Utah, known for its remarkable natural landscapes, is also a host to an array of water birds that add to the state’s unique biodiversity. With lots of water bird species making their home in this state, Utah’s waterways and wetlands have become vital habitats for these fascinating creatures.
Utah water birds
| Water Bird | Frequency | Where to Find in Utah |
|---|---|---|
| American White Pelican | Common | Great Salt Lake, Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge |
| Double-Crested Cormorant | Very Common | Statewide, especially Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge |
| Great Blue Heron | Very Common | Statewide in wetland areas and riverbanks |
| Great Egret | Common | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge |
| Snowy Egret | Common | Great Salt Lake, Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge |
| Green Heron | Uncommon | Jordan River Parkway |
| Black-Crowned Night-Heron | Common | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge |
| Mallard | Very Common | Statewide in wetland areas |
| Wood Duck | Uncommon | Logan River, Ogden River |
| Blue-Winged Teal | Common | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge |
| Northern Pintail | Common | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge, Great Salt Lake |
| Redhead | Common | Great Salt Lake |
| Ring-Necked Duck | Common | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge, Great Salt Lake |
| Bufflehead | Uncommon | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge during migration |
| Hooded Merganser | Uncommon | Provo River during migration |
| Common Merganser | Uncommon | Provo River during migration |
| American Coot | Very Common | Statewide in wetland areas |
| Sandhill Crane | Common | Great Salt Lake, Fish Springs National Wildlife Refuge |
| American Wigeon | Common | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge |
| Common Loon | Uncommon | Great Salt Lake during migration |
| Pied-Billed Grebe | Common | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge, Great Salt Lake |
Water Bird Species Found in Utah
American White Pelican


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pelecanus erythrorhynchos |
| Length | 50–70 in |
| Wingspan | 95–120 in |
| Weight | 3.5 and 13.6 kg |
The American White Pelican (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos) is one of North America’s largest birds, distinguished by its brilliant white plumage, elongated orange bill, and massive wingspan, which can extend up to 3 meters. This bird has a unique appearance with its distinctive pouch used for feeding and a “horn” on the upper part of the bill during the breeding season. Though a large bird, it is very graceful in flight, often seen soaring in flocks in a V formation.
American White Pelicans inhabit lakes, marshes, and salt bays, and despite their size, they are excellent swimmers. They feed primarily on fish, using a cooperative hunting strategy where they encircle schools of fish in shallow water and then scoop them up in their bill pouches. Unlike their brown pelican relatives, they do not dive for their food. During the breeding season, these pelicans will nest in colonies on islands in freshwater lakes.
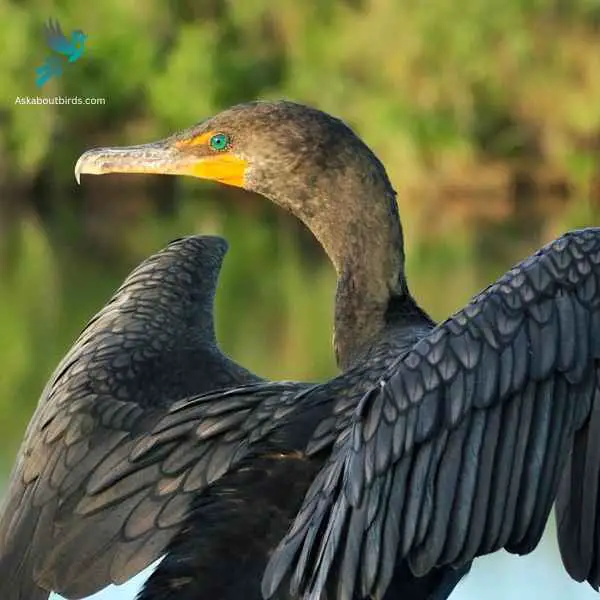
Double-crested cormorant


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Nannopterum auritum |
| Length | 28–35 in |
| Wingspan | 45–48 in |
| Weight | 1.2–2.5 kg |
The Double-Crested Cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus) is a large waterbird known for its long neck, hooked bill, and almost entirely black body. The species gets its name from the two small patches of tufted feathers or “crests” found on the heads of breeding adults, one on each side. These birds are strong swimmers that propel themselves underwater with their webbed feet, their bodies submerged and necks above the water surface, giving them a characteristic snake-like appearance when swimming.
Double-Crested Cormorants are widely distributed across North America and can be found in a variety of aquatic environments including freshwater lakes, coastal areas, and rivers. Their diet primarily consists of fish, which they catch by diving from the water’s surface. Often seen perched with wings outstretched to dry after fishing, these cormorants nest in trees, on the ground, or on cliff edges, usually in colonies. While they have rebounded from decreases in the mid-20th century due to DDT-related reproductive failures, they face ongoing threats from habitat loss, entanglement in fishing gear, and conflicts with fisheries over their consumption of fish. Protection and careful management of their habitats are key to their ongoing conservation.
Great Blue Heron


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ardea herodias |
| Length | 36–54 in |
| Wingspan | 66–79 in |
| Weight | 1.82–3.6 kgs |
Great Blue Herons are the largest heron species in North America, is distinguished by its tall stature and unique blue-gray plumage.
Measuring up to 4.5 feet tall with a wingspan of approximately 6.5 feet, the bird features a long, pointed bill, a white head with a black eye stripe extending to slender black plumes, and robust, elongated legs. Its distinctive flight pattern, forming a tight “S” shape with its neck, sets it apart from similar large birds, like cranes.
Inhabiting various wetland habitats, including marshes, lakes, rivers, and coastal regions throughout much of North and Central America, the Great Blue Heron is a wading bird. Often seen poised statue-like at the water’s edge, these birds are expert hunters, spearing fish and capturing small animals with their sharp bills.
Great Egret


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ardea alba |
| Length | 31 to 41 in |
| Wingspan | 52 to 67 in |
| Weight | 1.5 to 3.3 lbs |
The Great Egret (Ardea alba), also known as the Common Egret, is a large, elegant wading bird recognized for its brilliant white plumage, slender black legs, and long, dagger-like yellow bill.
With a height of up to 3.3 feet and a wingspan of 52 to 67 inches, this bird is amongst the largest of the heron species. Its stately appearance and serene comportment have made it a popular symbol in many cultures and an eye-catching sight in its habitats.
Found across all continents except Antarctica, the Great Egret resides in both fresh and saltwater wetlands, including marshes, ponds, and coastal areas. It feeds mainly on fish, but it also hunts amphibians, small mammals, and invertebrates.
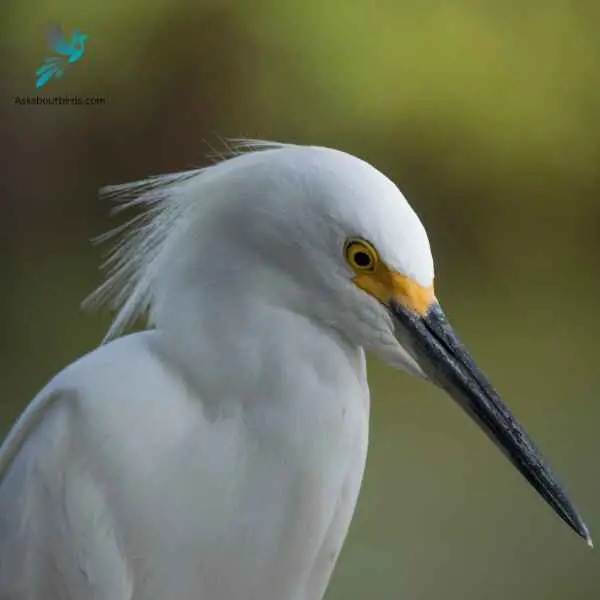
Snowy Egret


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Egretta thula |
| Length | 22.1–26.0 in |
| Wingspan | 39.4 in |
| Weight | 370 g |
The Snowy Egret (Egretta thula) is a small and active wading bird, celebrated for its delicate beauty. It sports an entirely white plumage that appears to glow against its black bill and legs, and striking yellow feet, which often play a crucial role in luring prey during feeding.
The Snowy Egret is further adorned with fine, plume-like feathers on its head, neck, and back during the breeding season, making it one of the more distinctive heron species.
Inhabiting wetland areas across the Americas, the Snowy Egret can be found in marshes, swamps, shorelines, and tidal flats where it feeds primarily on fish, but also consumes insects, crustaceans, and small reptiles.
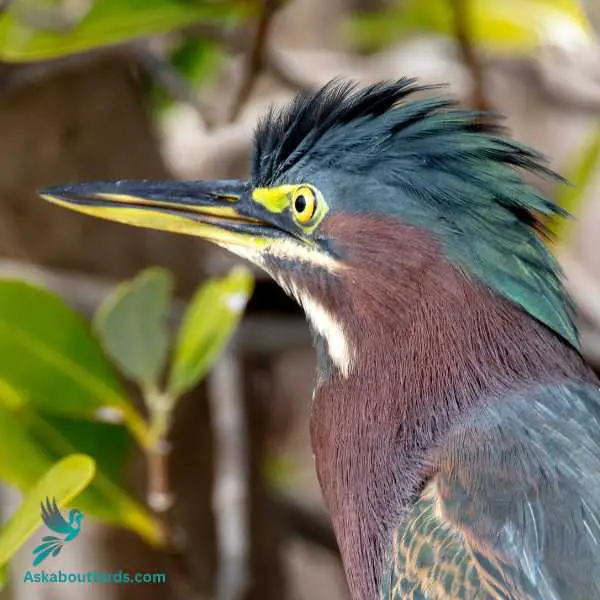
Green Heron


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Butorides virescens |
| Length | 16-18 inches |
| Wingspan | 25-27 inches |
| Weight | 6-7 ounces |
The Green Heron is a small heron found in North America, notable for its deep green back and chestnut body, as well as its unique fishing tactics.
Appearance: Green Herons are dark and compact birds with a glossy, greenish-black cap, a greenish back and wings, and chestnut neck and belly. The bill is long, dark and sharply pointed. Their legs are bright orange or yellow. Young birds are duller in color, with a dark top and streaked brown front.
Diet: The Green Heron’s diet is quite varied, consisting mostly of small fish, but also includes insects, spiders, and sometimes amphibians and small mammals. It’s known for its tool-using behavior where it drops bait onto the water’s surface to attract fish.
Reproduction: Green Herons are solitary birds except during the breeding season, where they form monogamous pairs. Nests are typically built in trees or shrubs near water. Females lay 2 to 5 pale blue-green eggs that both parents incubate.
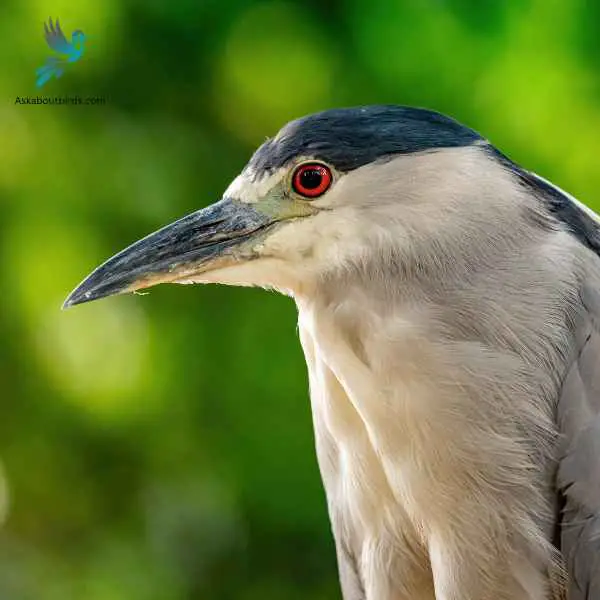
Black-Crowned Night-Heron


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Nycticorax nycticorax |
| Length | 22.8-26.0 in |
| Wingspan | 45.3-46.5 in |
| Weight | 727-1014 g |
The Black-Crowned Night-Heron (Nycticorax nycticorax) is a medium-sized heron species known for its distinct nocturnal habits and characteristic appearance. The bird displays a stocky silhouette, with a black crown and back, contrasting starkly with its light grey wings and white underparts.
Its eyes are large and red, adapted for its night-time activities, and its legs are relatively short for a heron. The bill is sturdy and black, and during the breeding season, two to three long white plumes extend from the back of the head.
Residing in a wide variety of wetland habitats, from freshwater marshes to coastal regions, the Black-Crowned Night-Heron is found across a large global range, including the Americas, Europe, Asia, and Africa. The species primarily feeds on fish and invertebrates, but it is known to be opportunistic and will also eat small mammals, birds, and eggs.
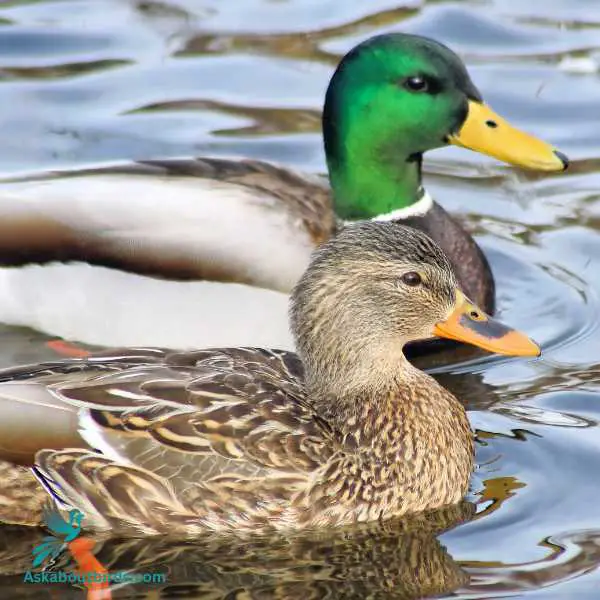
Mallard


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Anas platyrhynchos |
| Length | 20-26 inches |
| Wingspan | 32-39 inches |
| Weight | 1.6-3.5 pounds |
The Mallard, one of the most recognizable of all ducks, is distinguished by its classic “quack” and its common presence in city parks and wild wetlands.
Appearance: Mallards are large ducks with a hefty body and rounded head. The male is notable for its glossy green head, gray body, and black tail-curl, while the female is mottled brown with an orange-brown bill. Both sexes have a white-bordered, blue “speculum” patch in the wing.
Diet: Mallards are omnivorous, dabbling ducks that eat a wide variety of foods. They are known to feed on aquatic vegetation, insects, worms, and grains. In city parks, they are often seen eating bread, popcorn, and other food provided by humans, although such items are not part of their natural diet.
Reproduction: Mallards nest on the ground on dry land that is close to water, under cover of tall grass or other vegetation. The female typically lays around 8 to 13 eggs and incubates them herself.
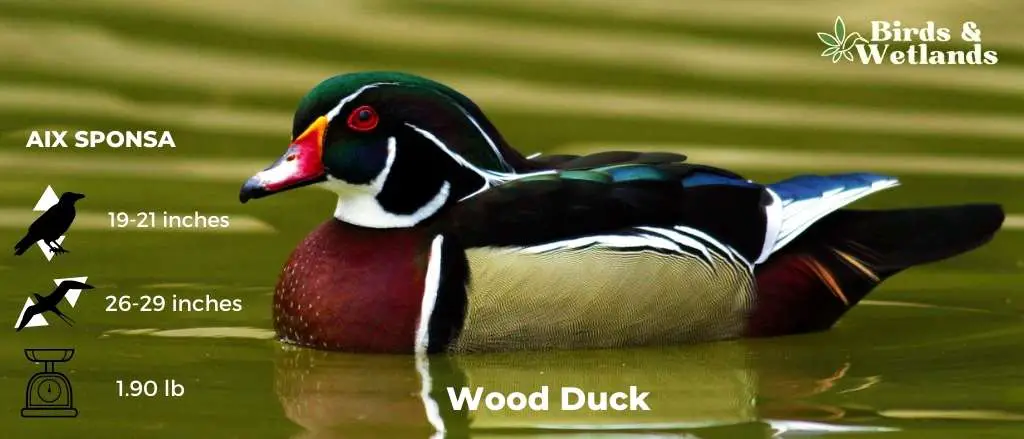
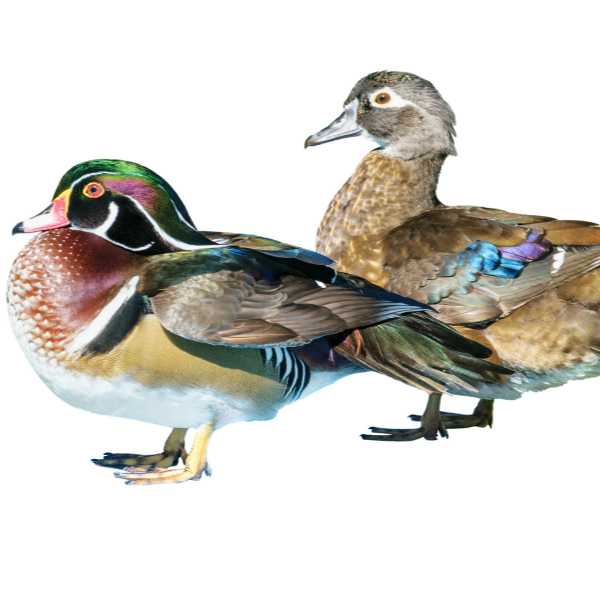
Wood Duck


Listen:
Scientific Name: Aix sponsa
Length: 19 to 21 in
Wingspan: 26 to 29 in
Weight: 16.0-30.4 oz
The Wood Duck is an exquisitely colorful waterfowl known for its unique nesting habits and is commonly seen in wooded swamps, marshes, and streams across North America.
Appearance: With their dazzling plumage, Wood Ducks are among the most stunning birds. Males display a multitude of colors, including a green and purple crested head, red eyes, and a white-striped chest, all contrasted with a bronze-colored body. Females, though more subdued with a gray-brown body and white eye-ring, also possess their own charm.
Diet: Wood Ducks have a diverse diet that includes seeds, fruits, and insects, as well as other invertebrates. Their broad diet helps them to adapt to a variety of habitats, whether in the wild or in urban areas with suitable nesting sites.
Reproduction: Unlike most other ducks, Wood Ducks prefer to nest in tree cavities near water, leading to their common name. They will also readily use nest boxes if they’re available. A typical clutch consists of 9 to 14 eggs, which the female incubates alone.
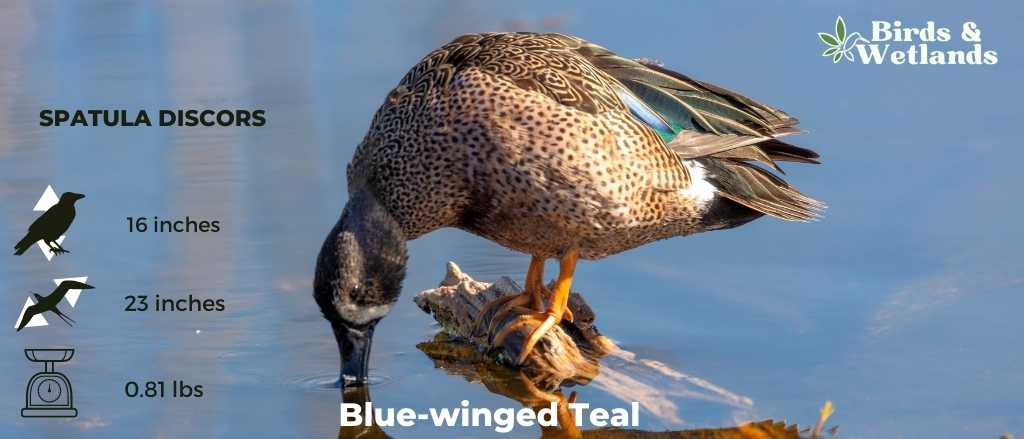
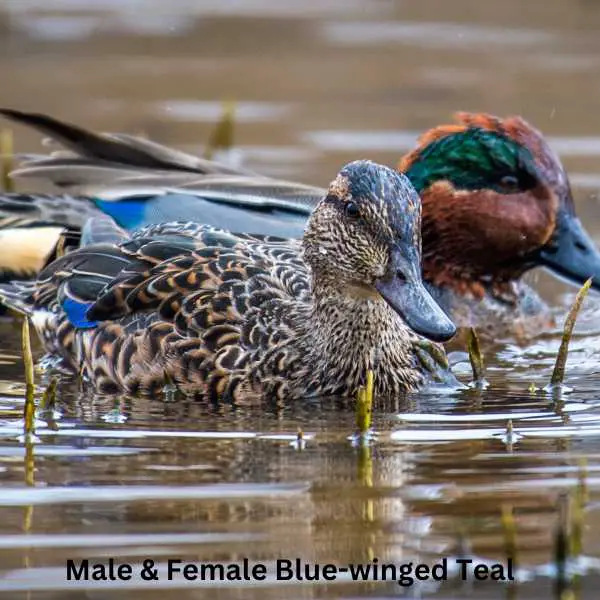
Blue-winged Teal


Listen to Blue-winged Teal
Scientific Name: Spatula discors
Length: 16 in
Wingspan: 23 in
Weight: 13 oz
The Blue-winged Teal is a small species of dabbling duck known for its striking plumage and its extensive migratory habits.
Appearance: Male Blue-winged Teals are quite colorful, with a slate gray head and neck, a white crescent in front of the eyes, and a predominantly brown body with specks of black. The name “Blue-winged” comes from the patch of blue feathers visible on their wings during flight. Females, in contrast, are primarily brown and subtly mottled to provide camouflage.
Diet: The Blue-winged Teal feeds mainly on plant matter, such as seeds and aquatic vegetation. However, they also supplement their diet with small invertebrates, especially during the breeding season. They are known for their “dabbling” behavior, where they feed at the surface of the water rather than diving.
Reproduction: Blue-winged Teals prefer to nest on the ground in grassy areas near water. The female typically lays a clutch of 9 to 13 eggs, which she incubates alone for about three weeks. After hatching, the ducklings can feed themselves but remain under the mother’s protection until they are capable of flying.
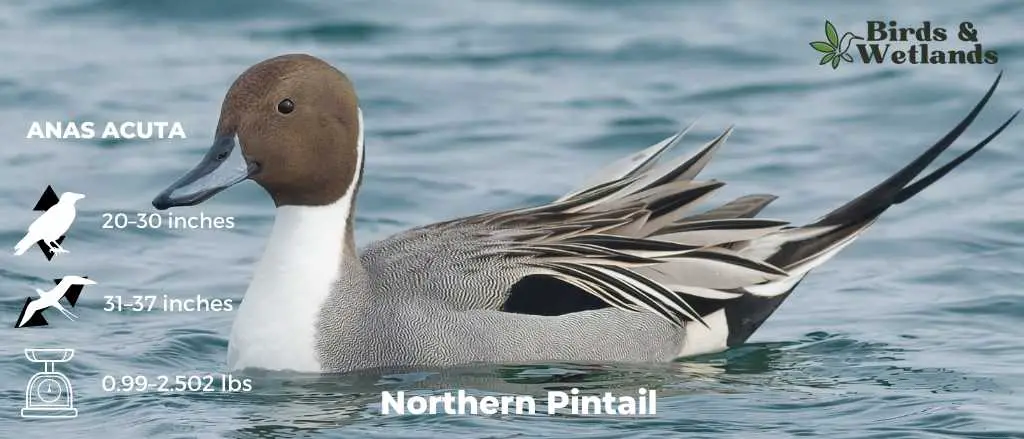
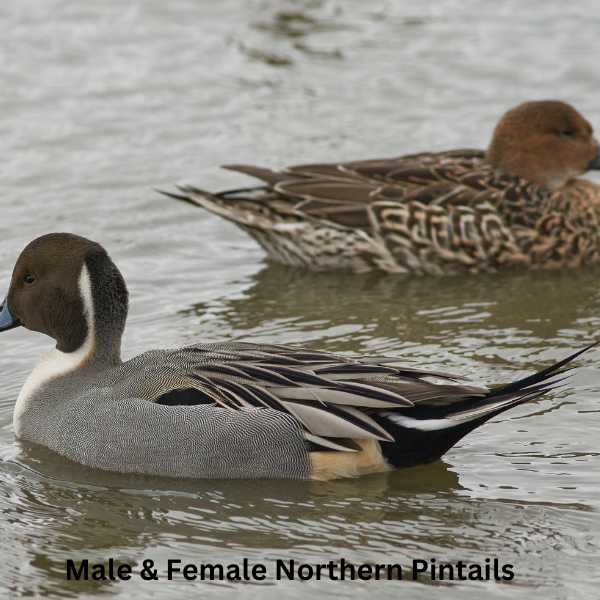
Northern Pintail


Listen to Northern Pintail
Scientific Name: Anas acuta
Length: 23–30 in
Wingspan: 31–37 in
Weight: 1 –3 lb
The Northern Pintail is a graceful species of duck recognized for their elegance in flight and their sleek bodies and long tails which is pin-shaped.
Male Northern Pintails are celebrated for their distinctive appearance, featuring a chocolate brown head, a white neck, and a grayish body. The most notable characteristic is the long, pointed tail feathers, which give this species its name. Females are more understated in color, sporting a mottled brown plumage.
Diet: Consists primarily of plant matter, including seeds and aquatic vegetation. They are also known to eat insects, especially during the breeding season. The Northern Pintail is often seen dabbling and upending in water bodies to forage for food.
Reproduction: Northern Pintails usually nest on the ground, near water bodies. The female lays a clutch of 7 to 9 eggs and is solely responsible for their incubation, which lasts for about three weeks.
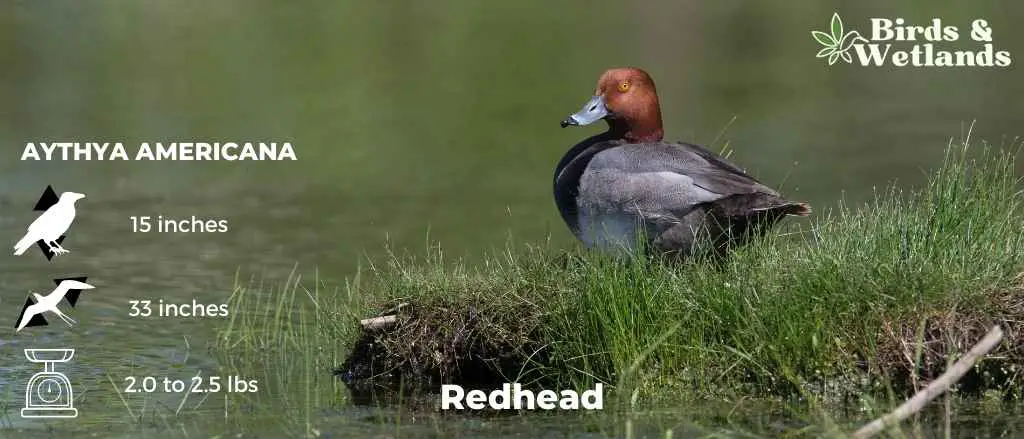
Redhead


Listen
Scientific Name: Aythya americana
Length: 15 in
Wingspan: 33 in
Weight: 2.0 to 2.5 lbs
The Redhead is a medium-sized diving duck species recognized by its rounded head and broad blue bill. This bird is frequently found in wetlands, ponds, and open water bodies across the United States.
Appearance: The male Redhead is particularly striking, characterized by a coppery red head, black breast, and a gray body. The female is less colorful, featuring a brownish body and a duller, brownish-red head. Both sexes have a prominent blue bill with a black tip.
Diet: Redheads feed on a variety of items, including aquatic plants, seeds, and tubers. They also consume aquatic invertebrates, particularly during the breeding season.
Reproduction: Redheads often nest in marshes and ponds with dense vegetation.Females often lay their eggs in the nests of other ducks, a phenomenon known as brood parasitism. When nesting themselves, the female typically lays a clutch of 7 to 10 eggs and incubates them for about three weeks.
Ring-necked Duck (Aythya collaris)


Listen
Scientific Name: Aythya collaris
Length: 15.3-18.1 in
Wingspan: 24.4-24.8 in
Weight: 17.3-32.1 oz
The Ring-Necked Duck is a small to medium-sized diving duck known for its distinctive markings and agile diving abilities.
Appearance: Male Ring-Necked Ducks are characterized by their bold black-and-white coloration, with a glossy black back, a striking white ring around the base of the bill, and two white “rings” on their flanks. Despite their name, the chestnut-colored ring around their neck is often hard to see. Females are more subtly colored with a gray-brown body and a white eye-ring.
Diet: These ducks have a varied diet that includes aquatic plants, seeds, and invertebrates, which they obtain by diving underwater in both shallow and deep water bodies.
Reproduction: The Ring-Necked Duck nests near water, often in densely vegetated areas. The female typically lays between 8 to 10 eggs, which she incubates alone, but both parents will care for the ducklings once they hatch.
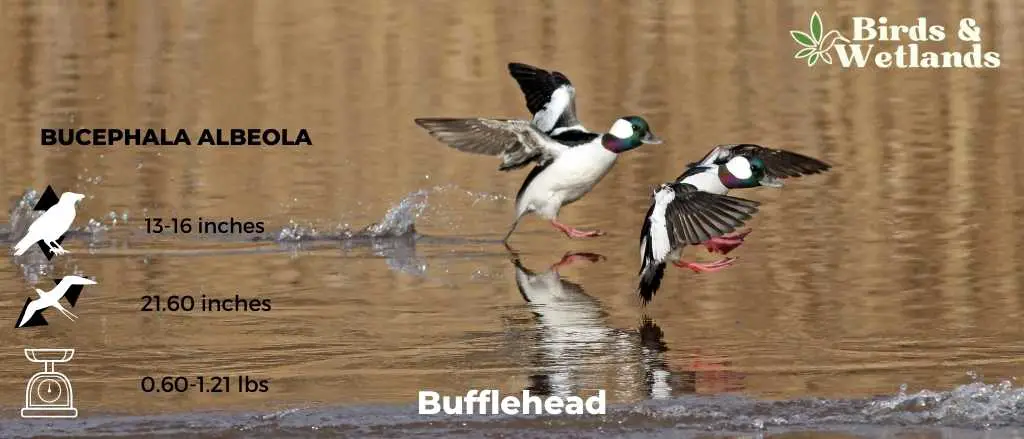
Bufflehead


Listen to Bufflehead
Scientific Name: Bucephala albeola
Length: 13–16 in
Wingspan: 21.6 in -23.2 in
Weight: 9.5–19.4 oz
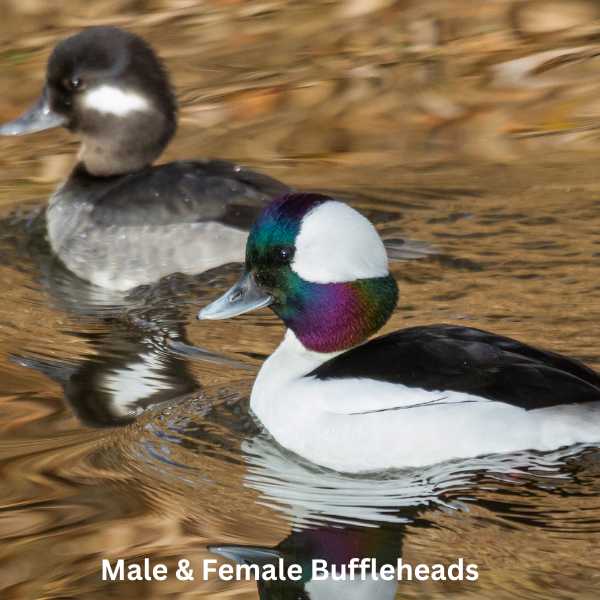
The Bufflehead is a small, compact species of diving duck known for its striking appearance and large heads and unique nesting habits.
Appearance: Male Buffleheads are easily recognized by their large, bulbous head with a green-purple iridescent sheen, a large white patch across the back of the head, and a predominantly black and white body. Females are more subtly colored, primarily in gray-brown tones with a smaller white cheek patch.
Diet: As diving ducks, Buffleheads feed by diving beneath the water’s surface. Their diet consists largely of aquatic invertebrates, such as insects, crustaceans, and mollusks, as well as some plant matter.
Reproduction: Uniquely among ducks, Buffleheads often nest in tree cavities, especially those made by Northern Flickers, a type of woodpecker. The female lays a clutch of about 6 to 11 eggs, which she incubates alone for roughly a month.
Hooded Merganser


Listen to Hooded Merganser
Scientific Name: Lophodytes cucullatus
Length: 15.8-19.3 in
Wingspan: 23.6-26.0 in
Weight: 16.0-31.0 oz
The Hooded Merganser is a distinctive species of diving duck known for its showy crest and its excellent diving skills.
Appearance: Male Hooded Mergansers are especially striking with a large, fan-shaped, black and white crest, which can be expanded or contracted. They have bright yellow eyes, a dark back, and a white chest. The females have a more understated appearance with a brownish body, a smaller, reddish-brown crest, and dark eyes.
Diet: Consists of small fish, aquatic insects, and crustaceans. Their eyes are specially adapted for underwater vision, allowing them to spot and catch prey while diving.
Reproduction: Similar to Buffleheads, Hooded Mergansers often nest in tree cavities near water bodies. The female lays a clutch of about 10 to 12 eggs and incubates them alone for about a month.
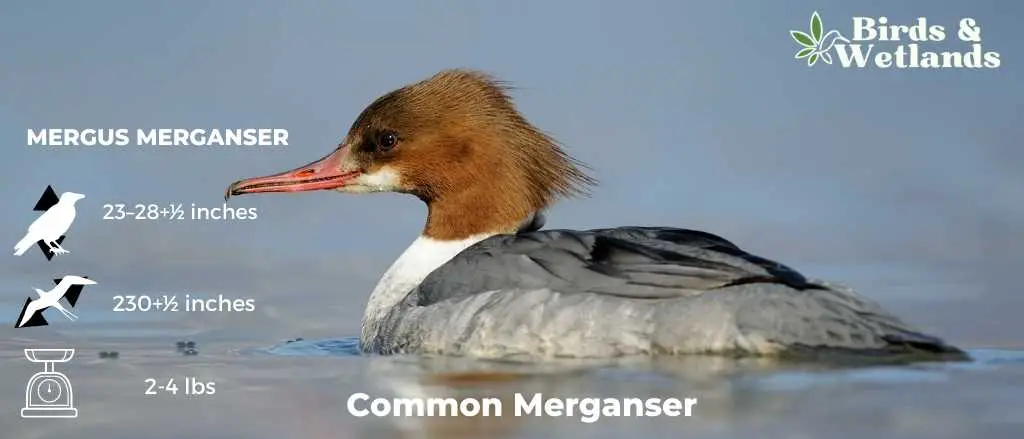
Common Merganser


Listen:
Scientific Name: Mergus merganser
Length: 23–28 in
Wingspan: 30 – 38 in
Weight: 2 lb 0 oz – 4 lb 10 oz
The Common Merganser is a large and elegant diving duck, famous for its unique fishing abilities and seen often in the lakes, rivers, and coastal areas across North America.
Appearance: The male Common Merganser is quite striking with its dark green, almost black, crested head, bright red bill, and white body tinged with salmon-pink. The females have a reddish-brown crested head, a white neck, and a grayish body, but share the same red bill as the males.
Diet: True to their diving duck status, Common Mergansers are exceptional hunters, primarily feeding on fish. They’re also known to consume aquatic invertebrates and, on occasion, small mammals and birds. Their serrated bills are specialized to hold slippery fish tightly.
Reproduction: Like the Wood Duck, Common Mergansers also nest in tree cavities or nest boxes close to water bodies, but can also use rock crevices or holes in the ground. A clutch usually contains 9 to 12 eggs, incubated solely by the female.
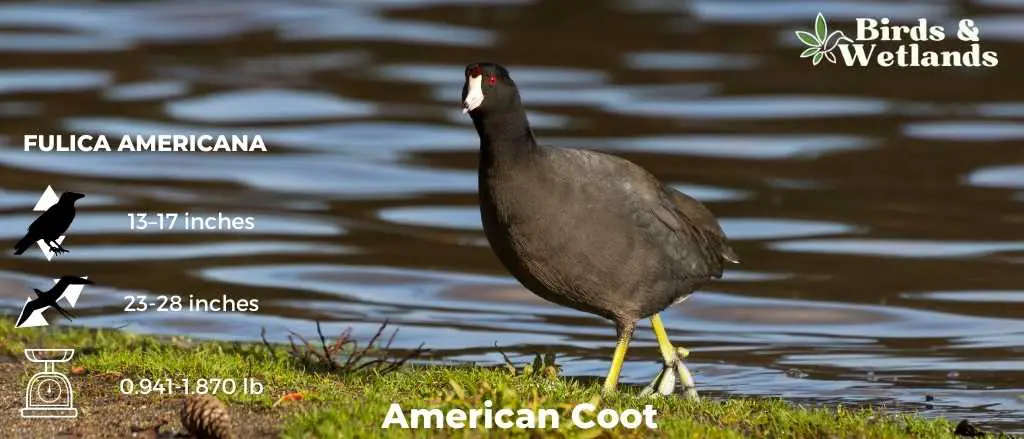
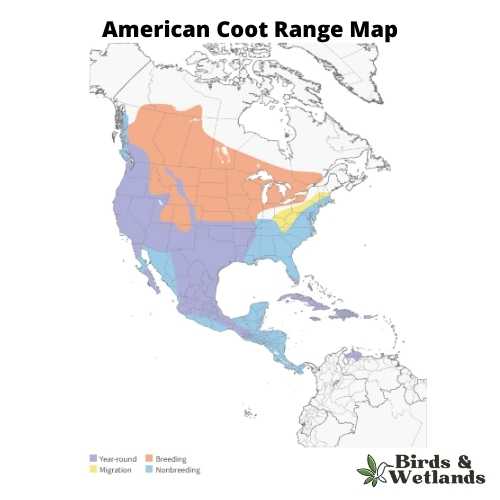
American Coot

Listen:
Scientific Name: Fulica americana
Length: 13–17 in
Wingspan: 23 to 28 in
Weight: 1.270 to 1.870 lb
The American Coot is a ubiquitous water bird commonly seen in the wetlands, lakes, and ponds of North America, recognized for its adaptability and striking features.
Appearance: American Coots are easily identifiable by their slate-gray bodies, offset by a white, chicken-like bill and a red eye. Their legs are also distinctive, equipped with lobed toes, as opposed to the webbed feet seen in ducks, which assist them in navigating both land and water adeptly.
Diet: While aquatic plants form the bulk of an American Coot’s diet, they aren’t strictly herbivores. These versatile birds also consume small invertebrates and fish, demonstrating their ability to adapt and survive in a variety of habitats.
Reproduction: Nesting for the American Coot usually happens in shallow water bodies, where they construct a floating nest hidden among the vegetation. A clutch can contain between 8 to 12 eggs, all of which are incubated by both parents.
Sandhill Crane


Listen:
Scientific Name: Antigone canadensis
Length: 2 ft 7-4 ft 6 in
Wingspan: 16.5–23.6 in
Weight: 4 – 4.5 kg
The Sandhill Crane is a tall, elegant bird known for its impressive size and striking appearance. They are found across North America, in habitats ranging from wetlands to grasslands.
Appearance: Sandhill Cranes are recognized for their tall stature, gray body, long legs, and long neck. Their most distinctive feature is a red forehead, which contrasts with their otherwise primarily gray plumage. During the breeding season, their gray feathers often take on a rusty-brown hue due to them rubbing iron-rich mud onto their feathers.
Diet: Sandhill Cranes are omnivorous birds and their diet is quite diverse, consisting of seeds, grains, berries, insects, small mammals, reptiles, and amphibians. They are known to forage while walking in shallow water or in fields.
Reproduction: Sandhill Cranes mate for life and their complex courtship dance is a sight to behold. They nest in marshy areas and the female typically lays two eggs.
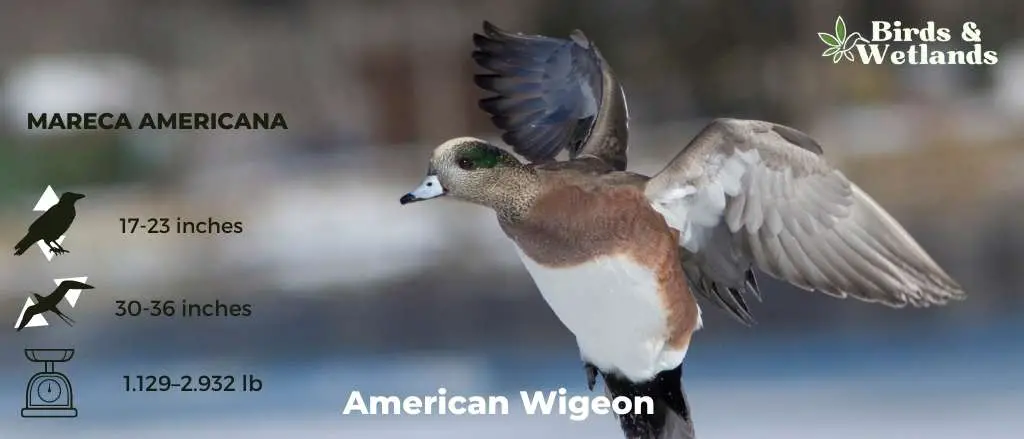
American Wigeon


Listen to American Wigeon
Scientific Name: Mareca americana
Length: 17–23 in
Wingspan: 30–36 in
Weight: 1 –3 lb
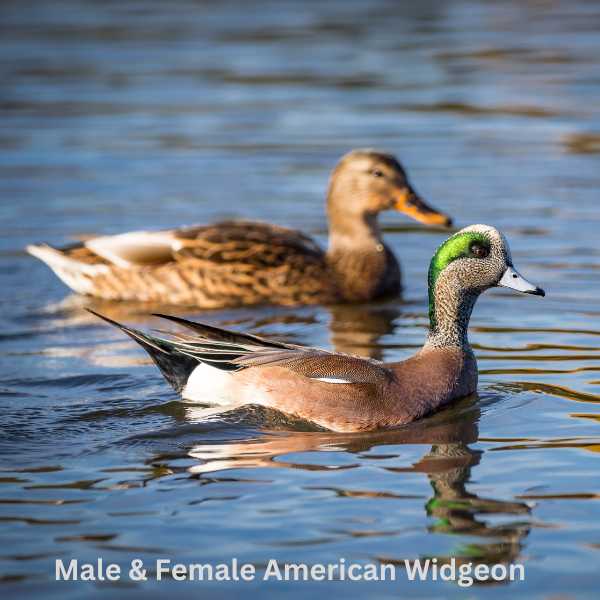
The American Wigeon is a medium-sized duck species that is a popular sight in wetlands, ponds, and lakes and is often seen in mixed flocks with other ducks.
Males of the species are recognized by their distinctive appearance. They sport a unique white forehead and crown, coupled with a green band stretching from the eye to the back of the head. The body is mainly gray with a pinkish hue on the chest. Females are more subdued in color, with primarily gray and brown tones.
Diet: comprising mainly plant material like aquatic vegetation and grasses, but it also includes insects and other small invertebrates. They are known for a feeding behavior called “kleptoparasitism,” where they often snatch food from other ducks.
American Wigeons usually breed in the northernmost parts of North America. The females create their nests on the ground, often hidden in tall grass near water bodies. They lay a clutch of 6 to 11 eggs which they incubate for about three to four weeks and the ducklings feed on small aquatic invertebrates and aquatic insects.
Common Loon

Listen:
Scientific Name: Gavia immer
Length: 24-39 in
Wingspan: 50-56 in
Weight: 6.4-13.6 lbs
The Common Loon is a large, iconic water bird that can be found in many parts of North America. It is known for its haunting calls, often heard in the early morning or late evening across the region’s lakes and ponds.
Appearance: The Common Loon is celebrated for its striking black-and-white breeding plumage, a red eye, and a robust, black bill. In winter, its plumage turns to a more subdued gray, but its large, sturdy body and pointed bill remain distinctive.
Diet: Common Loons primarily feed on fish, but also consume crustaceans, frogs, and aquatic insects. They are expert divers, capable of plunging deep underwater to catch their prey, and are often observed popping their heads above water before diving for their next meal.
Reproduction: The Common Loon nests near water, typically on lakes and larger ponds in the northern parts of North America. The female generally lays 1-2 eggs per year in a nest made from vegetation on the ground. Both parents share the responsibility of incubating the eggs and feeding the young.
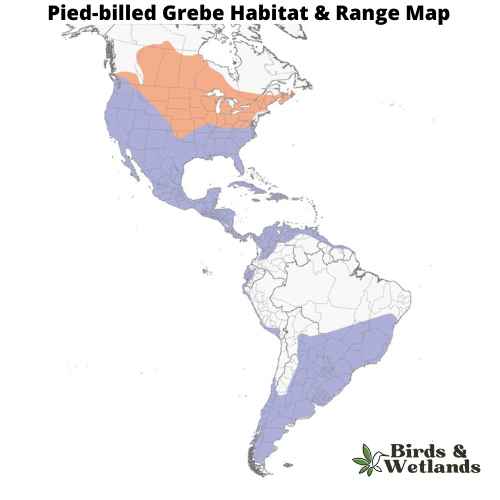
Pied-billed Grebe

Listen:
Scientific Name: Podilymbus podiceps
Length: 12–15 in
Wingspan: 18–24 in
Weight: 8.9–20.0 oz
The Pied-billed Grebe is a small, elusive water bird well-known for its unique ability to adjust its buoyancy and often “sink” out of sight. It can be found in a wide variety of wetland habitats across the United States.
Appearance: Pied-billed Grebes have a stocky build with a short neck and a chicken-like bill that is conspicuously ringed in black during the breeding season – hence the name “pied-billed”. Their plumage is primarily a muted brown, which can vary in tone depending on the season.
Diet: Their diet consists predominantly of aquatic invertebrates, small fish, and amphibians. Pied-billed Grebes are adept divers and can stay underwater for impressive lengths of time to catch their prey.
Reproduction: Pied-billed Grebes usually nest in dense marsh vegetation, where the female lays 5 to 7 eggs. Both parents share responsibilities for incubation. After hatching, the chicks are often seen riding on their parents’ backs while they learn to navigate their aquatic world.
Where to Spot Utah’s Water Birds
Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge, Brigham City: Located at the mouth of the Bear River and the northeast arm of the Great Salt Lake, the refuge is a major resting, nesting and feeding area for migratory birds, including a wide variety of waterfowl and shorebirds like the White-faced Ibis, American Avocet, and Northern Pintail.
Great Salt Lake: The lake itself, apart from being a natural wonder, is a globally important habitat for migrating and nesting birds. It supports millions of water birds, including Wilson’s Phalaropes, Red-necked Phalaropes, and American White Pelicans.
Fish Springs National Wildlife Refuge, Juab County: Nestled in the desert of western Utah, Fish Springs provides lush wetlands for water birds. A wide variety of species can be seen here, such as the White-faced Ibis, Sandhill Cranes, and numerous duck species.
Antelope Island State Park: Located in the Great Salt Lake, Antelope Island is home to a wide variety of bird species, including many water birds. It’s a great place to spot American Avocets, Black-necked Stilts, and various species of gulls.
Farmington Bay Waterfowl Management Area: This waterfowl management area located close to Salt Lake City is a crucial habitat for migrating water birds. Here, one can observe Bald Eagles, Tundra Swans, Northern Pintails, and other water birds in abundance during migration seasons.
| Neighboring State | Best Spots for Birdwatching |
|---|---|
| Idaho Water Birds | Deer Flat National Wildlife Refuge, Bear Lake National Wildlife Refuge, Coeur d’Alene River Wildlife Management Area |
| Wyoming Water Birds | Seedskadee National Wildlife Refuge, Bighorn River, National Elk Refuge |
| Colorado Water Birds | Alamosa National Wildlife Refuge, Barr Lake State Park, Rocky Mountain Arsenal National Wildlife Refuge |
| New Mexico Water Birds | Bosque del Apache National Wildlife Refuge, Bitter Lake National Wildlife Refuge, Rio Grande Nature Center State Park |
| Arizona Water Birds | Havasu National Wildlife Refuge, Patagonia Lake State Park, Kofa National Wildlife Refuge |
| Nevada Water Birds | Ruby Lake National Wildlife Refuge, Lahontan State Recreation Area, Stillwater National Wildlife Refuge |
FAQS on Waterbirds in Utah
What are some common waterfowl species in Utah?
Utah is home to a diverse array of waterfowl species, including Canada Geese, Green Winged Teal, Cattle Egrets, and Ruddy Ducks. These birds can often be found in the Great Salt Lake Wetlands, Bear River Bay, and the associated wetlands around the state.
Why are there so many birds in Utah?
Utah provides a diverse range of habitats for so many birds, including the dense vegetation of the Great Salt Lake Wetlands and the shallow wetlands of Farmington Bay WMA and Willard Spur. These environments provide ample food and shelter for both large birds and small birds, making Utah a haven for many species.
When do birds migrate south in Utah?
Waterfowl in Utah typically migrate south in the fall, with peak counts often occurring around mid-October. The state’s associated wetlands and water bodies like the Great Salt Lake and Bear River Bay serve as critical stopover points for these migratory shorebirds.
Where can I see large numbers of waterbirds in Utah?
Large numbers of waterbirds can be observed at the Great Salt Lake and its surrounding wetlands. Areas such as Farmington Bay WMA, Bear River Bay, and Willard Spur regularly host many species of birds, especially during the spring and fall migration periods.
What distinguishes the Green Winged Teal?
The Green Winged Teal, one of the three species of Teal found in Utah, is a small bird known for its excellent swimming abilities. Males have a bright green patch on their wings and are recognized by their vertical white stripe on the body. They are excellent swimmers and can often be seen foraging in dense vegetation for seeds and small animals.
How can I identify a Cattle Egret?
Cattle Egrets are relatively small, white wading birds with short bills and yellow legs. They are unique among herons and egrets in that they often feed in dry fields, catching insects and small animals disturbed by grazing cattle, hence their name. They are also often seen around golf courses and other grassy areas looking for an easy meal.
What is the role of the Utah Division of Wildlife Resources?
The Utah Division of Wildlife Resources works to manage the state’s wildlife and their habitats. They oversee the conservation of all wildlife species, including waterbirds, and manage the associated wetlands and water bodies that serve as these species’ habitats. They also conduct regular bird counts and provide resources to help the public identify and learn more about the state’s diverse bird species. long toes eared grebes wasatch front corn

