If you’re looking for a place to see some geese, Nebraska is the perfect spot. There are several types of geese that call Nebraska home, including the Canada goose, snow goose, and white-fronted goose.
You can find these birds all across the state, from the sandhills to the Platte River. In the spring and fall, you can see migrating flocks of geese heading to and from their nesting grounds.
Nebraska is a stopover point for many of these birds, so you’re likely to see a variety of species if you keep your eyes peeled.
What Geese Are in Nebraska?
There are five species of goose and two species of swans in Nebraska.
- Canada Goose
- Snow Goose
- Ross’s Goose
- Cackling Goose
- Greater White-fronted Goose
Swans in Nebraska include Tundra Swan and Trumpeter Swan.

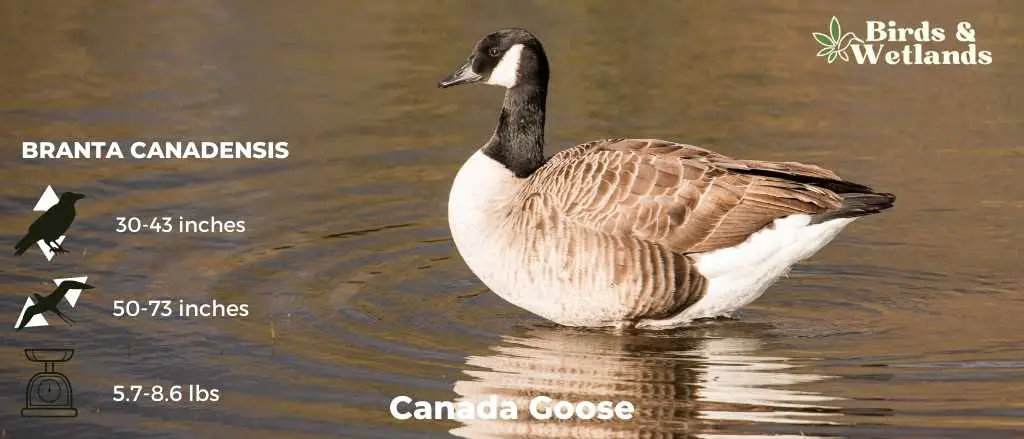
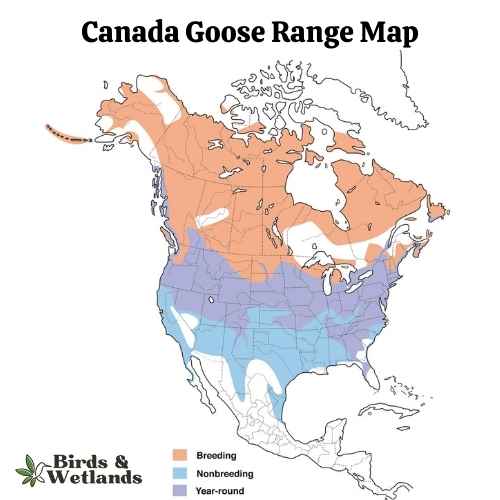
Canada Goose

Canada Goose Sound
Scientific Name: Branta canadensis
Length: 30 to 43 in
Wingspan: 50–73 in
Weight: 5.7–14.3 lb
The Canada Goose is a large, well-known species of waterfowl noted for its distinctive appearance, familiar “honk,” and migratory behavior.
Appearance: Both male and female Canada Geese have a similar appearance, featuring a black head and neck with distinctive white patches on the cheeks and chin. The body is primarily brown with a lighter, often white, underbelly.
Diet: Canada Geese primarily feed on plant matter, including grasses, aquatic vegetation, and grains. They can often be seen grazing in parks, lawns, and fields, as well as dabbling in water bodies.
Reproduction: Canada Geese typically nest on the ground near water bodies, often on islands or other isolated areas to avoid predators. The female lays a clutch of about 4 to 6 eggs, which she incubates alone for around a month.
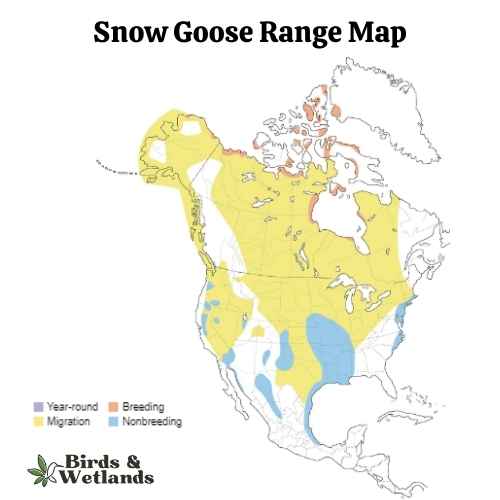
Snow Goose

Snow Goose Sound
Scientific Name: Anser caerulescens
Length: 25 to 31 in
Wingspan: 53 to 65 in
Weight: 4.5 to 6.0
The Snow Goose is a large species of waterfowl known for its vibrant white plumage and significant migratory flights.
Appearance: True to their name, Snow Geese are predominantly white with black wingtips. They also have a pink bill, pink legs and feet. A color morph, known as the “Blue Goose,” displays a bluish-gray body with a white head, but is considered the same species.
Diet: Snow Geese primarily feed on plant matter, such as grasses, sedges, and small grains. They can often be seen in large flocks foraging in fields and marshes, and during migration and winter, they can cause considerable damage to agricultural fields due to their feeding habits.
Reproduction: Snow Geese typically nest on the tundra, near water bodies. The female builds the nest and lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates alone for approximately three weeks. Once hatched, the goslings can feed themselves but stay with their parents for protection until they can fly.
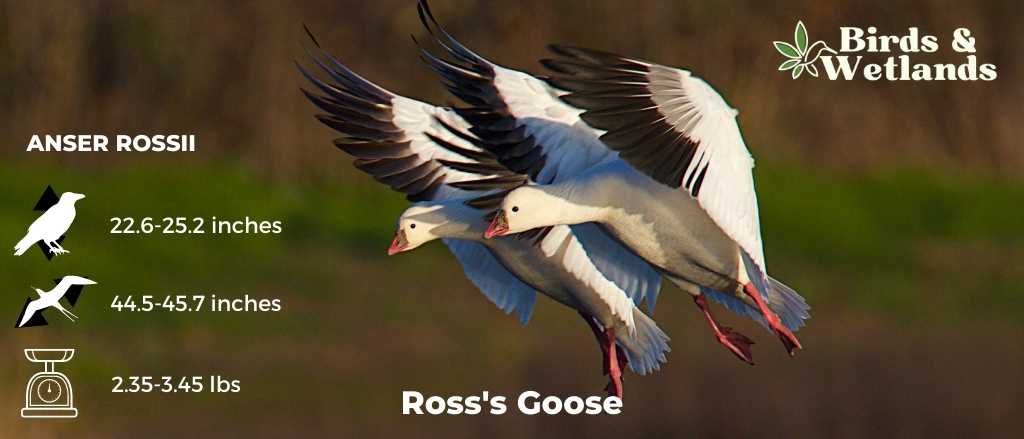
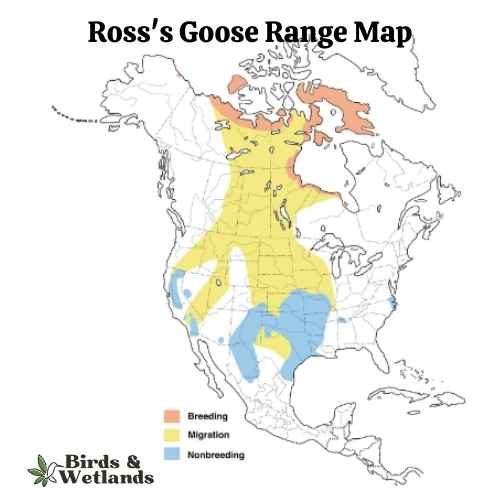
Ross’s Goose

Listen
Scientific Name: Anser rossii
Length: 23.2-25.2
Wingspan: 44.5-45.7 in
Weight:42.3-55.3 oz
The Ross’s Goose is a small species of waterfowl often found in North America’s tundra and wetland habitats.
Appearance: Known for its compact size, the Ross’s Goose is mostly white with black wingtips. It features a short, stubby bill and a rounded head. One key identifying feature is the blueish gray base of its bill, which has a warty structure during the breeding season.
Diet: This goose feeds mainly on vegetation, including seeds, leaves, and roots of grasses and sedges. During winter and migration, they also consume grains and seeds from agricultural fields.
Reproduction: The Ross’s Goose nests on the ground, often in colonies. The female lays a clutch of 2 to 5 eggs which she incubates for around three weeks. The young geese, known as goslings, are precocial – they can walk, swim, and feed themselves shortly after hatching, although they stay with their parents until they learn to fly.
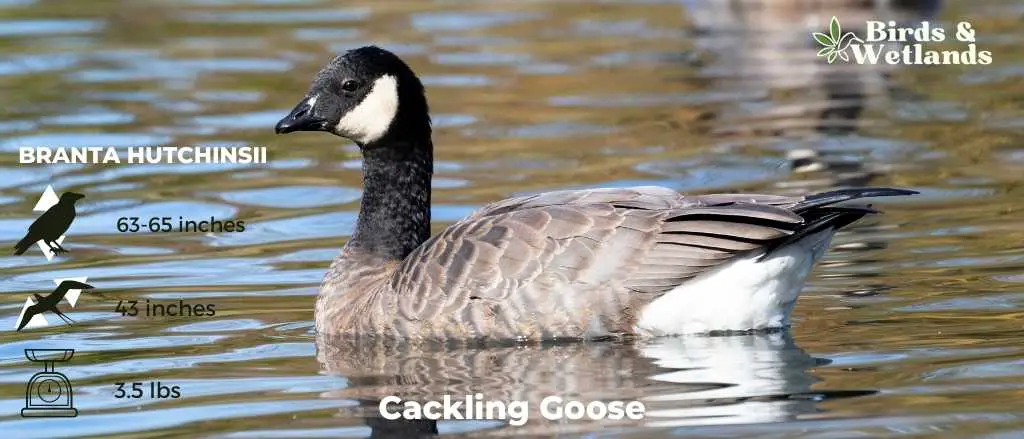
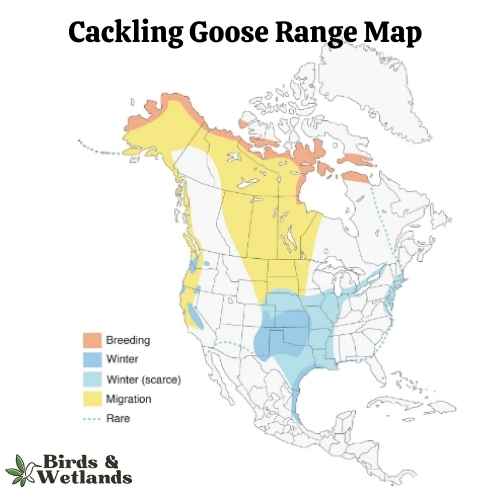
Cackling Goose

Listen
Scientific Name: Branta hutchinsii
Length: 24.8–25.6 in
Wingspan: 43-45.7 in
Weight:3.5 lbs
Cackling Geese are particularly known for their high-pitched, cackling calls, which is the source of their name. Despite their small size, these geese are renowned long-distance migrants, with some populations traveling thousands of miles between breeding and wintering grounds.
Appearance: With a similar color pattern to the larger Canada Goose, the Cackling Goose features a black head and neck, white chinstrap, light tan to cream chest, and brownish-grey body. One defining characteristic is its noticeably smaller size and stubbier neck compared to its larger counterparts.
Diet: Like many geese, the Cackling Goose’s diet mainly consists of plant matter. This includes grasses, seeds, and aquatic vegetation. They are often seen grazing on land or dabbling in shallow water.
Reproduction: Cackling Geese usually nest on the ground in elevated areas near water bodies, such as riverbanks or lakeshores. The female lays a clutch of 2 to 8 eggs and is responsible for incubation, while the male stands guard nearby. Incubation lasts for about a month.
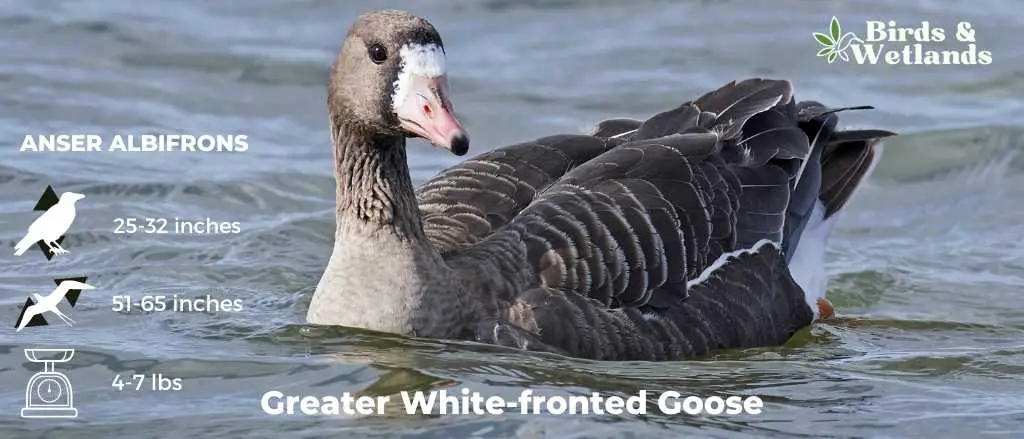
Greater White-fronted Goose

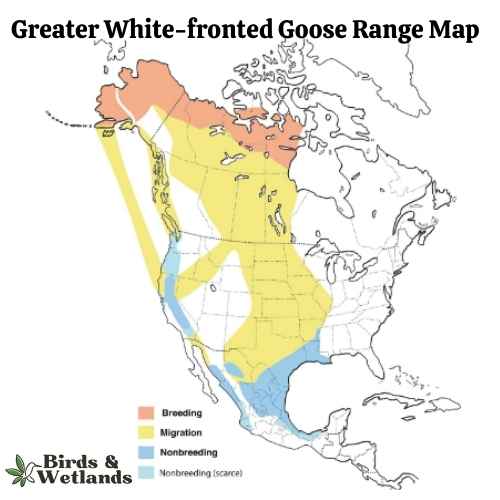
Listen
Scientific Name: Anser albifrons
Length: 25 to 31 in
Wingspan: 53 to 66 in
Weight: 3.3 to 6.6
The Greater White-fronted Goose is a medium to large waterfowl species, widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in North America.
Appearance: As the name suggests, these geese display a prominent white patch at the base of their bill. Their bodies are gray-brown, and their breasts are often marked with dark blotches. They possess a pinkish bill and orange legs and feet.
Diet: The Greater White-fronted Goose is a herbivore and feeds mainly on plant material. Its diet consists of grasses, sedges, grains, and berries. When wintering, these geese can often be found in agricultural fields, feasting on leftover grains and crops.
Reproduction: This species nests on the ground, often in areas with good visibility such as slopes or ridges. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for nearly a month. Once hatched, the young ones are taken care of by both parents until they are able to fly.
Hunting Geese in Nebraska
Yes, you can hunt geese in Nebraska. The state is home to a large number of different species of geese, including the Canada goose, the white-fronted goose, and the snow goose.
Hunting season for geese generally runs from September to February, although some areas have special rules and regulations regarding dates and bag limits.
Before heading out on a hunting trip, be sure to check with the Nebraska Game and Parks Commission for up-to-date information.
Can You Shoot Geese in Nebraska?
The use of unplugged shotguns and electronic calls is not allowed while hunting light geese or any other waterfowl during the regular season.
However, hunters are permitted to use nontoxic shotshells loaded with shot sizes no larger than T to take light geese.
Here are the daily bag and possession limits of goose in Nebraska:
| Daily Bag | Possession | |
| White-fronted Goose | 2 | 6 |
| Light Goose Regular Season (White and blue-phase snow geese and Ross’s Geese) | 50 | none |
| Light Goose Conservation Order | none | none |
Where Can I Hunt Geese in Nebraska?
Nebraska is home to a variety of different species of geese. Hunting season for geese generally runs from October to February, with the best time to hunt depending on the specific species you are targeting. The Light Goose Conservation Order runs from February to April.
As far as location goes, the Rainwater Basin and Platte River regions in the central part of the state are typically good spots to hunt geese, with eastern Nebraska and the Missouri River corridor being the best places to pursue light geese.
Large flocks of geese are migrating to Central Nebraska during the winter.
Regardless of where you choose to hunt, be sure to obtain all necessary permits and follow all regulations in order to ensure a safe and successful hunting trip.
Conclusion on Geese in Nebraska
If you’re ever in Nebraska and want to see some of the most beautiful birds around, keep your eyes peeled for geese and swans.
With five species of goose and two species of swans, there’s a good chance you’ll see at least one of these amazing creatures while you’re out and about.


