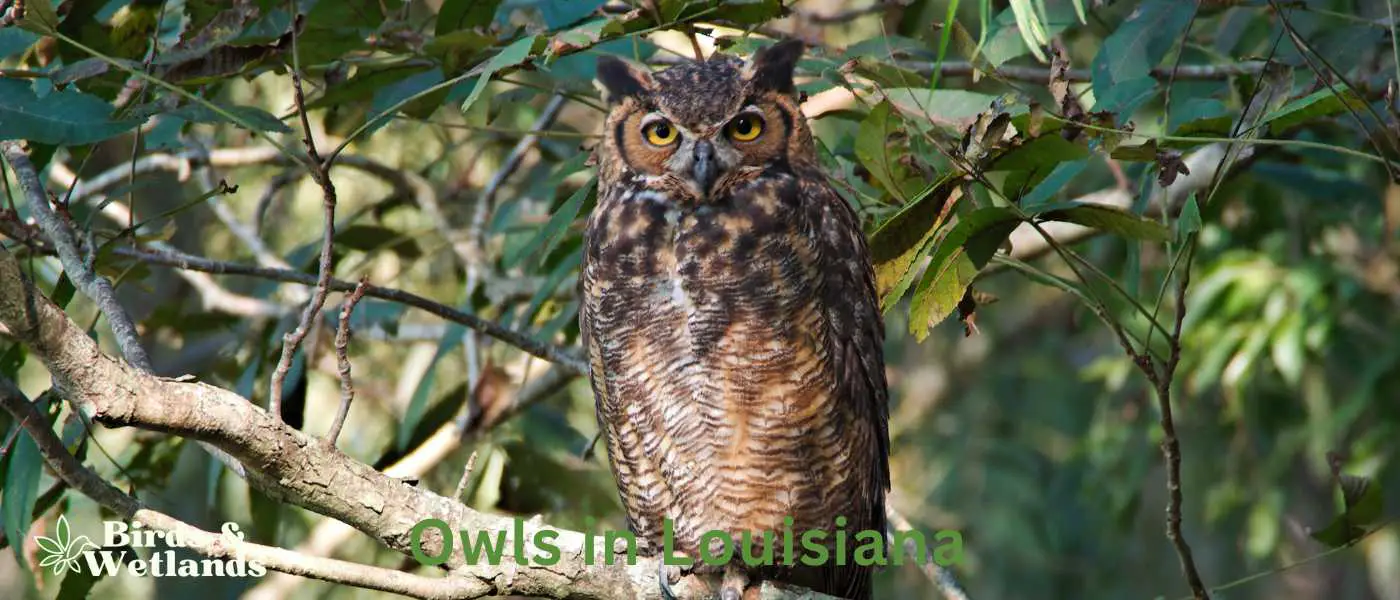
Within Louisiana’s diverse biomes, spanning from its dense swamps and marshlands to its pine forests and coastal plains, thrives an intriguing variety of owls. These night-time Louisiana birds of prey play a pivotal role within the state’s ecosystems, acting as predators, prey, and environmental health indicators.
Louisiana Owls
| Owl Species | Frequency in Louisiana | Presence in Louisiana | Where to Find in Louisiana |
|---|---|---|---|
| Great Horned Owl | High | Statewide | Kisatchie National Forest, near Alexandria; Atchafalaya National Wildlife Refuge, near Baton Rouge |
| Eastern Screech Owl | High | Statewide | City Park, New Orleans; Acadiana Park Nature Station, Lafayette |
| Barred Owl | High | Statewide | Jean Lafitte National Historical Park and Preserve, Marrero; Bogue Chitto National Wildlife Refuge, Slidell |
| Barn Owl | Moderate | Across Louisiana, primarily in Open Fields | Black Bayou Lake National Wildlife Refuge, Monroe; Cameron Prairie National Wildlife Refuge, Bell City |
| Long-eared Owl | Low | Scattered Across State | Catahoula National Wildlife Refuge, near Jena; Upper Ouachita National Wildlife Refuge, near Monroe |
| Short-eared Owl | Low | Open Fields and Grasslands | Sabine National Wildlife Refuge, Hackberry; Red River National Wildlife Refuge, Bossier City |
| Burrowing Owl | Low | Western Louisiana | Red River National Wildlife Refuge, Bossier City; Lacassine National Wildlife Refuge, Lake Arthur |
| Northern Saw-whet Owl | Very Low (Seasonal) | Northern Louisiana in Winter | Jimmie Davis State Park, Chatham; Claiborne Parish, Homer |
Owl Species Found in Louisiana
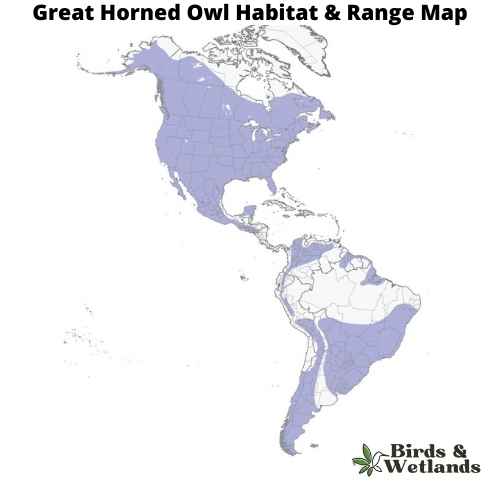
Great Horned Owl (Bubo virginianus)

Great Horned Owl Sound
Scientific Name:Bubo virginianus
Length: 18.1-24.8 in
Wingspan: 39.8-57.1 in
Weight: 32.1-88.2 oz
The Great Horned Owl is a large owl with long wings and a large head. It’s one of the most common owls in North America.
Great Horned Owls are large, stocky birds with soft feathers that are gray to brown on their backs and white on their chests. Their faces are characterized by two black “ear” tufts, which can be raised or flattened depending on the owl’s mood. The eyes are yellow, orange, or red in color.
The habitat of the Great Horned Owl is a variety of different environments such as forests and deserts. They also live near water sources such as lakes, streams and rivers where they can hunt for fish.
The diet of the Great Horned Owl consists primarily of small mammals such as mice and rats; however they will also eat other rodents such as squirrels, rabbits and porcupines. They have been known to eat skunks too.
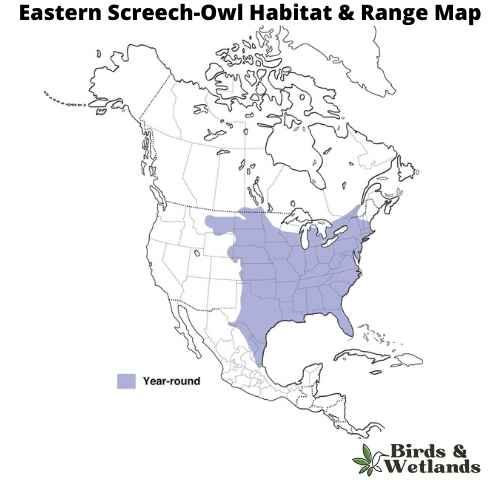
Eastern Screech-Owl (Megascops asio)

Eastern Screech-Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Megascops asio
Length: 6 to 10 in
Wingspan: 8 to 24 in
Weight: 4 – 8.5 oz
The Eastern Screech-Owl is a small owl species native to most wooded environments of the eastern half of North America, from the Canadian provinces to Florida and Texas.
Eastern Screech-Owls are relatively small and exhibit a complex pattern of gray or reddish-brown coloration, which provides excellent camouflage against tree bark.
These owls are known for their distinctive call, which is often described as a haunting trill or a whinny-like sound. Despite their name, they do not actually produce a “screech.”
Eastern Screech-Owls feed on a variety of prey, ranging from small mammals and birds to insects and even earthworms. It is primarily nocturnal, hunting at night from a low perch and swooping down onto prey.
Eastern Screech-Owls nest in tree cavities or abandoned woodpecker nests, but they readily adapt to nesting boxes where natural cavities are not available. They typically lay between 2 to 6 eggs, which are incubated primarily by the female.
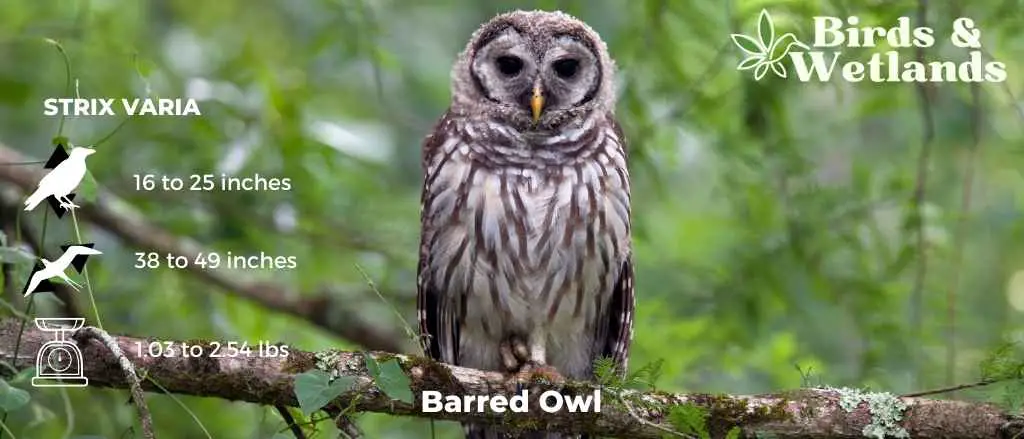
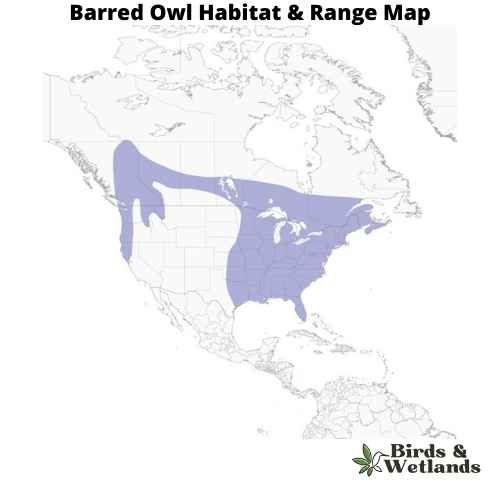
Barred Owl (Strix varia)

Barred Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Strix varia
Length: 40 to 63 cm (16 to 25 in)
Wingspan: 96 to 125 cm (38 to 49 in)
Weight: 468 to 1,150 g
The Barred Owl is a medium-sized owl with a barred pattern on its chest and belly. They have large yellow eyes that allow them to see well in low light conditions. Their ears are not very large which means they do not hear very well but they have excellent hearing abilities which allow them to detect sounds up to 1 mile away. Their feathers are brown and streaked with white, and they have black bars on their chests and wings.
Their habitats include forests, woodlands, orchards, parks, farmland and suburban backyards.
Barred Owls (also known as hoot owl) eat small mammals such as mice, rats and squirrels. They also eat insects such as beetles or grasshoppers. These owls hunt during the day when it is light out so that they can see their prey better than at night when they would be using senses other than sight like sound or smell to find their food source.
Barred owls are monogamous birds which means they mate for life. They build nests in trees or cavities on the ground and lay 2-4 eggs per year. The incubation period for these eggs lasts about 28 days before hatching takes place.
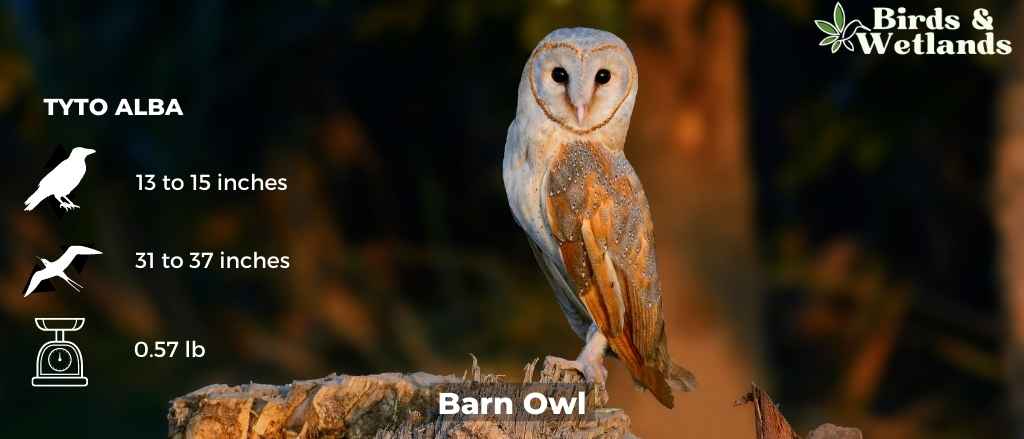
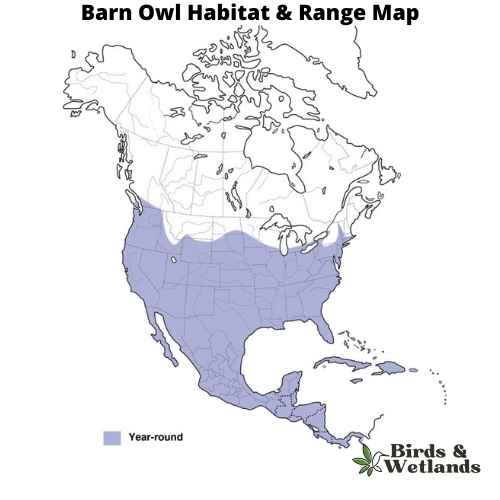
Barn Owl (Tyto alba)

Barn Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Tyto alba
Length: 13 to 15 in
Wingspan: 31 to 37 in
Weight: 9.2 oz
The Barn Owl is a widespread species of owl known for its distinctive heart-shaped facial disc.
Barn Owls are medium-sized owls, they are pale overall with golden-brown wings and back, contrasted by a white face, chest, and belly. Their most notable feature is their heart-shaped facial disc, which helps channel sound to their ears.
Barn Owls are typically found in open habitats, including farmland, woodland, and marshes. They are named for their habit of nesting in human structures such as barns, church towers, and in the hollows of large trees. These owls are nocturnal, hunting at night and roosting during the day.
The diet of Barn Owls primarily consists of small mammals, particularly rodents such as mice and rats. They are known for their silent flight, which allows them to sneak up on their prey without detection.
Barn Owls have a unique nesting behavior. They do not build nests, but instead, lay their eggs directly on the bare surface of a secluded ledge or cavity. A female typically lays 4-7 eggs, and both parents help incubate the eggs and care for the chicks.
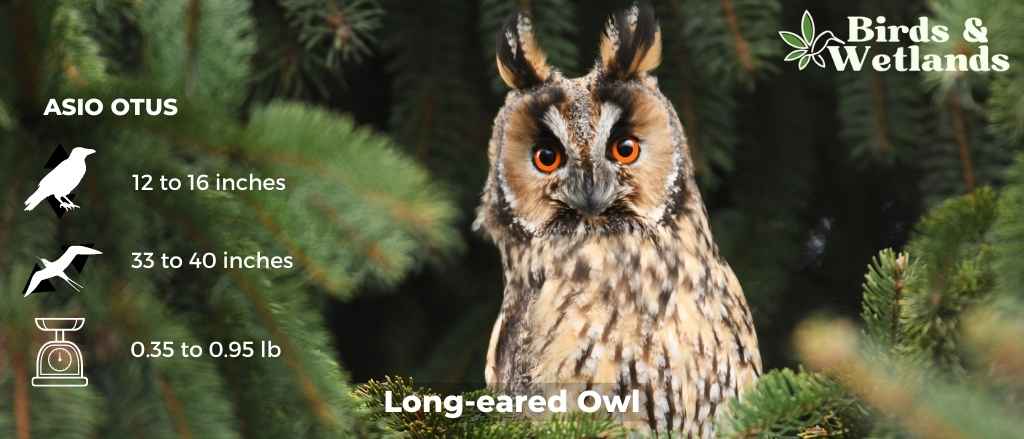
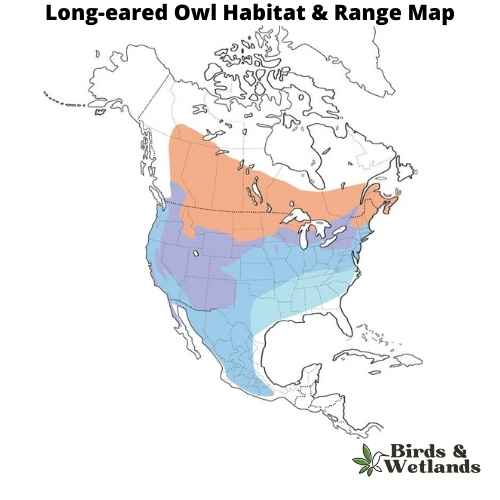
The long-eared owl (Asio otus)

Long-eared Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Asio otus
Length: 12 and 16 in
Wingspan: 2 ft 10 in to 3 ft 4 in
Weight: 5.6 to 15.3 oz
The Long-eared Owl is a medium-sized owl species known for its distinctively long ear tufts, which can be raised or lowered depending on the bird’s mood or intention.
Long-eared Owls have mottled brown and cream plumage, which provides excellent camouflage among the trees. Their most distinctive features are their long, black-tipped ear tufts, which are set closer to the center of the head than in most other owl species.
These owls inhabit a wide variety of habitats, including deciduous and coniferous forests, woodlands, and even semi-deserts.
The Long-eared Owl’s diet primarily consists of small mammals, especially voles, but they will also take small birds and insects. They are skillful hunters, often capturing prey from a perch or in flight.
In terms of nesting behavior, Long-eared Owls do not construct their own nests, instead they take over old nests built by other bird species, usually those of corvids or other large birds. They lay an average of 4 to 5 eggs, which are incubated by the female while the male provides food.
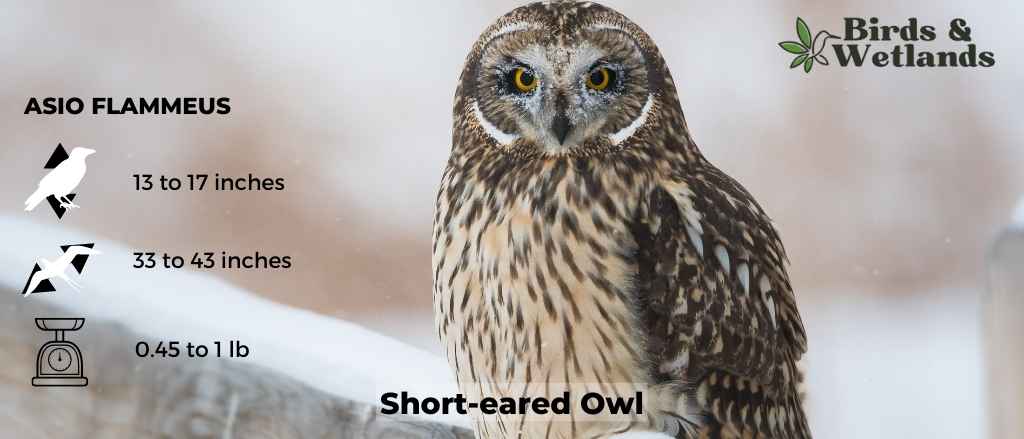
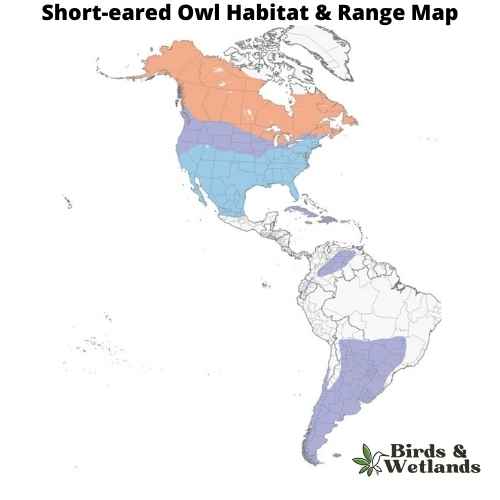
Short-eared Owl (Asio flammeus)

Short-eared Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Asio flammeus
Length: 13–17 in
Wingspan: 33 to 43 in
Weight: 7.3–16.8 oz
The Short-eared Owl is a medium-sized owl species with a wide distribution, found across North and South America, Europe, Asia, and many Pacific islands. Despite its name, the “ears” of the Short-eared Owl are not often visible, as they are small and tend to blend with the bird’s feathers.
The owls are predominantly brown with buff and white accents throughout their body and wings, and dark patches around their yellow eyes.
Short-eared Owls diet consists largely of small mammals, especially voles. However, they are opportunistic hunters and will also prey on a variety of other animals, including other birds, when available.
Their habitat is characterized by open areas like grasslands, marshes, and tundra. They nest on the ground, which is unusual for owls, and this makes them vulnerable to ground predators. As such, they often live in areas with tall grasses or other ground cover for protection.
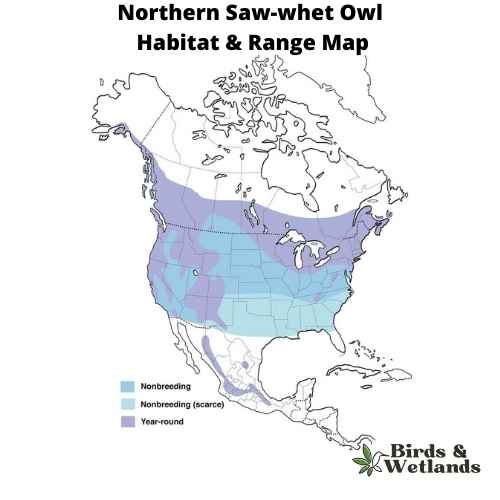
Northern Saw-whet Owl (Aegolius acadicus)

Northern Saw-whet Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Aegolius acadicus
Length: 17–22 cm (6.7–8.7 in)
Wingspan: 42–56.3 cm (16.5–22.2 in)
Weight: 54 to 151 g (1.9 to 5.3 oz)
The Northern Saw-whet Owl is a tiny, speckled gray owl and it’s one of the smallest owls in North America. It’s also known as the Little Owl or Wood Owl in some areas.
Northern Saw-whet Owls have dark brown eyes, white eyebrows, and yellow beak. It has brownish-grey feathers that are spotted with white. The owl’s legs are covered in feathers and appear nearly invisible when the bird is perched on a branch or tree.
In the winter they migrate south to warmer climates. They prefer to live in dense coniferous forest with large trees but will occasionally nest in shrubs or other vegetation that can protect them from predators.
The Northern Saw-whet Owl eats mice and voles (small rodents), small birds, frogs, salamanders, moles and shrews, but unlike most owls they chop their prey up and spread over a few meals. They will also eat insects like beetles and grasshoppers if they are available. It hunts from a perch at night using its excellent hearing to locate prey items within about 30 feet (9 meters) of its nest.
These owls nest in tree cavities usually located close to water sources such as lakes or rivers where they can find their food source (insects). They lay 2-4 eggs at one time which incubate for about 30 days before hatching.
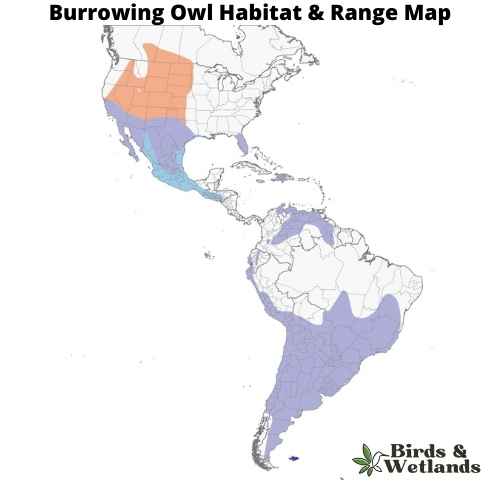
Burrowing Owl (Athene cunicularia)

Burrowing Owl Sound
Scientific Name: Athene cunicularia
Length: 7–11 in
Wingspan: 20–24 in
Weight:5–8 oz
The Burrowing Owl is a small, long-legged species of owl found in North and South America. Known for its unusual habit of living in burrows in the ground.
Burrowing Owls have a rounded head with no ear tufts and bright yellow eyes. Their overall coloration is mottled brown and white with a distinct white “eyebrow” above each eye.
Their primary habitat includes open landscapes such as grasslands, deserts, agricultural areas, golf courses, and even airports. As their name suggests, these owls often reside in burrows, many of which are abandoned by prairie dogs, ground squirrels, or other burrowing animals. In some cases, they may also dig their own burrows.
Burrowing Owls diet consists mainly of small mammals and insects, but they also eat birds and reptiles.
Burrowing Owls have a unique nesting behavior. They lay their eggs in an underground burrow to protect them from predators and extreme weather. Clutch sizes range from 6 to 11 eggs, which are incubated for about a month before hatching.
Where to Spot Louisiana’s Owls
Atchafalaya National Wildlife Refuge, Lottie: This refuge provides habitat to a variety of bird species, including owls such as Barred Owls, Eastern Screech Owls, and Great Horned Owls.
Jean Lafitte National Historical Park and Preserve, Marrero: Located near New Orleans, this preserve is an excellent location for spotting Barred Owls and Eastern Screech Owls, and occasionally the Great Horned Owl.
Kisatchie National Forest, Pineville: As the only national forest in Louisiana, Kisatchie is home to many bird species, including many other owls. You’ll find Eastern Screech Owls, Barred Owls, and Great Horned Owls here.
Tensas River National Wildlife Refuge, Tallulah: This refuge provides a home for several owl species, including the Barred Owl, Great Horned Owl, and Eastern Screech Owl.
Grand Isle, Jefferson Parish: Known for its migratory bird festival, this island is a great place to spot various bird species. You may see owls like the Eastern Screech Owl and Barred Owl, especially during migration season.
| State | Main Owl Watching Sites |
|---|---|
| Louisiana Owls | Atchafalaya National Wildlife Refuge, Kisatchie National Forest |
| Texas Owls | Big Bend National Park, Brazoria National Wildlife Refuge |
| Arkansas Owls | Hot Springs National Park, White River National Wildlife Refuge |
| Mississippi Owls | Noxubee National Wildlife Refuge, De Soto National Forest |
Tips on How to Spot Owls in Louisiana?
Explore Ideal Habitats: Louisiana’s diverse habitats, including swamps, marshlands, and forests, provide excellent homes for owls. Some of the best locations to spot owls include Atchafalaya National Wildlife Refuge, Jean Lafitte National Historical Park and Preserve, and the forests around Toledo Bend Reservoir.
Timing is Key: Owls are most active during the “crepuscular” hours – dawn and dusk. During the nesting season, which often occurs in late winter to early spring, owls may be more active during daylight hours as they hunt to feed their chicks.
Recognize Their Calls: Learning the distinct calls of various owl species can greatly increase your chances of identifying them, even when they’re hidden amongst foliage. There are many resources online, including apps and websites, to help you learn these sounds.
Move Quietly: Silence is essential when birdwatching for owls. Owls have very sharp hearing and can be easily disturbed by human noise. Walking quietly and whispering can increase your chances of spotting an owl.
Look for Signs: Pay attention to signs of owl activity such as owl pellets, distinctive white droppings, or feathers. This can often indicate an owl roosting nearby.
Equip Yourself: Equip yourself with a good pair of binoculars or a spotting scope. Because owls can be well-camouflaged and active during low light conditions, these tools can be extremely helpful.
Join Local Groups: Consider joining a local birdwatching group or participating in organized birding trips. Not only can you learn from the experienced members, but birding is also a social activity that can be enjoyed in a group.

