Nestled along the Eastern seaboard, Delaware is a veritable sanctuary for a variety of remarkable wildlife, and among these, the hawks certainly capture our attention. These stunning birds of prey in Delaware command the skies with their fierce grace, turning heads and inspiring awe in both locals and visitors alike. Offering a unique blend of habitats – from coastal marshes to woodland areas – Delaware provides an ideal setting for these majestic birds.
With an impressive number of hawk species making the state their home, Delaware’s skies become an unfolding narrative of predatory prowess and natural beauty, making it a must-visit location for bird enthusiasts. In this guide, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of Delaware’s hawks, exploring their species, behaviors, and the best spots to observe them in their natural habitat.
List of Hawks in Delaware
Red-tailed Hawk – This is arguably the most common hawk species in Delaware. Known for their broad, rounded wings and short, wide tails, Red-tailed Hawks can frequently be seen soaring in wide circles over open fields and wetlands. Their piercing call is a distinct soundtrack in Delaware’s Bombay Hook National Wildlife Refuge.
Cooper’s Hawk – The second most abundant in Delaware, Cooper’s Hawks are woodland birds that have adapted to city life, often seen darting through backyards in pursuit of songbirds. Ashland Nature Center and the surrounding forests are good spots for sighting these agile raptors.
Northern Harrier – Identified by their long tail and wings, Northern Harriers are unique among hawks for their owl-like face which helps them hunt by sound. They are commonly found hunting low over marshes and grasslands in Prime Hook National Wildlife Refuge.
Sharp-shinned Hawk – Despite being the smallest hawk in Delaware, the Sharp-shinned Hawk is a fearless hunter, renowned for its acrobatic flight skills. Birdwatchers can observe them in the dense forests of Lums Pond State Park.
Red-shouldered Hawk – Known for their distinctive reddish-brown shoulders and broad wings, these hawks are more commonly seen in Delaware’s wet deciduous forests, such as those in Brandywine Creek State Park.
Broad-winged Hawk – Most often sighted during migration season, the Broad-winged Hawk is famous for its large, dramatic flocks, or ‘kettles.’ Every fall, thousands can be seen over White Clay Creek State Park.
Northern Goshawk – Though less common, the Northern Goshawk is a force to be reckoned with. These elusive raptors inhabit large tracts of mature forest, with a few sightings recorded in the woodlands nestling on tall trees of Redden State Forest.
Rough-legged Hawk – These hawks are winter visitors in Delaware, known for their feathered legs. They can often be seen hovering over open fields and marshes, especially in the expansive wetlands of the Delaware Bay.
Delaware Hawks Photo Guide
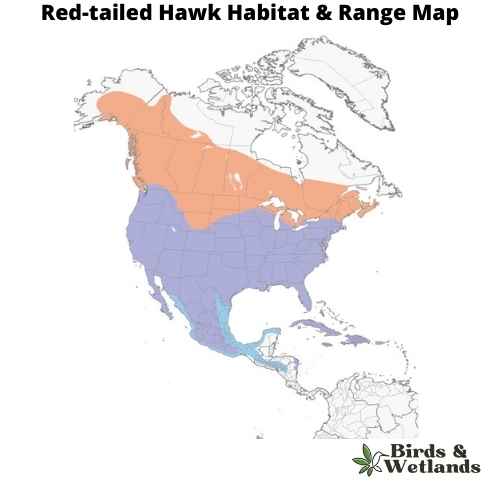
Red-tailed Hawk (Buteo jamaicensis)

The Red-tailed Hawk is a large bird of prey that is commonly found across North America. This species is part of the genus Buteo, which is often referred to as the “true hawks,” and includes more than two dozen species of raptors.
Red-tailed Hawks have a robust size, ranging from 18 to 26 inches in length and sporting a wingspan that can exceed 4 feet. They have a broad, rounded set of wings and a short, wide red tail. This species is most easily recognized by its rich, rust-colored tail, which gives it its common name. However, juvenile hawks might not yet have this distinctive feature.
Their feathers are generally dark brown on their dorsal side (back) with a lighter, often speckled, ventral side (front). The intensity and pattern of their plumage can vary significantly based on their age and geographic location, as there are about 14 recognized subspecies of Red-tailed Hawks.
As for their diet, Red-tailed Hawks are carnivores and have a broad diet that includes rodents, ground rabbits, reptiles, and other birds. They are skilled hunters that typically sit on high perches and use their keen eyesight to spot potential prey. Once they have identified a target, they swoop down to capture it with their powerful talons.
Red-tailed Hawks mate for life and build nests high off the ground, often in tall trees or on cliff edges. Their nests are made of sticks and can be quite large. They typically lay 1-3 eggs per year, which are incubated by both parents.
Red-tailed Hawk Sound
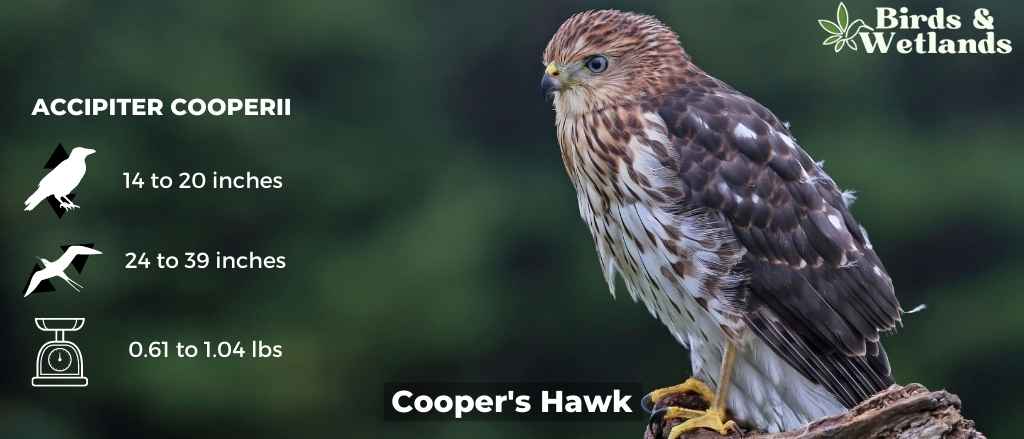
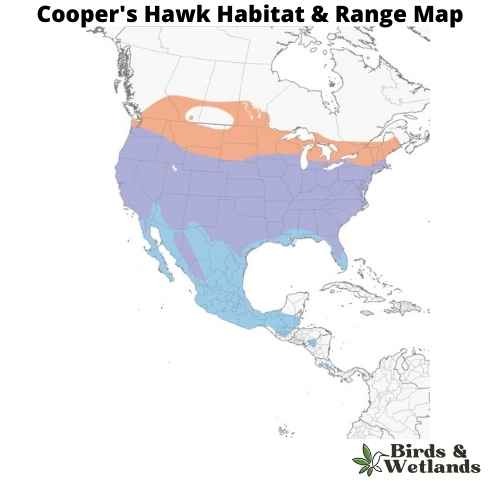
Cooper’s Hawk (Accipiter cooperii)

Listen:
The Cooper’s Hawk is a medium-sized bird of prey native to North America. Known for its agility and speed, it is part of the Accipitridae hawk species, which also includes other hawks, eagles, and kites.
Cooper’s Hawks are typically about 14 to 20 inches in length, with a wingspan ranging from 27 to 36 inches. They are known for their distinctive long, rounded tails and short, rounded wings. They have a steely blue gray top, with rusty bars on their underparts and thick, dark bands on their tails.
The Cooper’s Hawk is a skilled predator, primarily hunting birds and small mammals. They are adept at hunting in both dense forests and open areas, often catching prey mid-air in high-speed pursuits. They have also been known to visit the backyard bird feeder, not for the seed, but to prey on the smaller birds that gather there.
Cooper’s Hawks often build nests in dense tree canopies where they are well concealed. The female usually lays 3 to 5 eggs, and both parents share incubation duties. The young hawks fledge after about a month but will stay close to the nest, relying on their parents for food as they learn to hunt.
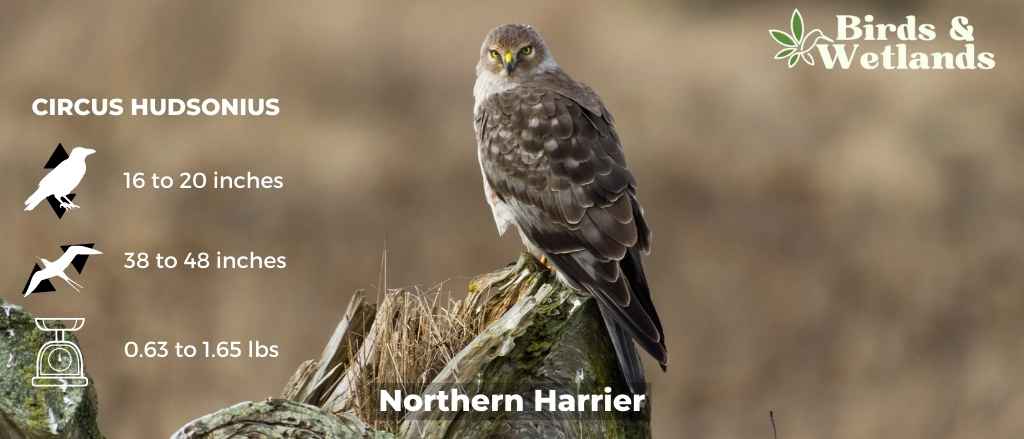
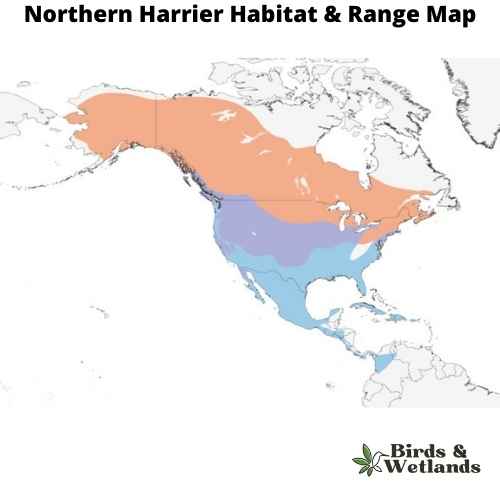
Northern Harrier (Circus hudsonius)

Listen:
The Northern Harrier is a medium-sized, slender hawk.
Adult birds are gray above, with pale bars on the wing feathers and white markings on the underwings and a white rump patch. The breast is barred with black and white, and the belly is streaked with brown.
They prefer open areas, such as grasslands and marshes, but can be found in almost any open habitat except dense woods.
Northern Harriers are opportunistic hunters that feed on small mammals such as mice, voles and rabbits as well as birds including quail, grouse and ducks. They hunt by flying low over open spaces such as fields or marshes.
Northern harrier nests on the ground in lowlands or hillsides near water bodies. It lays two to four eggs which hatch after 24 days of incubation by both parents. The chicks fledge after 30 days of hatching and remain dependent on their parents for another three weeks during which they learn how to fly.
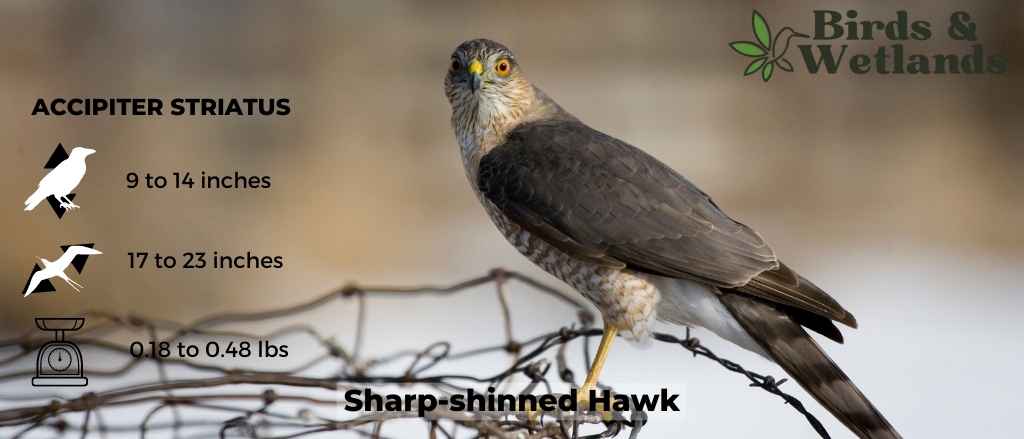
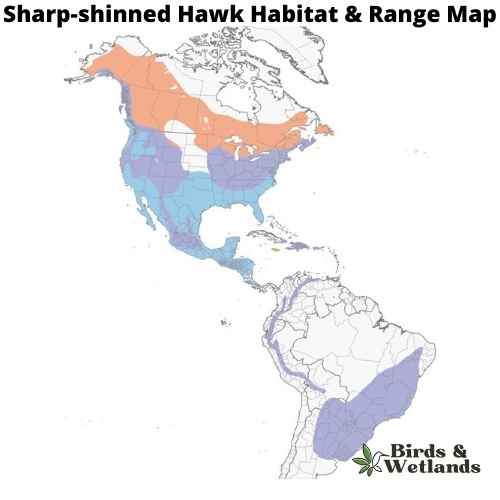
Sharp-shinned Hawk (Accipiter striatus)

Listen:
The adult bird is brown on top and white underneath, with a dark brown band across its chest. It has short, rounded wings and a long tail that makes it look larger than it actually is. Adult sharp shinned hawks have black eyes, which are surrounded by white feathers. The female Sharp-shinned Hawk is browner than the male, who has darker brown markings on his back.
Sharp-shinned Hawks prefer open country for their habitat, including fields and meadows where they can hunt for mice and other small animals. They can be found throughout the United States but are most common in the east.
Sharp-shinned Hawks eat mostly small birds, such as sparrows and warblers, as well as small mammals such as mice and gophers. They catch prey by surprise using their incredible speed and agility, diving out of the sky at speeds up to 200 mph.
Sharp-shinned Hawks have an unusual hunting style for hawks—they prefer to catch their prey from perches above trees or telephone wires, rather than swooping down from above like most other hawks do and can often be seen hunting near bird feeders.
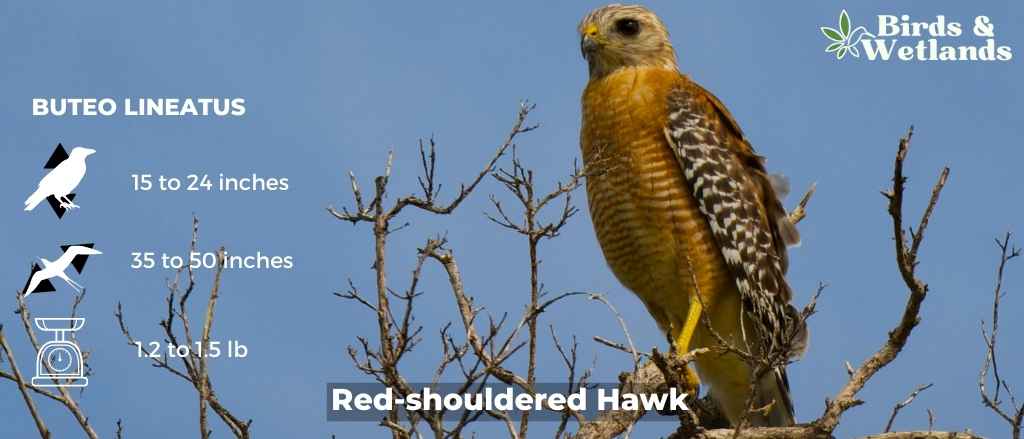
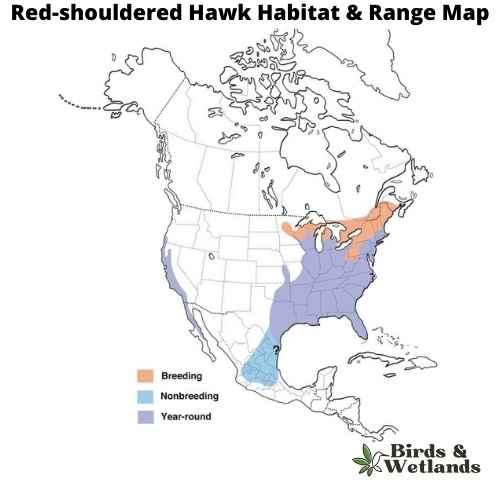
Red-shouldered Hawk (Buteo lineatus)

Listen:
The red-shouldered hawk are medium sized birds of prey, part of the buteo hawks family. It can be distinguished from other hawks by its reddish iris and pale legs.
The adult has rusty red upperparts, white underparts, a black chin and throat, and a reddish brown stripe over each eye, reddish brown heads and a strongly banded tail. The tail is reddish brown with two paler bands across it and they have white checkered wings. Juveniles are brown with dark barring and have pale fringes on the feathers of their wings.
Red-shouldered hawks nest in trees, though they also inhabit manmade structures including barns, bridges, and buildings. They prefer wooded areas with an open canopy but will use other places as well for nesting such as shrubs and hedges if needed.
The red-shouldered hawk’s diet – they eat small mammals such as ground squirrels, rabbits, voles, mice and rats. They also eat birds such as quail, pigeons and doves; reptiles including snakes; amphibians; fish; crustaceans; insects; and carrion (dead animals).
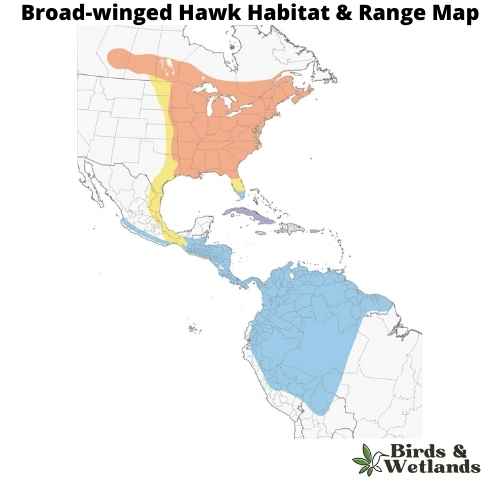
Broad-winged Hawk (Buteo platypterus)

Broad-winged Hawk Sound
The Broad-winged Hawk holds a commanding presence as one of the largest hawks in the world, known for its broad wings. Its formidable size is a testament to its prowess as a bird of prey, effortlessly navigating the open skies in search of food.
Their distinctive appearance sets them apart. The adults exhibit a striking black and white pattern, complemented by a rusty breast and buff underparts and brown wings. In contrast, juveniles are adorned with a brown plumage, marked by pale edges on their feathers, adding to their distinctive youthful charm.
These hawks are most commonly found in open areas, such as farmlands or grasslands interspersed with scattered trees, which provide optimal conditions for when hawks hunt.
When it comes to their diet, Broad-winged Hawks feed on small rodents like mice, rats, squirrels, rabbits, and voles. Broad winged hawks breed during the spring and summer months then migrate to central and south America.
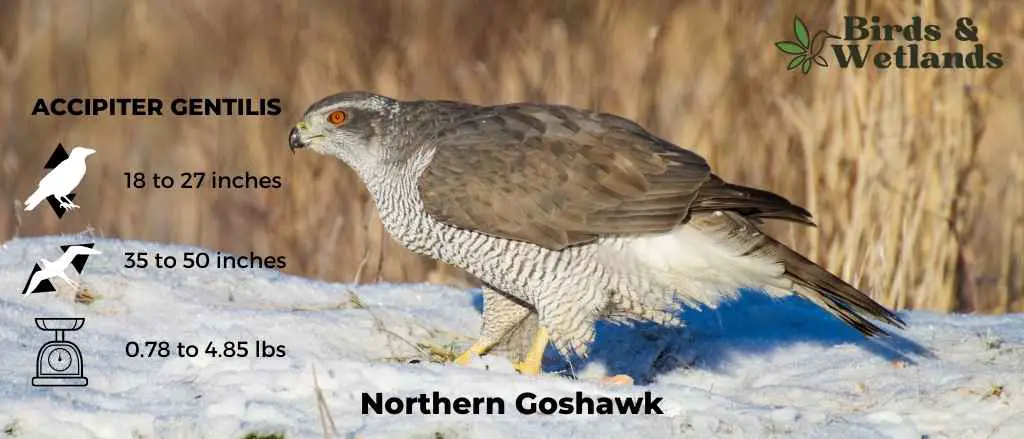
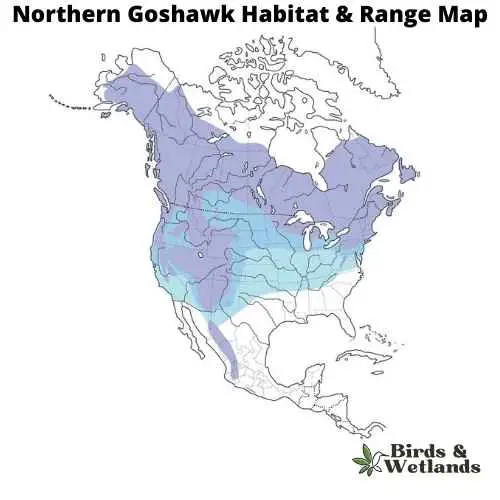
Northern Goshawk (Accipiter gentilis)

Listen:
The Northern Goshawk is a medium-sized hawk that is found in North America, Europe and Asia. It has brown eyes, a large sharp beak, and dark brown plumage on its upperparts and head, with white underparts that are spotted with brown barring. Its tail feathers are grayish-black with a dark band near the tip.
Northern goshawks eat squirrels, rabbits, grouse, woodchucks and other small mammals like voles or mice (which they often eat whole). They will also take larger prey such as deer fawns or even adult deer if they have no other choice. They have broad wings with long feathers that allow them to glide through the air when they catch their prey. They also have an excellent sense of smell which helps them locate their food source.
The Northern Goshawk builds its nest in a tree cavity or on a ledge, usually on the edge of an open area so it can easily see prey below. The female lays 3 to 5 eggs over two days and incubates them for 28 to 30 days while the male brings food to her every few hours until they hatch. The young fledge after about 6 weeks and leave the nest when they are about 10 weeks old.
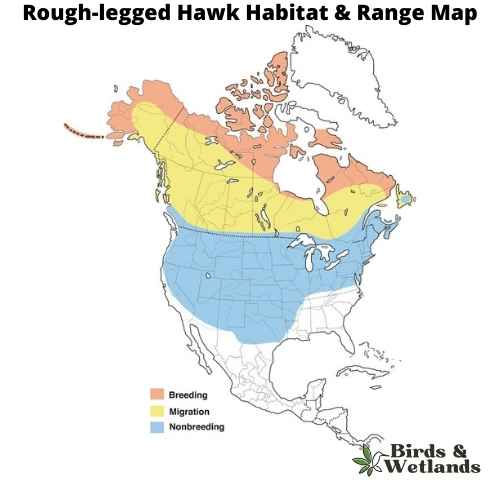
Rough-legged Hawk (Buteo lagopus)

Rough-legged Hawk Sound
The Rough-legged Hawk is a large, raptor that is native to North America. It is also known as the American Rough-legged Hawk. Scientific Name: Buteo lagopus
The Rough-legged Hawk is a medium-sized hawk with a distinctive appearance, with dark brown feathers on its back and light brown feathers on its underside and broad thin wings. The hawk’s legs are also covered in dark feathers, which help to distinguish it from other species of hawk. The tail is barred with black and white. They have yellow eyes and dark feet.
Rough-legged Hawks hunt from above ground level, swooping down to catch its prey in its talons. When hunting for food, they prefer to eat small mammals such as squirrels and rabbits but will also eat birds if there aren’t any small mammals available. Although they eat a variety of small animals including birds, rodents, bats and reptiles, they rely heavily on fish for food during breeding season because it provides them with protein and calcium needed to produce eggs.
Where to Spot Hawks in Delaware
Delaware offers several prime locations for observing the captivating diversity of hawks in the state. Here are the top spots for hawk-watching:
Bombay Hook National Wildlife Refuge: Situated along the Delaware Bay, this expansive refuge provides an ideal habitat for various hawk species. The diverse mix of marshes, fields, and forests attracts raptors like the Red-tailed Hawk, Northern Harrier, and occasional sightings of the Rough-legged Hawk during winter.
Ashland Nature Center: Nestled within the Piedmont region, Ashland Nature Center boasts rich woodlands, making it an excellent place to spot hawks. Cooper’s Hawks are commonly seen darting through the trees in pursuit of prey, while Red-shouldered Hawks can be found perched and calling from the forest canopy.
Prime Hook National Wildlife Refuge: This coastal refuge offers an abundance of wetlands and grasslands, attracting hawks like the Northern Harrier. These graceful raptors can be observed gliding low over the marshes in search of prey, offering fantastic opportunities for close encounters.
White Clay Creek State Park: During fall migration, birdwatchers flock to this park to witness the impressive spectacle of Broad-winged Hawks. Look to the skies as thousands of these hawks form large kettles as they migrate south and soar together on their journey.
The captivating allure of observing the Coopers Hawks in Delaware serves as a tantalizing beginning to an expansive hawk-watching journey. As you cross the state borders, the dramatic shift in scenery introduces the thrill of observing Maryland’s Sharp-shinned Hawks amidst their verdant woodland habitats. Further afield, Pennsylvania beckons with its breathtaking landscapes, home to the awe-inspiring Northern Harriers of Pennsylvania gracefully soaring over vast valleys.
FAQs About Hawks in Delaware
Are hawks in Delaware migratory birds?
Yes, many hawks in Delaware are migratory birds, with some species passing through during spring and fall migrations.
Do hawks in Delaware pose a threat to small pets?
While hawks primarily target small birds and mammals like ground squirrels in their natural habitat, it’s important to supervise small pets outdoors to minimize any potential risk.
Are there any conservation efforts in place to protect hawks in Delaware?
Yes, Delaware actively supports various conservation initiatives, including habitat preservation, nesting site protection, and educational programs to ensure the well-being of hawks and their ecosystems.
Do hawks play a role in controlling pest populations in Delaware?
Absolutely! Hawks are natural predators and help maintain a balance in ecosystems by controlling populations of rodents, small mammals, and other pest species.


