Geese are the largest birds in Rhode Island, and several different species can be found here. Some geese prefer to stay near the coast, while multiple species of birds migrate inland during the winter months. These aquatic birds eat a variety of plants and insects, but their diet can also vary depending on the time of year.
What Geese Are in Rhode Island?
There are eight types of geese in Rhode Island.
- Canada Goose
- Snow Goose
- Ross’s Goose
- Cackling Goose
- Greater White-Fronted Goose
- Barnacle Goose
- Pink-footed Goose
- Brant
Ross’s Geese, Pink-footed Geese, Barnacle Geese and Cackling Geese are considered vagrant in the state, which means these geese are accidental visitors.
In addition to geese, there are three swan species in Rhode Island including Tundra Swans, Trumpeter Swans and Mute Swans.

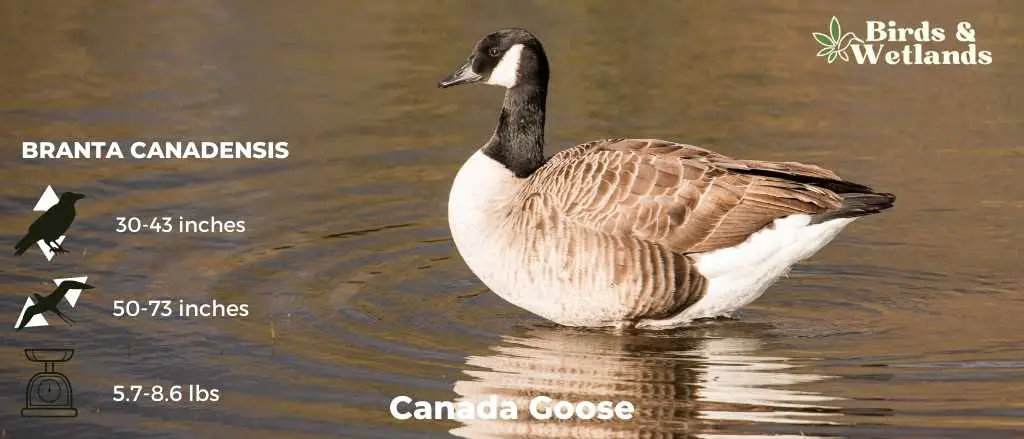
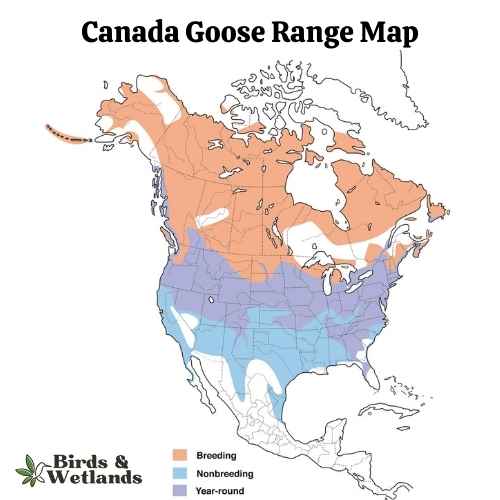
Canada Goose

Canada Goose Sound
Scientific Name: Branta canadensis
Length: 30 to 43 in
Wingspan: 50–73 in
Weight: 5.7–14.3 lb
The Canada Goose is a large, well-known species of waterfowl noted for its distinctive appearance, familiar “honk,” and migratory behavior.
Appearance: Both male and female Canada Geese have a similar appearance, featuring a black head and neck with distinctive white patches on the cheeks and chin. The body is primarily brown with a lighter, often white, underbelly.
Diet: Canada Geese primarily feed on plant matter, including grasses, aquatic vegetation, and grains. They can often be seen grazing in parks, lawns, and fields, as well as dabbling in water bodies.
Reproduction: Canada Geese typically nest on the ground near water bodies, often on islands or other isolated areas to avoid predators. The female lays a clutch of about 4 to 6 eggs, which she incubates alone for around a month.
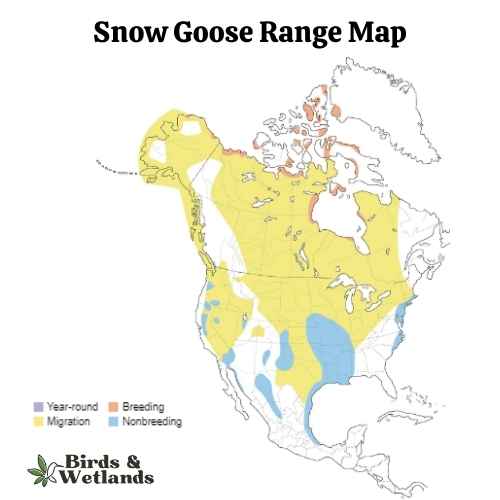
Snow Goose

Snow Goose Sound
Scientific Name: Anser caerulescens
Length: 25 to 31 in
Wingspan: 53 to 65 in
Weight: 4.5 to 6.0
The Snow Goose is a large species of waterfowl known for its vibrant white plumage and significant migratory flights.
Appearance: True to their name, Snow Geese are predominantly white with black wingtips. They also have a pink bill, pink legs and feet. A color morph, known as the “Blue Goose,” displays a bluish-gray body with a white head, but is considered the same species.
Diet: Snow Geese primarily feed on plant matter, such as grasses, sedges, and small grains. They can often be seen in large flocks foraging in fields and marshes, and during migration and winter, they can cause considerable damage to agricultural fields due to their feeding habits.
Reproduction: Snow Geese typically nest on the tundra, near water bodies. The female builds the nest and lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates alone for approximately three weeks. Once hatched, the goslings can feed themselves but stay with their parents for protection until they can fly.
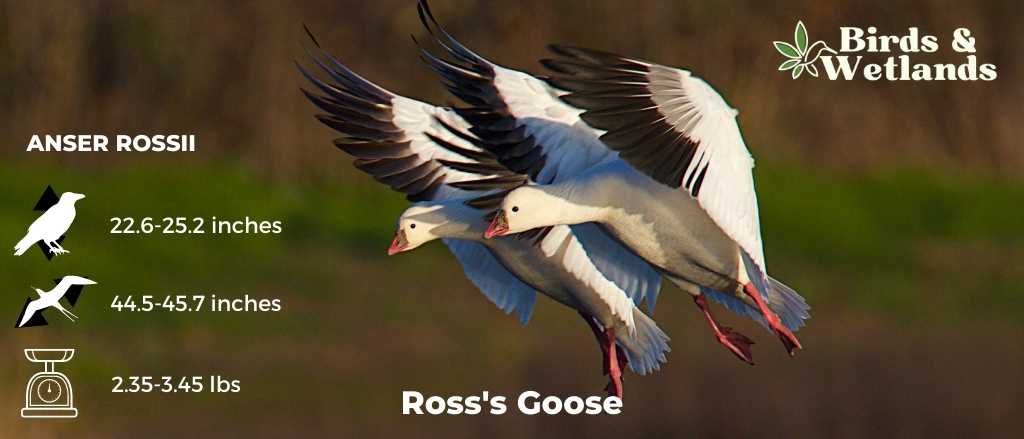
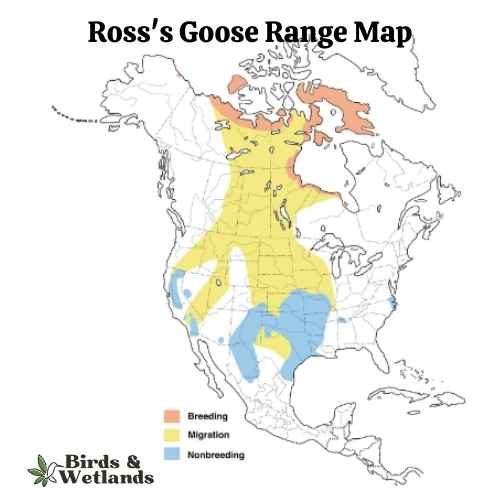
Ross’s Goose

Listen
Scientific Name: Anser rossii
Length: 23.2-25.2
Wingspan: 44.5-45.7 in
Weight:42.3-55.3 oz
The Ross’s Goose is a small species of waterfowl often found in North America’s tundra and wetland habitats.
Appearance: Known for its compact size, the Ross’s Goose is mostly white with black wingtips. It features a short, stubby bill and a rounded head. One key identifying feature is the blueish gray base of its bill, which has a warty structure during the breeding season.
Diet: This goose feeds mainly on vegetation, including seeds, leaves, and roots of grasses and sedges. During winter and migration, they also consume grains and seeds from agricultural fields.
Reproduction: The Ross’s Goose nests on the ground, often in colonies. The female lays a clutch of 2 to 5 eggs which she incubates for around three weeks. The young geese, known as goslings, are precocial – they can walk, swim, and feed themselves shortly after hatching, although they stay with their parents until they learn to fly.
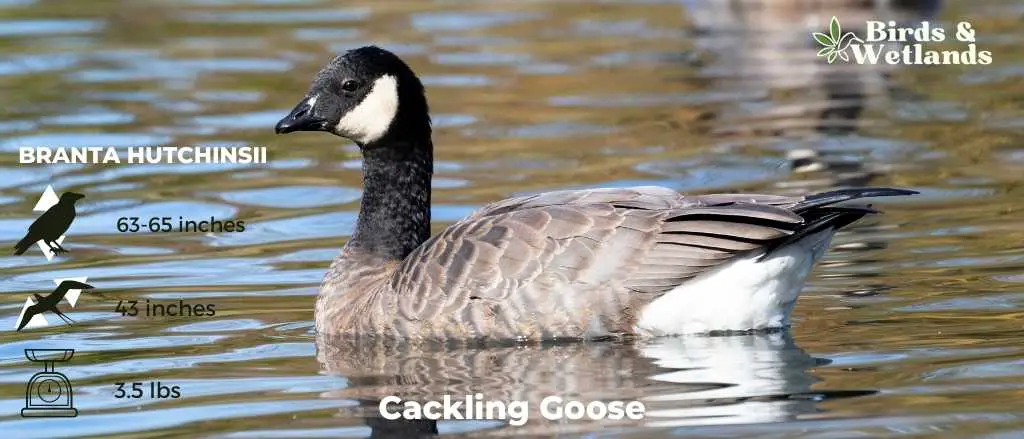
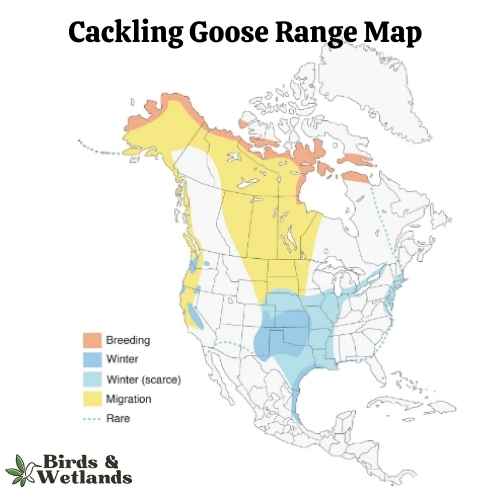
Cackling Goose

Listen
Scientific Name: Branta hutchinsii
Length: 24.8–25.6 in
Wingspan: 43-45.7 in
Weight:3.5 lbs
Cackling Geese are particularly known for their high-pitched, cackling calls, which is the source of their name. Despite their small size, these geese are renowned long-distance migrants, with some populations traveling thousands of miles between breeding and wintering grounds.
Appearance: With a similar color pattern to the larger Canada Goose, the Cackling Goose features a black head and neck, white chinstrap, light tan to cream chest, and brownish-grey body. One defining characteristic is its noticeably smaller size and stubbier neck compared to its larger counterparts.
Diet: Like many geese, the Cackling Goose’s diet mainly consists of plant matter. This includes grasses, seeds, and aquatic vegetation. They are often seen grazing on land or dabbling in shallow water.
Reproduction: Cackling Geese usually nest on the ground in elevated areas near water bodies, such as riverbanks or lakeshores. The female lays a clutch of 2 to 8 eggs and is responsible for incubation, while the male stands guard nearby. Incubation lasts for about a month.
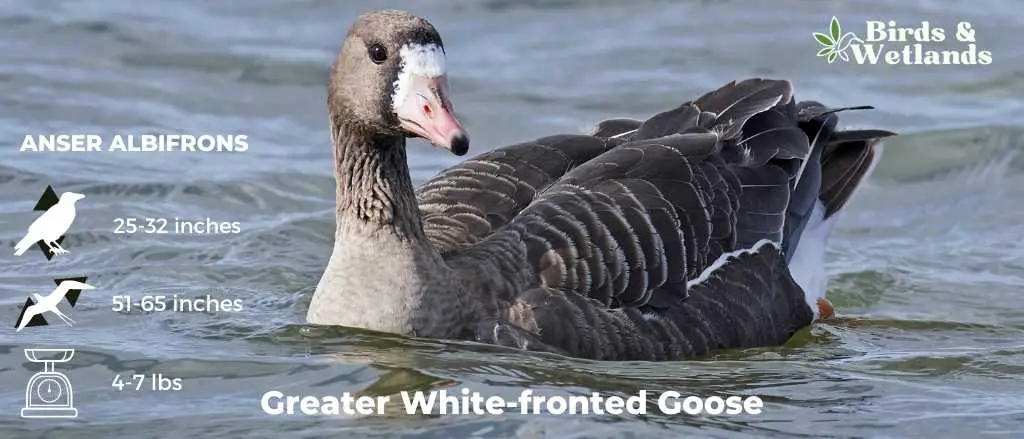
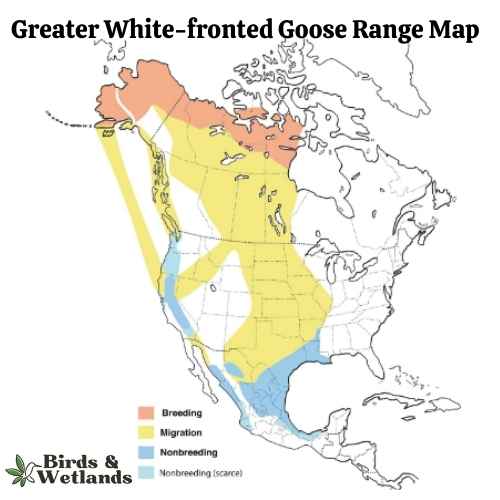
Greater White-fronted Goose

Listen
Scientific Name: Anser albifrons
Length: 25 to 31 in
Wingspan: 53 to 66 in
Weight: 3.3 to 6.6
The Greater White-fronted Goose is a medium to large waterfowl species, widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in North America.
Appearance: As the name suggests, these geese display a prominent white patch at the base of their bill. Their bodies are gray-brown, and their breasts are often marked with dark blotches. They possess a pinkish bill and orange legs and feet.
Diet: The Greater White-fronted Goose is a herbivore and feeds mainly on plant material. Its diet consists of grasses, sedges, grains, and berries. When wintering, these geese can often be found in agricultural fields, feasting on leftover grains and crops.
Reproduction: This species nests on the ground, often in areas with good visibility such as slopes or ridges. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for nearly a month. Once hatched, the young ones are taken care of by both parents until they are able to fly.
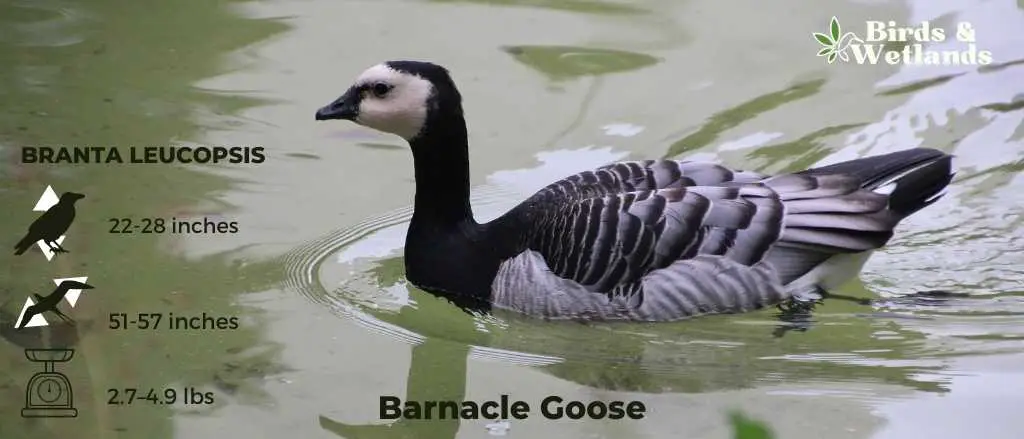
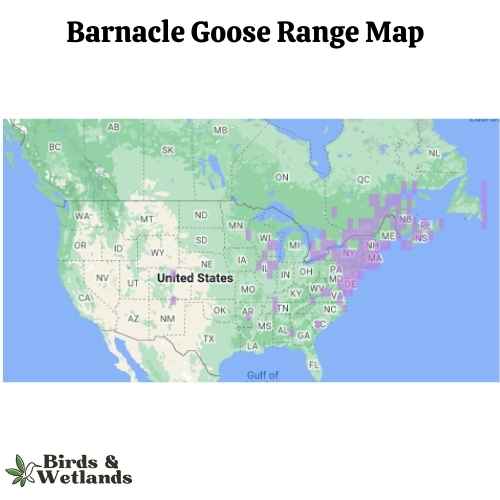
Barnacle Goose (Branta leucopsis)

Rare in North America and when spotted its usually within a flock of Canada Geese.
- Scientific Name: Branta leucopsis
- Height: 55–70 cm (22–28 in)
- Wingspan: 130–145 cm (51–57 in)
- Weight: 1.21–2.23 kg (2.7–4.9 lb)
Barnacle Goose Description
The barnacle goose is a small goose with a white body and black wings, a black neck, with a white face and black bill. Its crown, eye line and legs are black.
Listen to Barnacle Goose
Barnacle Goose Habitat & Range
Barnacle geese are migratory geese that are native to the Arctic and northern Europe. They spend winters in southern Europe, Africa, India, and Australia. They breed in Iceland, Greenland, Northern Scandinavia, and Canada.
Barnacle Goose Diet
Barnacle Geese feed primarily on grasses, leaves, and other aquatic plants, grains, and algae during their breeding season but also consume insects during migration periods when food may be scarce.
Barnacle Goose Nesting
The Barnacle Goose lays 4-6 eggs in a nest lined with down but on the rock edge. The young Barnacle Goslings have to undergo significant challenges making their way from cliff edges to the water below a few hours after hatching.
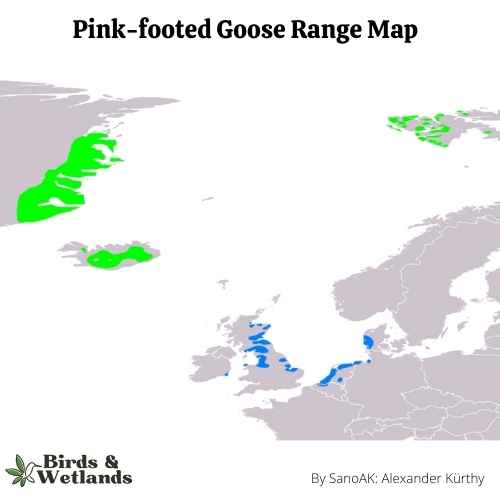
Pink-footed Goose (Anser brachyrhynchus)

- Scientific Name: Anser brachyrhynchus
- Height: 60–75 cm (24–30 in)
- Wingspan: 135–170 cm (53–67 in)
- Weight: 1.8–3.4 kg (4.0–7.5 lb)
This is a rare visitor to North Eastern US, but becoming increasingly more common as it migrates with other geese species. It is a small goose which breeds in the Artic.
Pink-footed Goose Description
The Pink-footed Goose is a medium-sized goose with a pinkish bill and legs, as well as a white belly. It has a white head and neck with a black stripe running down its back and a black tail. The body is white except for a black breast, belly, and vent. The bill is yellow and red, with yellow on top and red on the bottom. The legs are pink.
Listen to Pink-footed Goose
Pink-footed Goose Habitat & Range
It’s a migratory goose that breeds in Iceland, Greenland, and Scandinavia. It winters on the coasts of North America and Europe. They are also known for gathering in large flocks to feed or roost together during migration.
In winter, they migrate south to warmer climates in Europe or Africa. The population is large enough that they can survive in areas where there is no natural water source for them to nest in—they simply dig holes in dry grassland instead.
Pink-footed Goose Diet
Pink-footed geese feed on aquatic plants, including algae and tubers such as sedges and grasses; they also eat small fish and invertebrates such as snails or worms when they can find them.
Pink-footed Goose Nesting
They breed on the Arctic tundra near ponds or lakes that have open water in summer. Their nests are made formed in rocky crags. They lay 3-6 eggs per clutch and both parents incubate them for about 25 days.
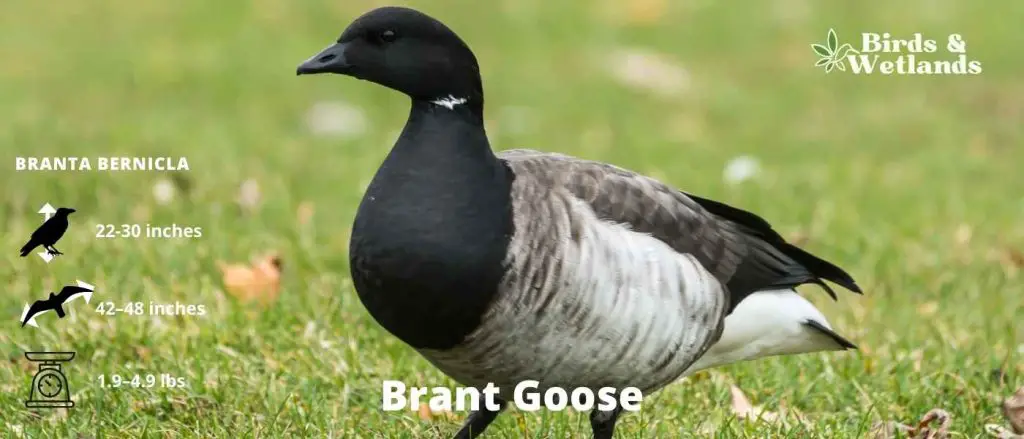
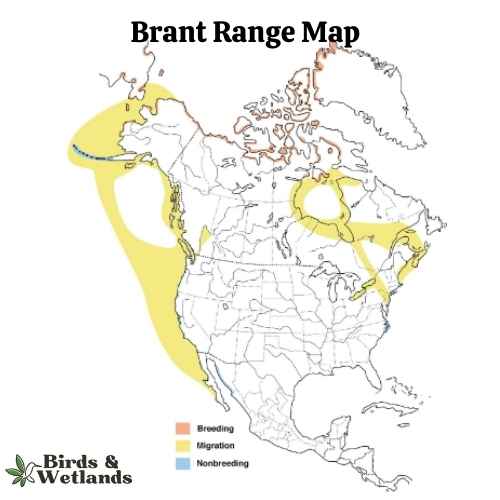
Brant

Listen
Scientific Name: Branta bernicla
Length: 22–26 in
Wingspan: 42–48 in
Weight: 1.9–4.9 lb
The Brant is a compact species of goose that is known for its striking appearance and interesting migratory patterns.
Appearance: The Brant is recognized for its dark, sooty color with a white crescent on the neck. The body is mostly black to dark gray, contrasting with the lighter underparts. Its small size, as compared to other geese, and short, stubby bill are other distinct features.
Diet: The Brant’s diet primarily consists of aquatic plants, especially eelgrass and sea lettuce. During the breeding season, they may also feed on grasses, sedges, and insects.
Reproduction: Brants typically breed in the high Arctic tundra. The female lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs in a ground nest, which she incubates for about a month.
Notably, Brants make an impressive long-distance migration every year. They spend their winters along both the east and west coasts of the United States and travel to the Arctic regions of Canada, Alaska, and even Russia to breed.
Are There Any Resident Flocks of Geese In Rhode Island?
There are between 3,000 and 7,000 Canada geese that live in Rhode Island year-round. Most of these geese reside near urban areas along Narragansett Bay. These locations include Apponaug and Pawtuxet coves in Warwick, the Seekonk River in Providence and East Providence, and Newport and Middletown.
Most Canada geese will migrate south for the winter, but some choose to stay in Rhode Island because the state provides an abundance of food and shelter. Canada geese usually return to their breeding grounds in early spring. For resident Canada geese in the state of Rhode Island, this means returning to areas near urban areas along Narragansett Bay and in the northern part of Washington County.
The reason why Canada geese tend to stick near urban areas is that these areas have a large amount of open space, like parks and golf courses, which provide plenty of food and shelter for the geese. One of the main reasons Canada geese are attracted to these areas is the presence of people. People often feed Canada geese, which provides the geese with an easy food source. In addition, people generally don’t bother Canada geese and leave them alone, which the geese find a safe and comfortable environment.
However, some people view these waterfowl as nuisance. Property owners have started growing a natural vegetative buffer between their lawn and the water’s edge to dissuade nuisance geese from nesting. Geese prefer a location where they can clearly see incoming possible predators.
Geese Hunting in Rhode Island
In order to hunt geese in Rhode Island, you must have a valid hunting license and permit. You can obtain a hunting license from the Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management (DEM). A permit is required in order to hunt geese in specific areas, and you can apply for a permit through the DEM website. Hunting licenses and permits are typically valid for one year. Additionally, waterfowl hunters also need to obtain a RI Harvest Information Program (HIP) Permit.
Can You Shoot Geese in Rhode Island?
In Rhode Island, it is illegal to shoot geese with anything other than a non-toxic shot. Additionally, you are not allowed to use a shotgun that can hold more than three shells unless it is plugged with a one-piece filler that cannot be removed without disassembling the gun.
Additionally, Rhode Island has a daily bag limit and possession limit on waterfowl hunting. These state and federal regulations are in place to protect waterfowl populations from being decimated by hunters.
Where Can You Hunt Geese and Other Waterfowl in Rhode Island?
Hunting geese can be a fun and rewarding experience, but it’s important to know where to go to find them. In Rhode Island, popular hunting spots include Providence, Bristol and Kent counties, as well as portions of Washington County and the South Shore Management Area. Each of these areas offers its own unique challenges and rewards, so it’s important to do some research before heading out.
Is There a Goose Hunting Season in Rhode Island?
Rhode Island offers a variety of hunting opportunities for residents and visitors alike. One type of game that can be hunted in the state is geese. The season for hunting geese typically runs from September to January, with different dates depending on the species of goose.
Conclusion on Geese in the State of Rhode Island
Rhode Island is a great place to see geese and swans. If you are looking for an interesting birding experience, be sure to visit Rhode Island! There are plenty of places where you can see these beautiful birds.


