skies in search of food.
Their distinctive appearance sets them apart. The adults exhibit a striking black and white pattern, complemented by a rusty breast and buff underparts and brown wings. In contrast, juveniles are adorned with a brown plumage, marked by pale edges on their feathers, adding to their distinctive youthful charm.
These hawks are most commonly found in open areas, such as farmlands or grasslands interspersed with scattered trees, which provide optimal conditions for when hawks hunt.
When it comes to their diet, Broad-winged Hawks feed on small rodents like mice, rats, squirrels, rabbits, and voles. Broad winged hawks breed during the spring and summer months then migrate to central and south America.
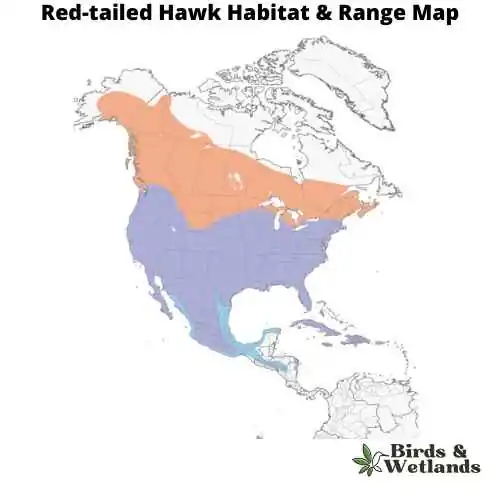
Red-tailed Hawk (Buteo jamaicensis)

The Red-tailed Hawk is a large bird of prey that is commonly found across North America. This species is part of the genus Buteo, which is often referred to as the “true hawks,” and includes more than two dozen species of raptors.
Red-tailed Hawks have a robust size, ranging from 18 to 26 inches in length and sporting a wingspan that can exceed 4 feet. They have a broad, rounded set of wings and a short, wide red tail. This species is most easily recognized by its rich, rust-colored tail, which gives it its common name. However, juvenile hawks might not yet have this distinctive feature.
Their feathers are generally dark brown on their dorsal side (back) with a lighter, often speckled, ventral side (front). The intensity and pattern of their plumage can vary significantly based on their age and geographic location, as there are about 14 recognized subspecies of Red-tailed Hawks.
As for their diet, Red-tailed Hawks are carnivores and have a broad diet that includes rodents, ground rabbits, reptiles, and other birds. They are skilled hunters that typically sit on high perches and use their keen eyesight to spot potential prey. Once they have identified a target, they swoop down to capture it with their powerful talons.
Red-tailed Hawks mate for life and build nests high off the ground, often in tall trees or on cliff edges. Their nests are made of sticks and can be quite large. They typically lay 1-3 eggs per year, which are incubated by both parents.
Red-tailed Hawk Sound
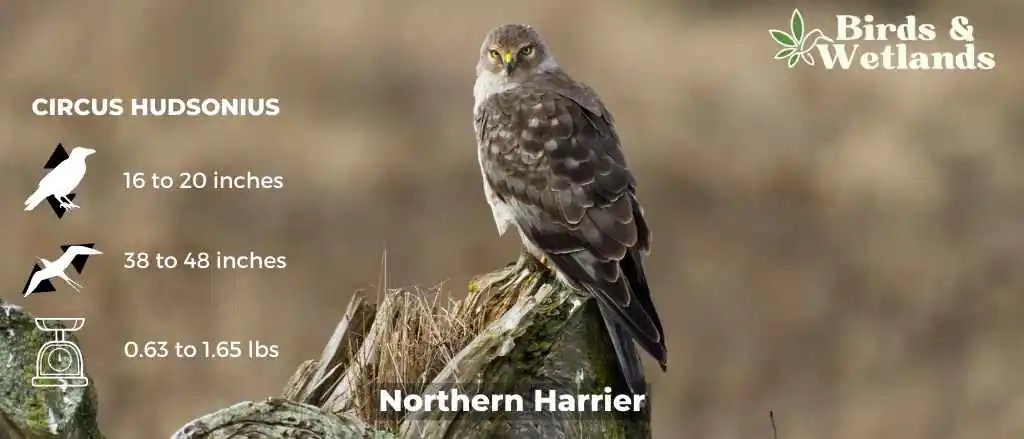
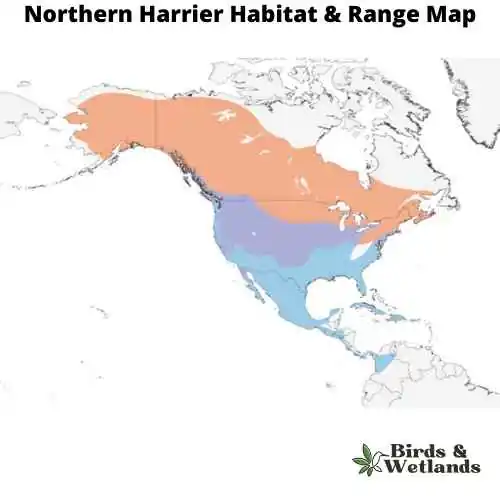
Northern Harrier (Circus hudsonius)

Listen:
The Northern Harrier is a medium-sized, slender hawk.
Adult birds are gray above, with pale bars on the wing feathers and white markings on the underwings and a white rump patch. The breast is barred with black and white, and the belly is streaked with brown.
They prefer open areas, such as grasslands and marshes, but can be found in almost any open habitat except dense woods.
Northern Harriers are opportunistic hunters that feed on small mammals such as mice, voles and rabbits as well as birds including quail, grouse and ducks. They hunt by flying low over open spaces such as fields or marshes.
Northern harrier nests on the ground in lowlands or hillsides near water bodies. It lays two to four eggs which hatch after 24 days of incubation by both parents. The chicks fledge after 30 days of hatching and remain dependent on their parents for another three weeks during which they learn how to fly.
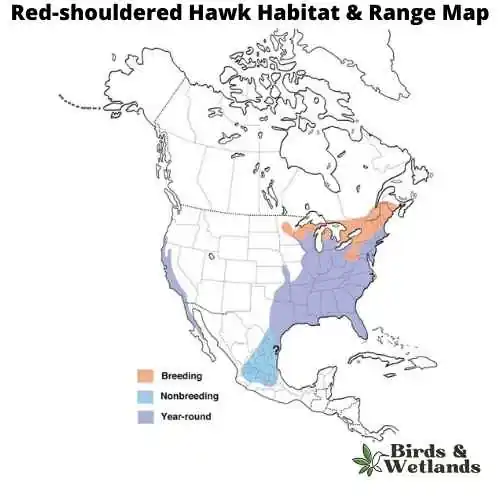
Red-shouldered Hawk (Buteo lineatus)
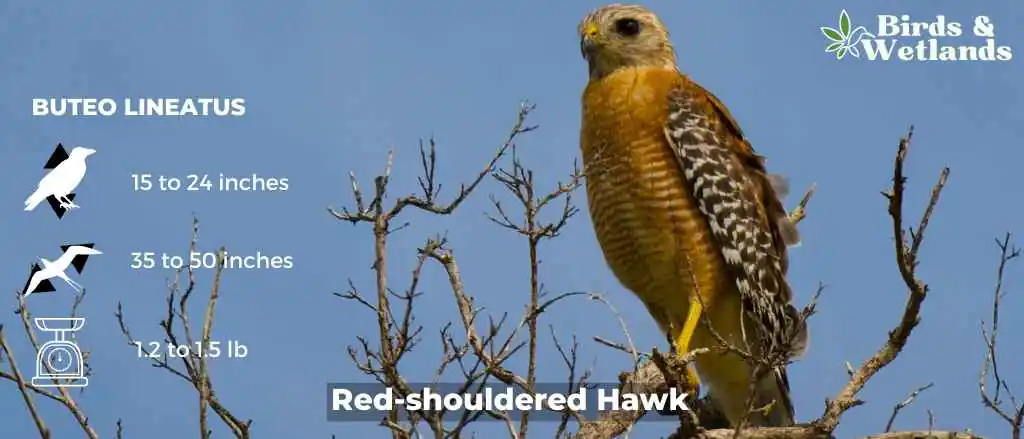

Listen:
The red-shouldered hawk are medium sized birds of prey, part of the buteo hawks family. It can be distinguished from other hawks by its reddish iris and pale legs.
The adult has rusty red upperparts, white underparts, a black chin and throat, and a reddish brown stripe over each eye, reddish brown heads and a strongly banded tail. The tail is reddish brown with two paler bands across it and they have white checkered wings. Juveniles are brown with dark barring and have pale fringes on the feathers of their wings.
Red-shouldered hawks nest in trees, though they also inhabit manmade structures including barns, bridges, and buildings. They prefer wooded areas with an open canopy but will use other places as well for nesting such as shrubs and hedges if needed.
The red-shouldered hawk’s diet – they eat small mammals such as ground squirrels, rabbits, voles, mice and rats. They also eat birds such as quail, pigeons and doves; reptiles including snakes; amphibians; fish; crustaceans; insects; and carrion (dead animals).
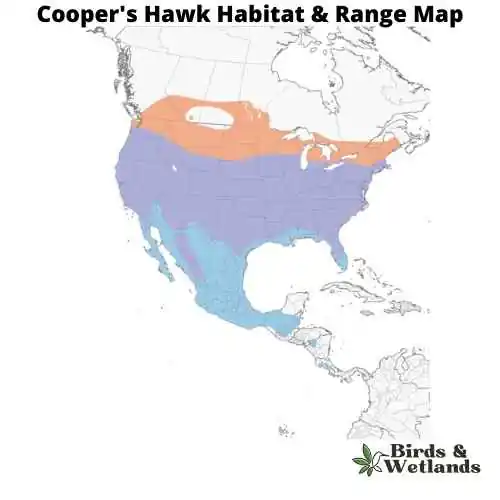
Cooper’s Hawk (Accipiter cooperii)
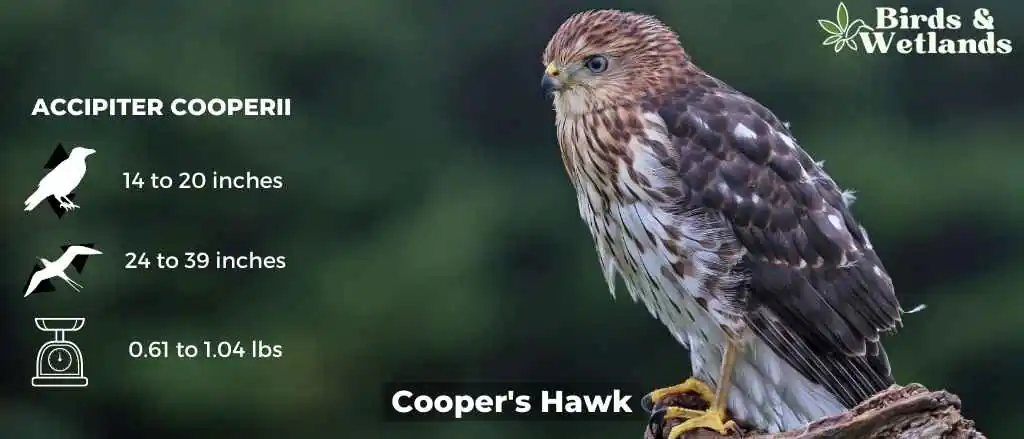

Listen:
The Cooper’s Hawk is a medium-sized bird of prey native to North America. Known for its agility and speed, it is part of the Accipitridae hawk species, which also includes other hawks, eagles, and kites.
Cooper’s Hawks are typically about 14 to 20 inches in length, with a wingspan ranging from 27 to 36 inches. They are known for their distinctive long, rounded tails and short, rounded wings. They have a steely blue gray top, with rusty bars on their underparts and thick, dark bands on their tails.
The Cooper’s Hawk is a skilled predator, primarily hunting birds and small mammals. They are adept at hunting in both dense forests and open areas, often catching prey mid-air in high-speed pursuits. They have also been known to visit the backyard bird feeder, not for the seed, but to prey on the smaller birds that gather there.
Cooper’s Hawks often build nests in dense tree canopies where they are well concealed. The female usually lays 3 to 5 eggs, and both parents share incubation duties. The young hawks fledge after about a month but will stay close to the nest, relying on their parents for food as they learn to hunt.
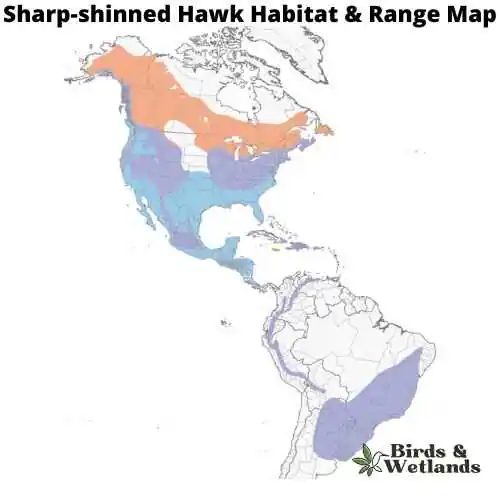
Sharp-shinned Hawk (Accipiter striatus)
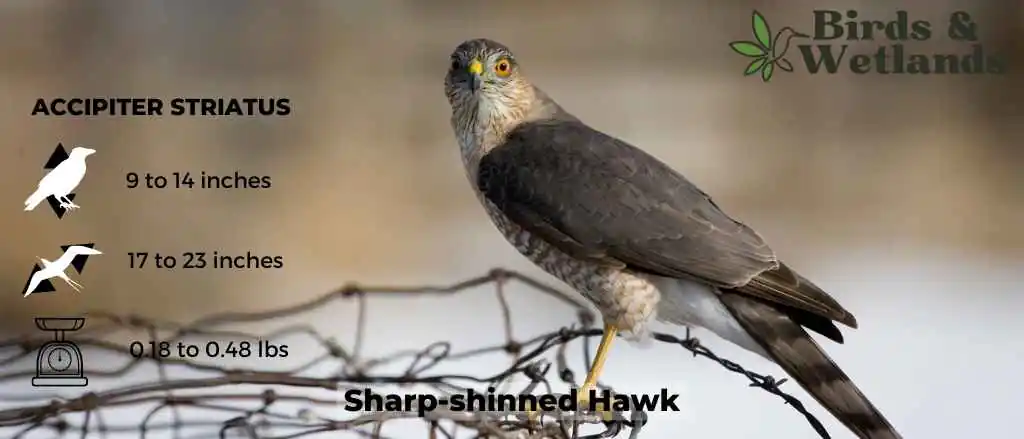

Listen:
The adult bird is brown on top and white underneath, with a dark brown band across its chest. It has short, rounded wings and a long tail that makes it look larger than it actually is. Adult sharp shinned hawks have black eyes, which are surrounded by white feathers. The female Sharp-shinned Hawk is browner than the male, who has darker brown markings on his back.
Sharp-shinned Hawks prefer open country for their habitat, including fields and meadows where they can hunt for mice and other small animals. They can be found throughout the United States but are most common in the east.
Sharp-shinned Hawks eat mostly small birds, such as sparrows and warblers, as well as small mammals such as mice and gophers. They catch prey by surprise using their incredible speed and agility, diving out of the sky at speeds up to 200 mph.
Sharp-shinned Hawks have an unusual hunting style for hawks—they prefer to catch their prey from perches above trees or telephone wires, rather than swooping down from above like most other hawks do and can often be seen hunting near bird feeders.
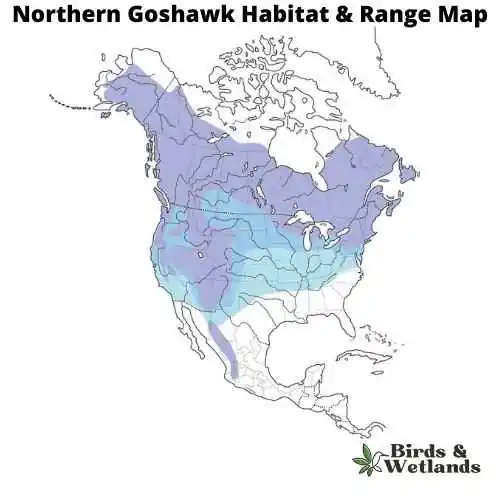
Northern Goshawk (Accipiter gentilis)
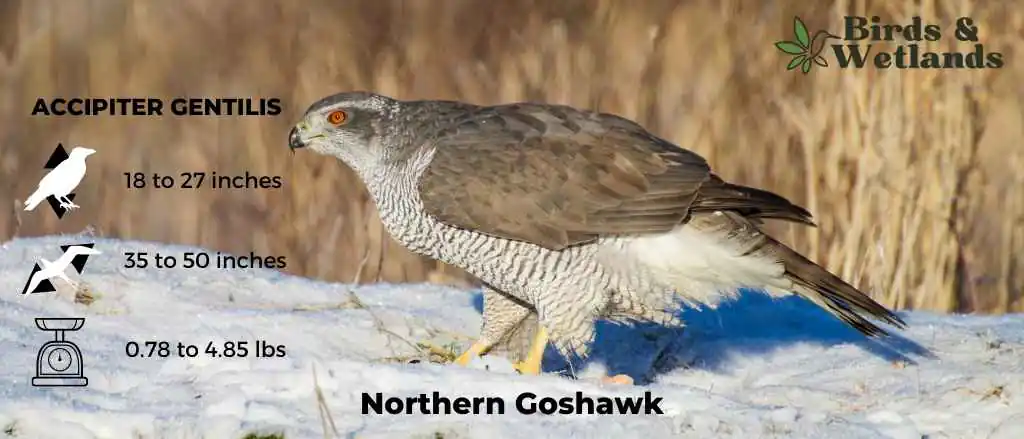

Listen:
The Northern Goshawk is a medium-sized hawk that is found in North America, Europe and Asia. It has brown eyes, a large sharp beak, and dark brown plumage on its upperparts and head, with white underparts that are spotted with brown barring. Its tail feathers are grayish-black with a dark band near the tip.
Northern goshawks eat squirrels, rabbits, grouse, woodchucks and other small mammals like voles or mice (which they often eat whole). They will also take larger prey such as deer fawns or even adult deer if they have no other choice. They have broad wings with long feathers that allow them to glide through the air when they catch their prey. They also have an excellent sense of smell which helps them locate their food source.
The Northern Goshawk builds its nest in a tree cavity or on a ledge, usually on the edge of an open area so it can easily see prey below. The female lays 3 to 5 eggs over two days and incubates them for 28 to 30 days while the male brings food to her every few hours until they hatch. The young fledge after about 6 weeks and leave the nest when they are about 10 weeks old.
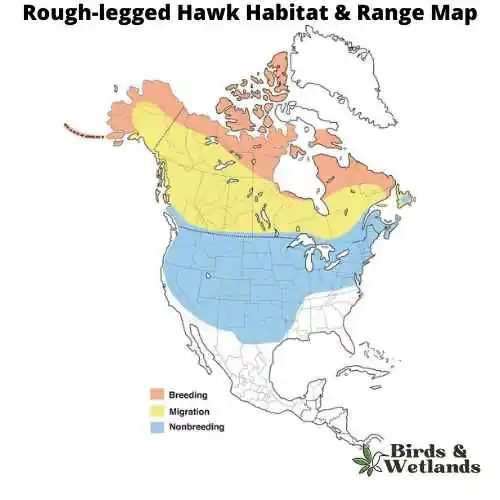
Rough-legged Hawk (Buteo lagopus)

Rough-legged Hawk Sound
The Rough-legged Hawk is a large, raptor that is native to North America. It is also known as the American Rough-legged Hawk. Scientific Name: Buteo lagopus
The Rough-legged Hawk is a medium-sized hawk with a distinctive appearance, with dark brown feathers on its back and light brown feathers on its underside and broad thin wings. The hawk’s legs are also covered in dark feathers, which help to distinguish it from other species of hawk. The tail is barred with black and white. They have yellow eyes and dark feet.
Rough-legged Hawks hunt from above ground level, swooping down to catch its prey in its talons. When hunting for food, they prefer to eat small mammals such as squirrels and rabbits but will also eat birds if there aren’t any small mammals available. Although they eat a variety of small animals including birds, rodents, bats and reptiles, they rely heavily on fish for food during breeding season because it provides them with protein and calcium needed to produce eggs.
American Kestrel (Falco sparverius)

American Kestrel Sound
Scientific Name: Falco sparverius
Length: 8.7 to 12.2 in
Wingspan: 20–24 in
Weight: 3.0–5.8 oz
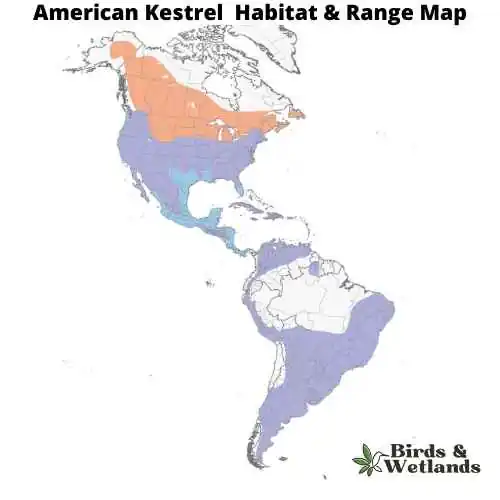
The American Kestrel, often recognized as the smallest and most brightly colored falcon in North America, exhibits a stunning array of rufous, blue and gray hues in its plumage. This bird, ranging in size from a mere 22 to 31 cm, carries distinct black facial markings that contrast with its white cheeks and has blue gray wings. Despite its small stature, the American Kestrel is a formidable predator, employing a unique hunting strategy that involves hovering at a height before swooping down on prey, primarily consisting of insects, small mammals, and occasionally small birds.
Residing predominantly in North and South America, the American Kestrel exhibits a preference for open habitats such as meadows, grasslands, and deserts. They are also found in both urban and suburban environments, nesting in cavities in trees, cliffs, buildings, and other structures. Kestrels are monogamous, with both sexes participating in the courtship displays that involve aerial acrobatics and feeding rituals. Nesting duties are a shared responsibility, with the male initially scouting for suitable locations and the female making the final selection. Both parents contribute to the incubation of the eggs and care of the young, ensuring the perpetuation of this captivating species.
Merlin (Falco columbarius)


Merlin Sound
Scientific Name: Falco columbarius
Length: 9.4–13.0 in
Wingspan: 20–29 in
Weight: 5.8 – 8.1 ozz
The Merlin is a small, robust falcon known for its blue-gray or dark brown upperparts and thinly streaked, buff to orange underparts. Unlike other falcons, it has faint facial markings, offering a more uniform look.
This compact bird, renowned for its hunting prowess, chases down small birds in mid-air, exemplifying its impressive speed and agility.
Residing across northern North America, Europe, and Asia, the Merlin prefers open or semi-open landscapes. Rather than constructing their own nests, they tend to reuse old crow or raptor nests, or choose to nest on the ground in open habitats.
During courtship, males perform elaborate aerial displays. Both parents share egg incubation duties, with the male also responsible for feeding the family, reflecting the Merlin’s fascinating role in the biodiversity of its ecosystems.
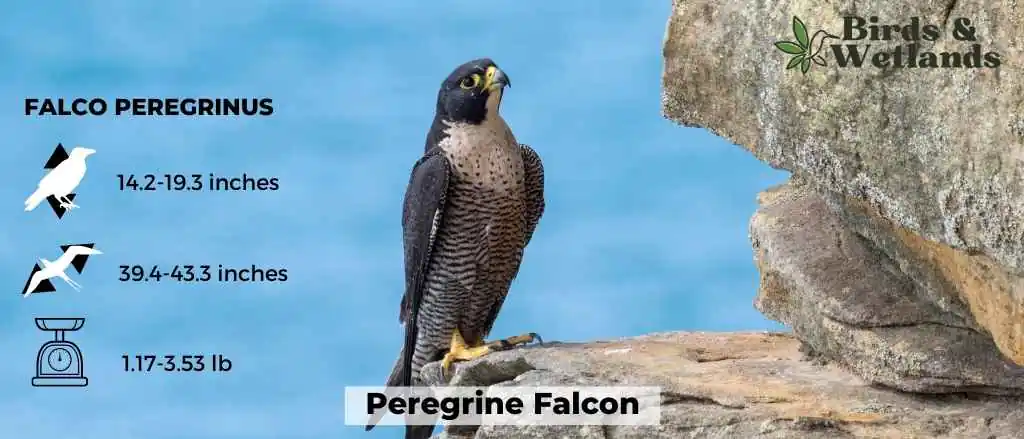
Peregrine Falcon (Falco peregrinus)


Peregrine Falcon Sound
Scientific Name: Falco peregrinus
Length: 14.2-19.3 in
Wingspan: 39.4-43.3 in
Weight: 530-1600 g
Known for its blue-gray plumage and unique cheek bars, the Peregrine Falcon stands as a beacon of power and swiftness. Despite its modest size, it reigns as the world’s fastest creature, reaching staggering speeds up to 240 mph during hunting dives.
Its diet mainly includes birds, occasionally bats, caught in an enthralling aerial display of agility and precision. Adapting to diverse habitats, this bird graces every continent except Antarctica, finding home in environments from city skyscrapers to towering cliffs.
Peregrine Falcons, monogamous in nature, often pair for life, expressing their bonds through complex courtship flights filled with intricate aerial maneuvers. They construct simple scrape nests on high ledges, often without adding materials.
Their parenting duties are shared, from egg incubation to feeding and caring for the chicks, ensuring their offspring are ready to take on the skies in their own time.
Golden Eagle (Aquila chrysaetos)


Golden Eagle Sound
Scientific Name:Aquila chrysaetos
Length: 26 to 40 in
Wingspan: 5 ft 11 in to 7 ft 8 in
Weight: 8.9 and 14.0 lb
The Golden Eagle is a large bird of prey known for its strength, speed, and hunting prowess.
Adult Golden Eagles are large birds, and are named for the golden-brown plumage on their heads and necks, which contrasts with their darker brown body feathers. Their eyes, legs, and bill are all yellow.
These eagles prefer open, rugged terrain, including mountains, hills, grasslands, and deserts. They are most often found in areas that provide good opportunities for soaring and hunting.
Golden Eagles have a varied diet but primarily prey on small to medium-sized mammals such as rabbits, hares, and ground squirrels. They are also capable of taking larger prey, like young deer or livestock, but these are not typically part of their diet.
Golden Eagles build large nests or eyries, usually on cliffs or in tall trees. The nests are often reused and added to each year, becoming enormous structures over time. The female typically lays 1 to 4 eggs, which both parents incubate.
Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus)

Bald Eagle Sound
Scientific Name: Haliaeetus leucocephalus
Length: 28–40 in
Wingspan: 5 ft 11 in and 7 ft 7 in
Weight: 6.6 -13.9 lb
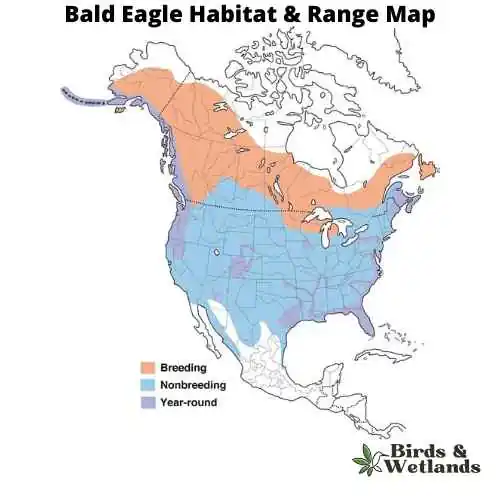
The Bald Eagle, primarily found in Canada and Alaska, is instantly identifiable by its white head, dark brown body, yellow beak, and a piercing cry. Its sharp, orange-yellow eyes aid in efficient night hunting.
Predominantly residing in North America, occasionally venturing into Asia and Europe, it thrives near water bodies. It perches atop trees, providing a bird’s-eye view of its prey. It feeds on fish, carrion, small mammals like rabbits and squirrels, and reptiles. Hunting involves a swift downward swoop to seize the prey, carrying it back to the nest.
Bald Eagles are monogamous, forming lifelong pairings. They construct vast nests from sticks, lined with moss or grasses. They typically lay 1-3 eggs annually, which hatch around 35 days later. The fledglings leave the nest roughly 6 weeks after hatching, but continue to rely on their parents for nourishment for a further 5-6 months, until they become proficient hunters.
Barn Owl (Tyto alba)

Barn Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Tyto alba
Length: 13 to 15 in
Wingspan: 31 to 37 in
Weight: 9.2 oz
The Barn Owl is a widespread species of owl known for its distinctive heart-shaped facial disc.
Barn Owls are medium-sized owls, they are pale overall with golden-brown wings and back, contrasted by a white face, chest, and belly. Their most notable feature is their heart-shaped facial disc, which helps channel sound to their ears.
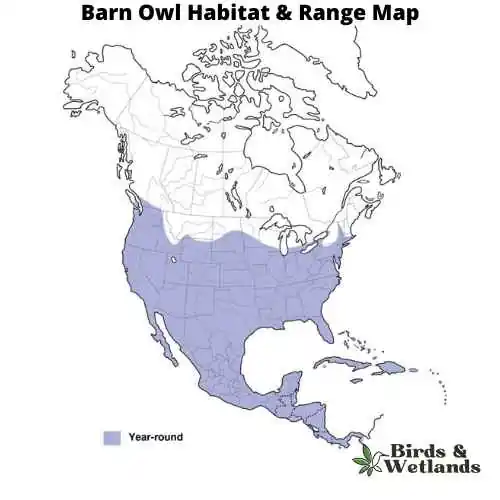
Barn Owls are typically found in open habitats, including farmland, woodland, and marshes. They are named for their habit of nesting in human structures such as barns, church towers, and in the hollows of large trees. These owls are nocturnal, hunting at night and roosting during the day.
The diet of Barn Owls primarily consists of small mammals, particularly rodents such as mice and rats. They are known for their silent flight, which allows them to sneak up on their prey without detection.
Barn Owls have a unique nesting behavior. They do not build nests, but instead, lay their eggs directly on the bare surface of a secluded ledge or cavity. A female typically lays 4-7 eggs, and both parents help incubate the eggs and care for the chicks.
Eastern Screech-Owl (Megascops asio)

Eastern Screech-Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Megascops asio
Length: 6 to 10 in
Wingspan: 8 to 24 in
Weight: 4 – 8.5 oz
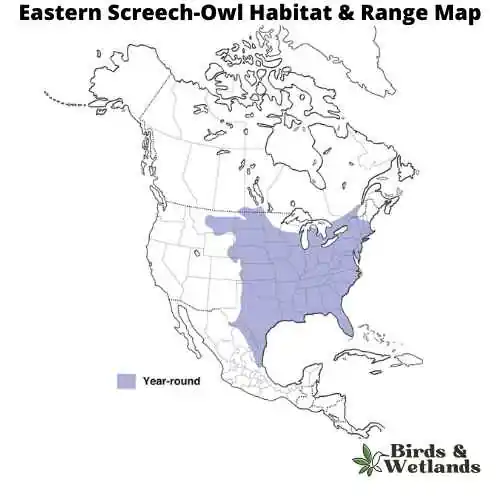
The Eastern Screech-Owl is a small owl species native to most wooded environments of the eastern half of North America, from the Canadian provinces to Florida and Texas.
Eastern Screech-Owls are relatively small and exhibit a complex pattern of gray or reddish-brown coloration, which provides excellent camouflage against tree bark.
These owls are known for their distinctive call, which is often described as a haunting trill or a whinny-like sound. Despite their name, they do not actually produce a “screech.”
Eastern Screech-Owls feed on a variety of prey, ranging from small mammals and birds to insects and even earthworms. It is primarily nocturnal, hunting at night from a low perch and swooping down onto prey.
Eastern Screech-Owls nest in tree cavities or abandoned woodpecker nests, but they readily adapt to nesting boxes where natural cavities are not available. They typically lay between 2 to 6 eggs, which are incubated primarily by the female.
Great Horned Owl (Bubo virginianus)


Great Horned Owl Sound
Scientific Name:Bubo virginianus
Length: 18.1-24.8 in
Wingspan: 39.8-57.1 in
Weight: 32.1-88.2 oz
The Great Horned Owl is a large owl with long wings and a large head. It’s one of the most common owls in North America.
Great Horned Owls are large, stocky birds with soft feathers that are gray to brown on their backs and white on their chests. Their faces are characterized by two black “ear” tufts, which can be raised or flattened depending on the owl’s mood. The eyes are yellow, orange, or red in color.
The habitat of the Great Horned Owl is a variety of different environments such as forests and deserts. They also live near water sources such as lakes, streams and rivers where they can hunt for fish.
The diet of the Great Horned Owl consists primarily of small mammals such as mice and rats; however they will also eat other rodents such as squirrels, rabbits and porcupines. They have been known to eat skunks too.
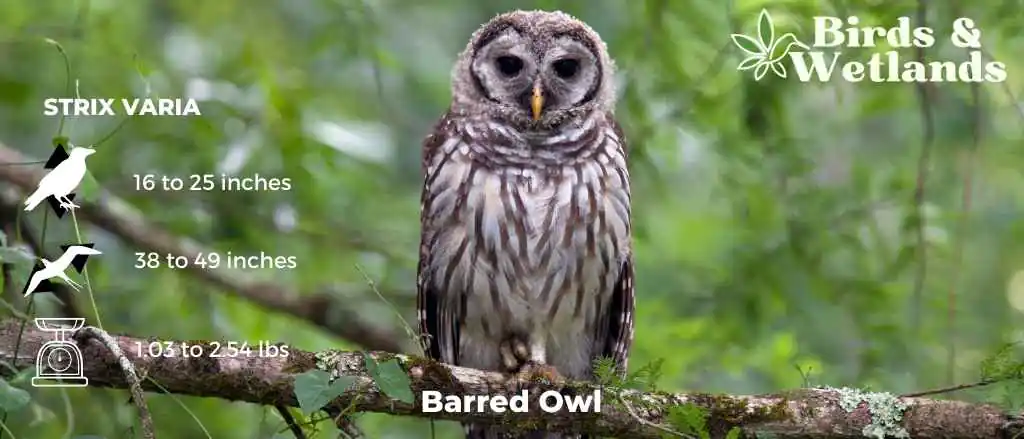
Barred Owl (Strix varia)


Barred Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Strix varia
Length: 40 to 63 cm (16 to 25 in)
Wingspan: 96 to 125 cm (38 to 49 in)
Weight: 468 to 1,150 g
The Barred Owl is a medium-sized owl with a barred pattern on its chest and belly. They have large yellow eyes that allow them to see well in low light conditions. Their ears are not very large which means they do not hear very well but they have excellent hearing abilities which allow them to detect sounds up to 1 mile away. Their feathers are brown and streaked with white, and they have black bars on their chests and wings.
Their habitats include forests, woodlands, orchards, parks, farmland and suburban backyards.
Barred Owls (also known as hoot owl) eat small mammals such as mice, rats and squirrels. They also eat insects such as beetles or grasshoppers. These owls hunt during the day when it is light out so that they can see their prey better than at night when they would be using senses other than sight like sound or smell to find their food source.
Barred owls are monogamous birds which means they mate for life. They build nests in trees or cavities on the ground and lay 2-4 eggs per year. The incubation period for these eggs lasts about 28 days before hatching takes place.
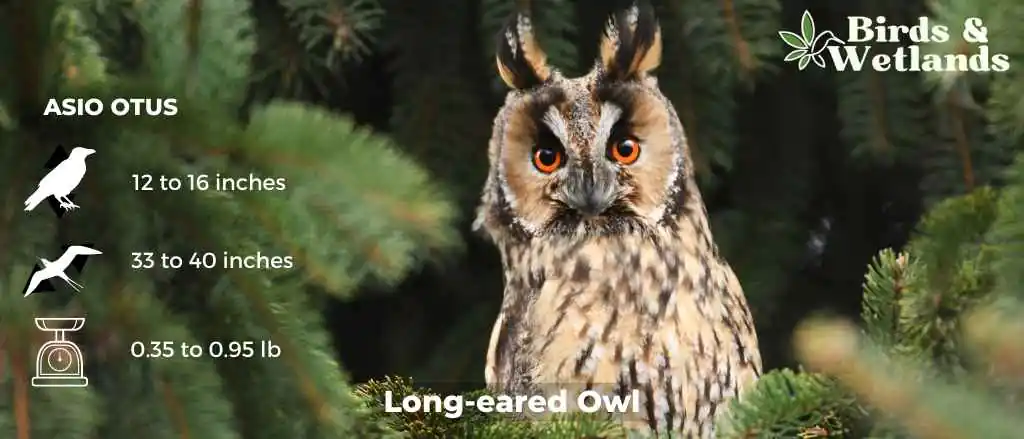
The long-eared owl (Asio otus)


Long-eared Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Asio otus
Length: 12 and 16 in
Wingspan: 2 ft 10 in to 3 ft 4 in
Weight: 5.6 to 15.3 oz
The Long-eared Owl is a medium-sized owl species known for its distinctively long ear tufts, which can be raised or lowered depending on the bird’s mood or intention.
Long-eared Owls have mottled brown and cream plumage, which provides excellent camouflage among the trees. Their most distinctive features are their long, black-tipped ear tufts, which are set closer to the center of the head than in most other owl species.
These owls inhabit a wide variety of habitats, including deciduous and coniferous forests, woodlands, and even semi-deserts.
The Long-eared Owl’s diet primarily consists of small mammals, especially voles, but they will also take small birds and insects. They are skillful hunters, often capturing prey from a perch or in flight.
In terms of nesting behavior, Long-eared Owls do not construct their own nests, instead they take over old nests built by other bird species, usually those of corvids or other large birds. They lay an average of 4 to 5 eggs, which are incubated by the female while the male provides food.
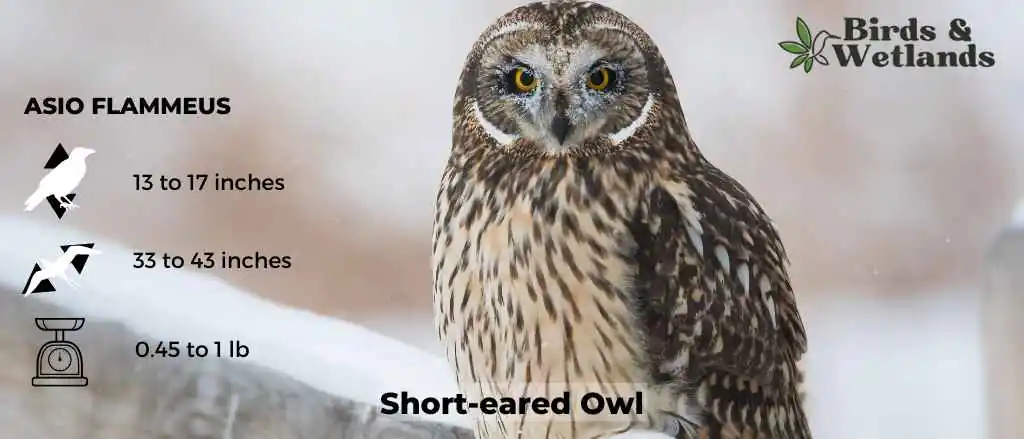
Short-eared Owl (Asio flammeus)

Short-eared Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Asio flammeus
Length: 13–17 in
Wingspan: 33 to 43 in
Weight: 7.3–16.8 oz
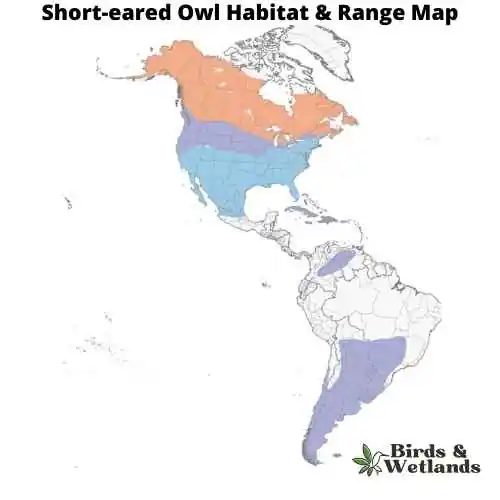
The Short-eared Owl is a medium-sized owl species with a wide distribution, found across North and South America, Europe, Asia, and many Pacific islands. Despite its name, the “ears” of the Short-eared Owl are not often visible, as they are small and tend to blend with the bird’s feathers.
The owls are predominantly brown with buff and white accents throughout their body and wings, and dark patches around their yellow eyes.
Short-eared Owls diet consists largely of small mammals, especially voles. However, they are opportunistic hunters and will also prey on a variety of other animals, including other birds, when available.
Their habitat is characterized by open areas like grasslands, marshes, and tundra. They nest on the ground, which is unusual for owls, and this makes them vulnerable to ground predators. As such, they often live in areas with tall grasses or other ground cover for protection.
Northern Saw-whet Owl (Aegolius acadicus)


Northern Saw-whet Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Aegolius acadicus
Length: 17–22 cm (6.7–8.7 in)
Wingspan: 42–56.3 cm (16.5–22.2 in)
Weight: 54 to 151 g (1.9 to 5.3 oz)
The Northern Saw-whet Owl is a tiny, speckled gray owl and it’s one of the smallest owls in North America. It’s also known as the Little Owl or Wood Owl in some areas.
Northern Saw-whet Owls have dark brown eyes, white eyebrows, and yellow beak. It has brownish-grey feathers that are spotted with white. The owl’s legs are covered in feathers and appear nearly invisible when the bird is perched on a branch or tree.
In the winter they migrate south to warmer climates. They prefer to live in dense coniferous forest with large trees but will occasionally nest in shrubs or other vegetation that can protect them from predators.
The Northern Saw-whet Owl eats mice and voles (small rodents), small birds, frogs, salamanders, moles and shrews, but unlike most owls they chop their prey up and spread over a few meals. They will also eat insects like beetles and grasshoppers if they are available. It hunts from a perch at night using its excellent hearing to locate prey items within about 30 feet (9 meters) of its nest.
These owls nest in tree cavities usually located close to water sources such as lakes or rivers where they can find their food source (insects). They lay 2-4 eggs at one time which incubate for about 30 days before hatching.
Osprey (Pandion haliaetus)

Osprey Sound
Scientific Name: Pandion haliaetus
Length: 50–66 cm (19+1⁄2–26 in)
Wingspan: 127–180 cm (50–71 in)
Weight: 0.9–2.1 kg (2 lb 0 oz – 4 lb 10 oz)
The Osprey, a fascinating bird of prey, is universally known for its exceptional hunting prowess and striking physical characteristics. Osprey are dark brown hawks on the upperparts, contrasting beautifully with the predominantly white underparts, and a distinctive dark band that stretches across the eyes towards the sides of its head.
Equipped with specialized talons and a reversible outer toe, the Osprey’s hunting strategy involves a spectacular plunge-dive into bodies of water, often emerging with a fish securely gripped in its claws.
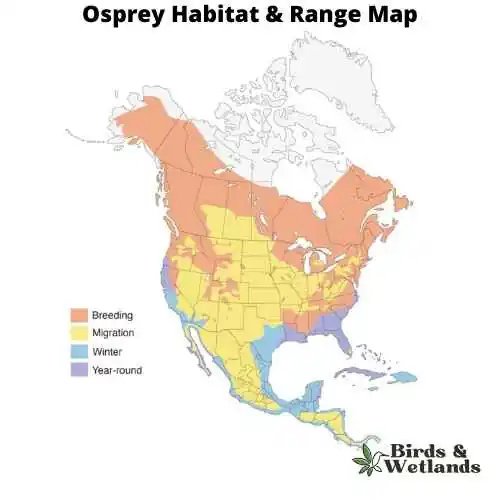
Found on every continent except Antarctica, the Osprey is a cosmopolitan species favoring habitats near water bodies such as lakes, rivers, and coastal areas, reflecting its piscivorous diet. This bird has a diet almost exclusively of fish, making it a unique member of the raptor family and often referred to as the sea hawk or fish hawk. They locate their prey from the air, often hovering before plunging feet-first to capture a fish. When it comes to breeding, Ospreys are monogamous, often mating for life.
They construct large, bulky nests made of sticks, lined with softer materials, and prefer elevated or isolated areas such as treetops or artificial structures like utility poles. Both parents share the responsibility of incubating the eggs and rearing the chicks.
Where to Spot Connecticut’s Birds of Prey
Sherwood Island State Park, Westport: This is Connecticut’s first state park, covering 238 acres of beach, wetlands, and woodland. The diverse habitats make it an excellent place to spot birds of prey like hawks, osprey, and eagles. Additionally, the park’s Nature Center offers birdwatching events and education about local species.
Hammonasset Beach State Park, Madison: Hammonasset is the state’s largest shoreline park, providing a fantastic diversity of bird species. It’s especially renowned during the migration season where various hawks, falcons, and owls make an appearance. The Meigs Point Nature Center within the park also provides interactive displays and programs about local wildlife.
Litchfield Hills, Northwest Connecticut: The Litchfield Hills region, especially around White Memorial Conservation Center, is prime birding territory. It’s particularly known for sightings of the majestic Bald Eagles during winter months, and various hawk species can be seen in the spring and fall migration periods.
Great Island Wildlife Area, Old Lyme: This coastal woodland and salt marsh site is an exceptional location to observe Ospreys, Bald Eagles, and Northern Harriers, among other raptors. Boat tours around the estuary offer unique perspectives for bird watching and photography.
Shepaug Dam Bald Eagle Observation Area, Southbury: From December through March, the Shepaug Dam is a well-known spot to observe Bald Eagles that come to fish in the waters below the dam. Reservation for viewing is required, but the sight of these majestic birds is well worth it.
The Atlantic coastline of Connecticut is a perfect stage for the drama of raptors. Discover the grace and agility of Rhode Island’s Birds of Prey, reflecting the state’s rich maritime legacy. Or, immerse in the varied landscapes of New York, embodied by New York’s Feathered Hunters. Broaden your understanding of these winged wonders through our comprehensive Birds of Prey Guide.

