Nevada is a large state. It is known for being very dry. In fact, Nevada is the nation’s most arid state.
However, the state has diverse landscapes with many birding locations. It has forests, mountains, marshes, rivers and lakes.
Some migratory birds spend their winters here, while others use the state’s varied habitats as a stopover before they continue their journey further south.
In this blog post, we will discuss all the ducks that live or spend time each year in the state of Nevada. We included nesting habits, diets and pictures so birders can identify these waterfowl in the wild.
What Ducks Are in Nevada?
There are 31 different breeds of ducks that pass through or live in the state of Nevada.
Barrow’s Goldeneye
Black-bellied Whistling-duck
Bufflehead
Canvasback
Cinnamon Teal
Gadwall
Mallard
Northern Shoveler
Redhead
Ring-necked Duck
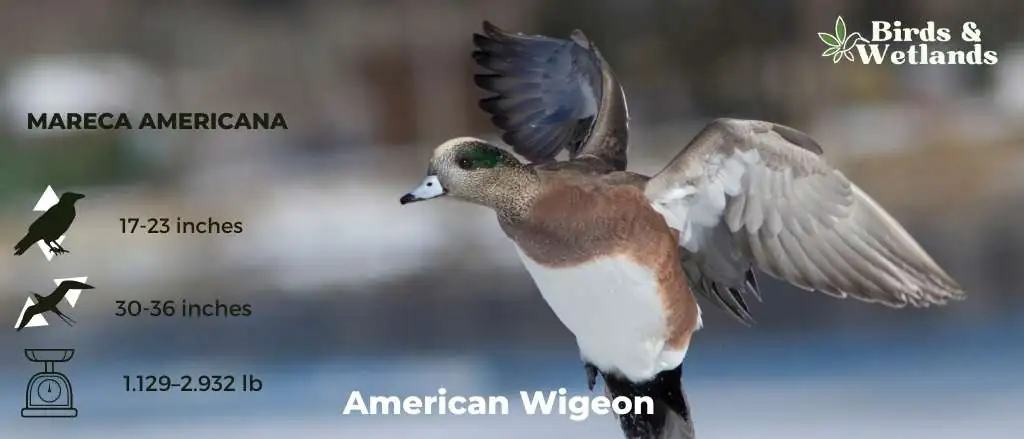



American Wigeon
Listen to American Wigeon
The American Wigeon, also known as the baldpate, is a medium-sized duck that is native to North America, Europe, Asia, and northern Africa.
American Wigeon is known for its bright plumage: males have a blue head and neck with a white breast and belly; females have a brown head with a white eye stripe and yellowish markings on the breast and belly. They also have short legs with two toes on each foot which enable them to walk easily on land or water.
Their diet consists of aquatic plants and seeds. They mainly eat aquatic plants, but also take some small invertebrates such as insects or snails from the water’s edge.
This species prefers areas with dense vegetation because they provide an excellent source of food for these birds during the breeding season (i.e., they can feed on aquatic plants). Additionally, they eat more animals as protein source for the breeding seasons. They are usually found in freshwater marshes, ponds, lakes, and river deltas.
They are not migratory and typically remain at the same location year-round. The current population of this bird is estimated at around 2 million individuals worldwide.
Scientific Name: Mareca americana
Height: 42–59 cm (17–23 in)
Wingspan: 76–91 cm (30–36 in)
Weight: 512–1,330 g (1.129–2.932 lb)

Listen to Barrow’s Goldeneye Duck
The Barrow’s Goldeneye Duck is a medium-sized diving duck with a black head and neck, a white breast, a brownish-gray back and sides, grey wings, and a white belly. It has a long, black, narrow bill that is slightly upturned at the tip.
The Barrow’s Goldeneye Duck has a diet of aquatic insects, mollusks, crustaceans such as shrimp or crayfish, and small fish.
These ducks live in both saltwater and freshwater habitats, where they breed during the springtime. They are migratory birds, traveling south during the winter months to spend time in warmer climates.
The Barrow’s Goldeneye Duck is found in the northern hemisphere from Alaska to Greenland, Europe, Asia, and northern Africa. In North America it breeds in Canada and Alaska; in winter it can be found south of California and New York.
Scientific Name: Bucephala islandica
Length:
Male: 19.2 in (49 cm)
Female: 17 in (43 cm)
Wingspan: 27.6-28.7 in (70-73 cm)
Weight:
Male: 2.13 lb (970 g)
Female: 1.31 lb (590 g)

Listen to Black-bellied Whistling-Duck
The Black-bellied Whistling-Duck has an orange bill, dark brown eyes and brown legs. The male has a white throat and red breast while the female has a brown breast. The male’s bill is longer than the female’s bill but both sexes have long tails.
The Black-bellied Whistling-Duck can be found in wetland habitats such as lakes and ponds where there are reeds or other tall grasses for them to hide in when threatened by predators like foxes or dogs.
Black-bellied Whistling-Ducks are monogamous, meaning they form lifelong pair bonds with one partner. The male builds a nest out of sticks, and the female lays 5 to 8 eggs in it. The eggs hatch after about 28 days of incubation by both parents.
The main diet of the Black-bellied Whistling-Duck consists of aquatic plants, insects and mollusks. They use their bills to dig up food from mud or soft soil by digging with their feet as well as using their bills to scoop up prey items from shallow water or soft soil.
Scientific Name: Dendrocygna autumnalis
Height: 17-24 inches
Wingspan: 31.5-34.3 inches
Weight: 1.5-2.7 lbs
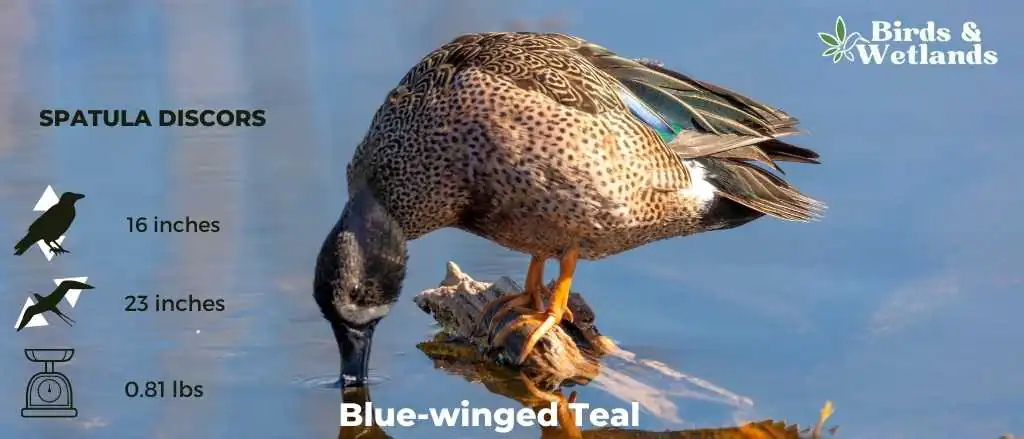

Blue-winged Teal
Listen to Blue-winged Teal
The Blue-winged Teal is a small duck that lives in North America.
Breeding males have a glossy blue-gray head with a white crescent-shaped patch in front of the dark eyes. They also have black wings and rears.
Females have mostly brown bodies with black bills, dark caps and eyeliners on the head.
The Blue-winged Teal’s diet consists mostly of aquatic plants like pondweed, but it will also eat insects when they are available. This duck often feeds by pecking at the surface of the water rather than diving for food. It will sometimes form small groups to feed together or fly in single file formation when migrating south for winter.
Blue-winged teals are found in marshes, ponds, lakes, and rivers throughout the United States south of Canada, and north of Mexico.
They fly south for the winter months to warmer climates. It winters along the Atlantic coast from southern New England to Virginia and then moves further south as far as Mexico.
Scientific Name: Spatula discors
Height: 40 cm (16 in)
Wingspan: 58 cm (23 in)
Weight: 370 g (13 oz)
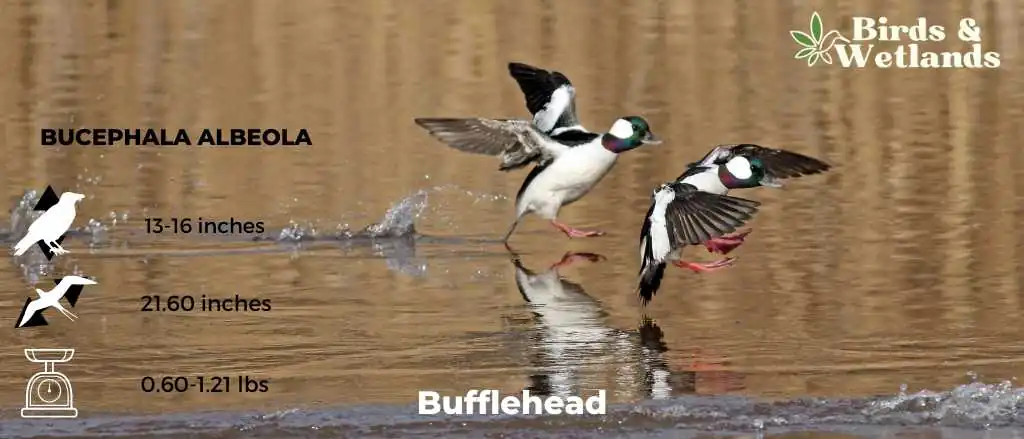

Bufflehead
Listen to Bufflehead
Buffleheads are striking ducks. They are small ducks with relatively large heads.
Males have a huge white patch on their iridescent purple-green heads. They also have short dark bills, white chests and flanks.
Females have a distinct white patch on the cheeks, rounded heads and brownish bodies.
The Bufflehead is a strong flier, but rarely flies more than several hundred yards at a time. It lives on the coast of North America, spending most of its time in salt water.
Buffleheads are sea ducks that can eat many different types of foods including clams, crayfish (also known as crawfish), insects such as beetles and flies as well as other small animals such as mice or voles (small rodents). It also feeds on insects and crustaceans found along the bottom of streams or lakes, as well as small fish such as minnows or suckers.
Buffleheads spend most of their time in freshwater habitats such as lakes, ponds, rivers, estuaries, and bays. They are able to survive in such diverse environments because they are excellent swimmers and divers.
Scientific Name: Bucephala albeola
Length: 32–40 cm (13–16 in)
Wingspan: 21.6 in (55 cm)
Weight: 270–550 g (9.5–19.4 oz)
Canvasback (Aythya valisineria)
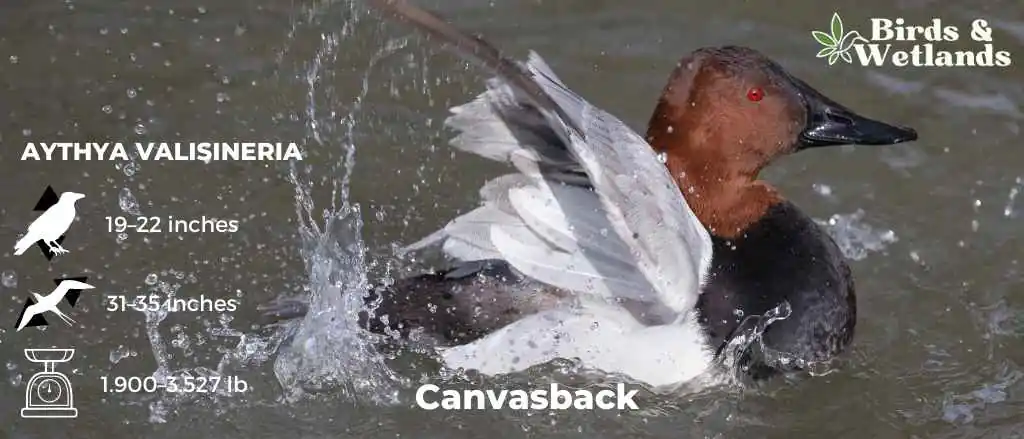

Canvasback
Listen to Canvasbacks
Canvasbacks are large diving ducks with sloping foreheads and dark bills. The male has red eyes, a black chest and a white body. The female has black eyes, a brown head and a pale gray body.
Scientific Name: Aythya valisineria
Height: 48–56 cm (19–22 in)
Wingspan: 79–89 cm (31–35 in)
Weight: 862–1,600 g (1.900–3.527 lb)
Canvasback Habitat & Range
The habitat of the canvasback includes lakes and ponds in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. Canvasbacks breed in North America’s Prairie Pothole Region. They like to build their nests above water in permanent Prairie wetlands with emergent plants such as cattails and bulrushes for protection.
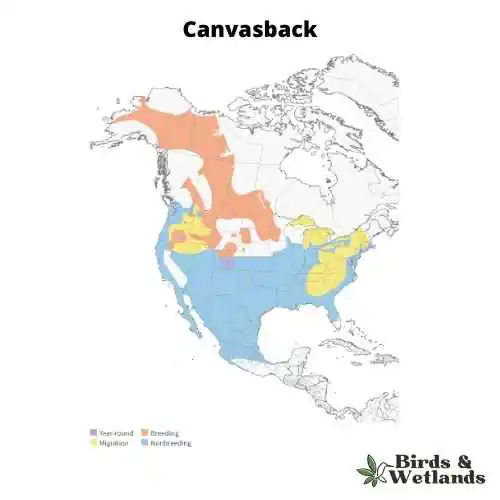
Canvasback
Canvasback Diet
The canvasback is a versatile feeder that can consume plants ranging in size from tiny strands to large leafy growths. It has been seen feeding upon countless species of vegetation, including pond weeds and wild celery as well! The bird also takes interest in snails or other mollusks for food sources not related directly with waterfowl production- think gastropods (slugs & snail shells) insects , small fish – which it may catch while hunting its own kind underwater among foliage near shallow coastal waters where these animals breed.
Canvasback Nesting
They nest in tree cavities and will lay anywhere from 8-15 eggs. The female incubates the eggs for 28-30 days while the male sits on them to keep them warm. When they hatch they are able to swim immediately!

Cinnamon Teals
Listen to Cinnamon Teals
Cinnamon Teal is a small duck with distinctive bright cinnamon-colored feathers on its back and white markings above the eye that is native to North America and Central America.
The diet of this bird includes seeds, insects, and other invertebrates that are found near water sources where they live. Like most ducks, it feeds on aquatic vegetation such as pondweed, watercress, pondweed, and water lilies.
These small birds are found in the northern hemisphere and are particularly common in North America, where they breed from Alaska to Canada. They winter south of the U.S., as well as in parts of Mexico and Central America.
The Cinnamon Teal is a very social bird, often living in large flocks during the breeding season and congregating around lakes and rivers during migration. They tend to be shy and elusive, so it can be difficult to see them in their natural habitat.
These birds mate for life and build nests on the ground near water sources—usually shallow ponds or marshes with tall grasses nearby for cover when young are being reared.
Scientific Name: Spatula cyanoptera
Height: 21.3-22.4 in (54-57 cm)
Wingspan: 22-inch (560 mm)
Weight: 11.8-14.1 oz (335-401 g)

Listen to Common Goldeneyes
The Common Goldeneye Duck is a medium-sized diving duck that breeds across the northern hemisphere in North America, Asia, and Europe. It winters in the southern hemisphere.
Males have dark green heads with bright yellow eyes. They also have a distinctive white cheek patch. Their bodies are white with black back and rump.
Females have dark brown heads but with a short dark bill with a yellow tip at the end. They have gray overalls, a white neck collar and pale yellow eyes.
Common Goldeneyes are also known for their unique calls. It sounds like a squeaky rubber toy being squeezed repeatedly. This makes them easy to identify by ear in addition to sight!
As one of North America’s most abundant ducks, Common Goldeneyes live in lakes, ponds, rivers, and marshes. Most of these ducks also live near shorelines where there is plenty of fish and vegetation available for food sources.
The Common Goldeneye Duck is listed as “least concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), which means that it isn’t threatened with extinction
Scientific Name: Bucephala clangula
Length:
Male: 45–51 cm (18–20 in)
Female: 40–50 cm (16–20 in)
Wingspan: 30.3-32.7 in (77-83 cm)
Weight:
Male: 1,000 g (2.2 lb)
Female: 800 g (1.8 lb)
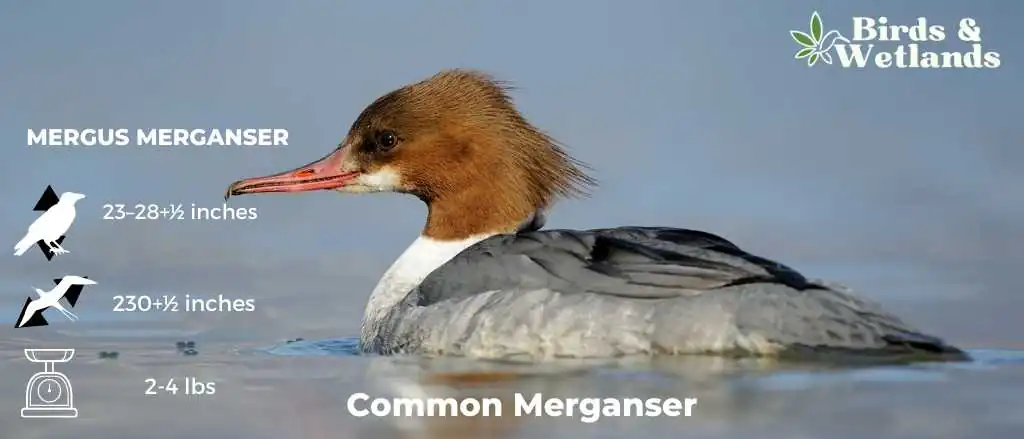

Common Merganser
Listen to Common Merganser
The common merganser, sometimes known as the goosander, is a huge sea duck found in wooded parts of Europe, Asia, and North America. They have a long bill that is pointed at the end and has a black tip on it. Their plumage is mostly dark with a white underside. They have very large feet and webbed toes to help them swim. Their legs are long and slender as well.
Common mergansers are omnivores, eating both plants and animals such as small fish or insects. They eat their prey by diving underwater and spearing it with their long bill before swallowing it whole.
The habitat of this bird is lakes, rivers, ponds, and marshes. They prefer quieter bodies of water with plenty of vegetation along the shores where they can rest during the day before moving on to hunt at night.
The current population of this bird is considered stable due to its ability to thrive even when there are threats present due to its adaptability as well as its wide range across North America.
Scientific Name: Mergus merganser
Length: 58–72 cm (23–28+1⁄2 in)
Wingspan: 78–97 cm (30+1⁄2–38 in)
Weight: 0.9–2.1 kg (2 lb 0 oz – 4 lb 10 oz)
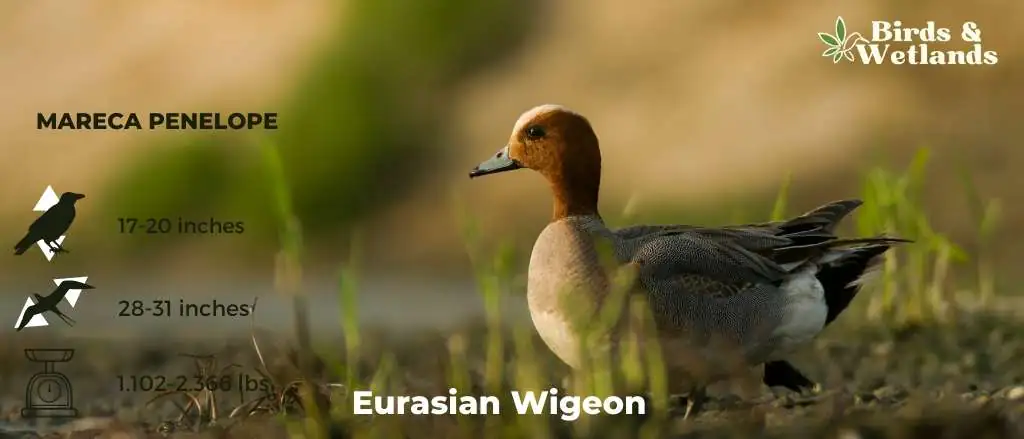

Eurasian Wigeon
Listen to Eurasian Wigeon
The Eurasian Wigeon, or European Wigeon, is a medium-sized duck with a long, pointed bill and a distinctive white crescent on the side of its face. The male Eurasian Wigeon has a light brown body with a dark green head and white cheek stripes on either side of its face. The female Eurasian Wigeon has a lighter brown body with a black head and white cheek stripes on either side of its face.
The diet of Eurasian Wigeon consists of vegetation such as roots, bulbs, tubers, and rhizomes from aquatic plants such as sedges, bulrushes, and other grasses as well as insects such as dragonflies or water boatmen. In wintertime, they feed on aquatic plants like duckweed or reeds in shallow water.
They are found in central and eastern Europe, Scandinavia, Russia, China, Korea, Japan, north-east Siberia and Alaska. They migrate between the breeding grounds in central Asia and southern Europe. They prefer nesting near lakes or ponds but they can also be found nesting on small streams.
The current population of Eurasian Wigeons is estimated at around 1 million birds worldwide with populations declining in many areas due to habitat loss.
Scientific Name: Mareca penelope
Height: 42–52 cm (17–20 in)
Wingspan: 71–80 cm (28–31 in)
Weight: 500–1,073 g (1.102–2.366 lb)

Fulvous Whistling-Duck
Listen to Fulvous Whistling-Duck
The Fulvous Whistling-Duck is a medium-sized duck that is found in Mexico, Central and South America, and the Caribbean. It has a light brown body and a yellow head with a white underside. They have a blackhead, neck, back, and tail. The males are more brightly colored than the females.
The habitat of this bird includes marshes, lakes, and ponds where they feed on seeds, aquatic plants, insects, and occasionally small fish. The Fulvous Whistling-Duck usually nests on the ground near water but may also nest in trees or cattails.
Their diet consists mostly of seeds from grasses or sedges as well as aquatic plants such as pondweeds or duckweed. They also eat invertebrates such as mollusks (snails), crustaceans (crayfish), or insects like dragonflies or beetles depending on what’s available in their habitat at different times of year.
The population of this species has been declining due to habitat loss caused by agriculture and urbanization; however, there are currently no known threats to its continued existence.
Scientific Name: Dendrocygna bicolor
Height: 16 to 20 inches (40 to 50 centimeters)
Wingspan: 85 to 93 cm
Weight: 748–1,050 g (26.4–37.0 oz)
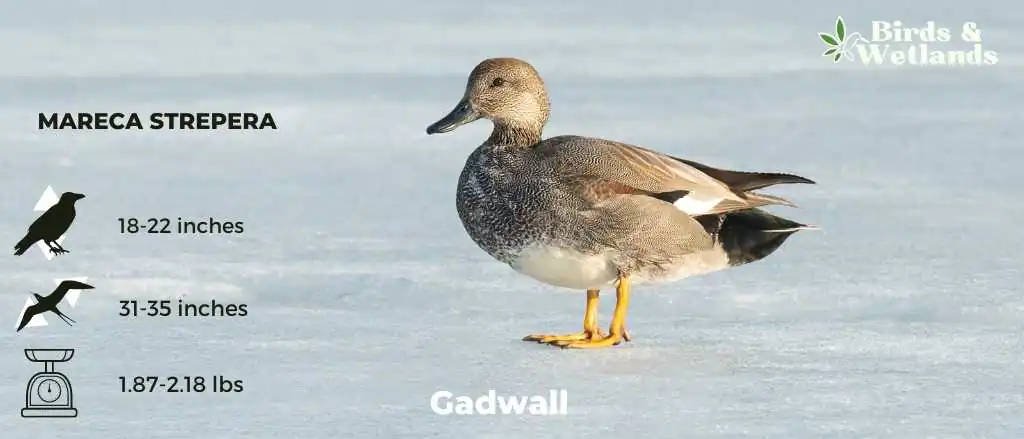

Gadwall
Listen to Gadwall
Gadwall is a duck that’s known for its dark bill and the white patch on its cheek. It is native to North America, Europe, and Asia. It has a black head and breast, white cheeks, and a buff-colored body. The bill of the male Gadwall is dark.
When it comes to calls, the females’ quack may sound similar to Mallards.
The Gadwall’s color varies depending on its location—in North America, they are a dull brownish-gray, while in Europe their feathers are more of a chestnut brown. Their bills are black with a white tip, and their legs are yellowish-green above black webbed feet.
The only thing that sets them apart from other duck breeds is their eyes: they have dark brown eyes with a distinctive red circle around them.
Gadwalls are slightly smaller than mallards, with males weighing between 2 and 3 pounds and females weighing between 1.5 and 2 pounds.
Gadwalls eat worms, crustaceans like crayfish, frogs, and tadpoles as well as small fish when available. They will also eat seeds from grasses and plants like watercress
The Gadwall’s habitat is near water; it can be found in marshes, rice paddies, ponds, and lakes.
Gadwalls breed in northern North America and in Europe as far east as Siberia. They also breed in Asia where they are found in Japan, Korea, and China as well as Mongolia and Siberia.
They fly south in the winter to warmer climates. They migrate south to winter in the southern USA, Mexico, and Central America as well as southern Europe (Spain), Central Africa (Ethiopia), and India. They are usually found in pairs or small flocks during migration and mating season but tend to be solitary during winter months when they migrate southward.
This species of duck has experienced an increase in population over the last 100 years due to conservation efforts by governments and organizations such as Ducks Unlimited Canada (DUC).
Scientific Name: Mareca strepera
Height: 46–56 cm (18–22 in)
Wingspan: 78–90 cm (31–35 in)
Weight
Male: 990 g (35 oz)
Female: 850 g (30 oz
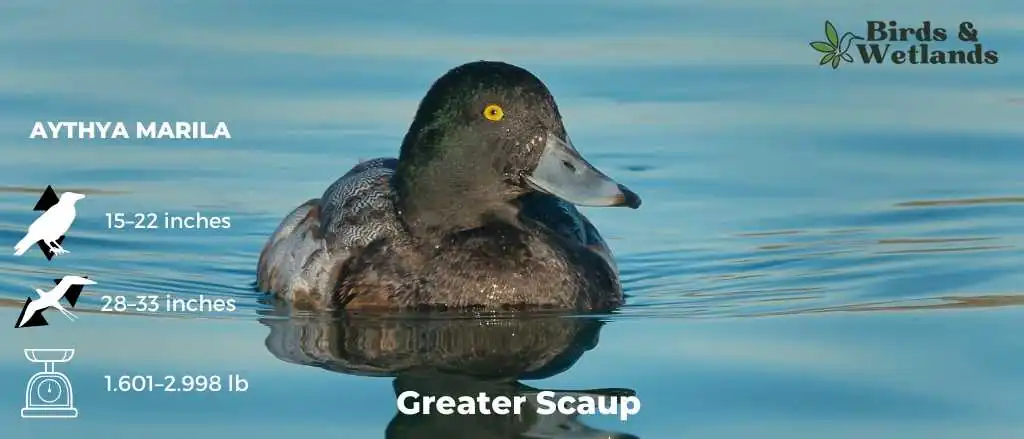

Greater Scaup
Listen to Greater Scaup
The Greater Scaup is a large diving duck with a distinctive white band on its head. The rest of its body is brown with a blue-grey sheen on its back and tail (which can be seen when they fly). The male is larger than the female, with a more pronounced bill and more white wing feathers. It has a black bill, black feet and legs, and gray plumage.
They prefer shallow water close to shore where they can feed on aquatic vegetation and small fish. They are omnivorous creatures who feed on mollusks, crustaceans, insects (especially water beetles), worms, and other small invertebrates like larval dragonflies which comprise about 60% of their diet.
This species breeds in the northern taiga regions of Canada and Alaska and winters in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, as well as some inland lakes. It is an uncommon sight in North America but can be found in many areas across Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia. In winter, it migrates to southern Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
Scientific Name: Aythya marila
Height: 39–56 cm (15–22 in)
Wingspan: 71–84 cm (28–33 in)
Weight: 726–1,360 g (1.601–2.998 lb)
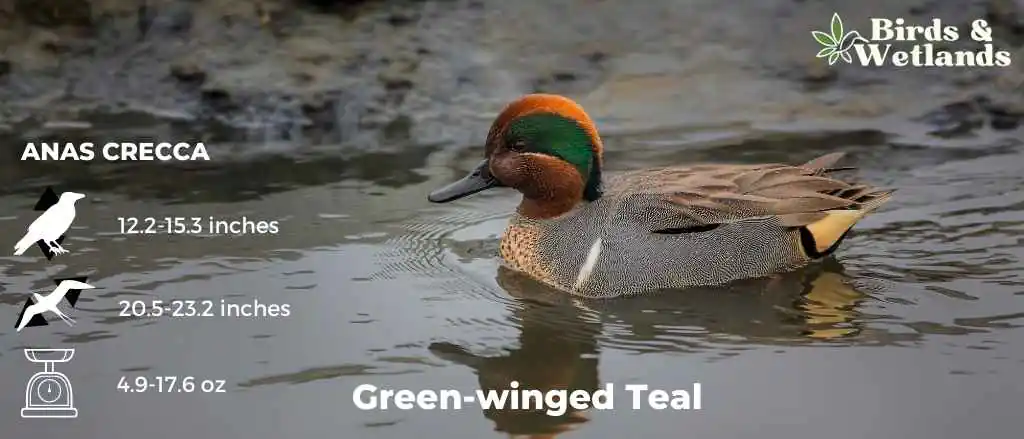

Green-winged Teal
Green-winged Teals are among the most common ducks in the northern regions of North America except on the Aleutian Islands. They are the smallest dabbling ducks on the continent.
Breeding males have chestnut-colored heads with a green streak behind the eye. They also have gray-barred bodies with a vertical white stripe on the sides.
Females have a mottled brown plumage, similar to that of female Mallards. They have a dark eye-line.
Both males and females have a green patch on the wings which are hidden often hidden while they are resting but visible when in flight.
Scientific Name: Anas crecca
Height: 12.2-15.3 in (31-39 cm)
Wingspan: 20.5-23.2 in (52-59 cm)
Weight: 4.9-17.6 oz (140-500 g)
Green-winged Teal Sound
Green-winged Teal Habitat & Range
This duck has been introduced into many parts of Europe and Asia where it has become an invasive species due to its ability to adapt to new environments quickly. As a result, it is now considered one of the world’s most invasive birds according to BirdLife International’s Global Invasive Species Database (GISD).
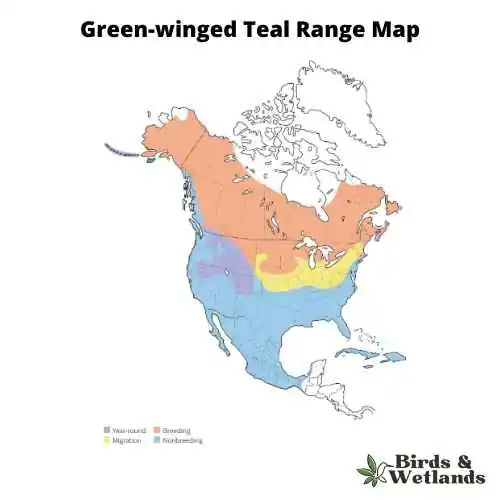
Green-winged Teal
Green-winged Teal Diet
In the winter months, they eat seeds, grains, and insects but during the summer months they switch over to eating aquatic plants like pondweeds, watercress, and duckweed which make up about 70% of their diet.
Green-winged Teal Nesting
The Green-winged teal nests on the ground near water sources such as streams or ponds. The female lays between 7-15 eggs per clutch (which means cluster) which incubate for 25 days before hatching out into young ducklings!
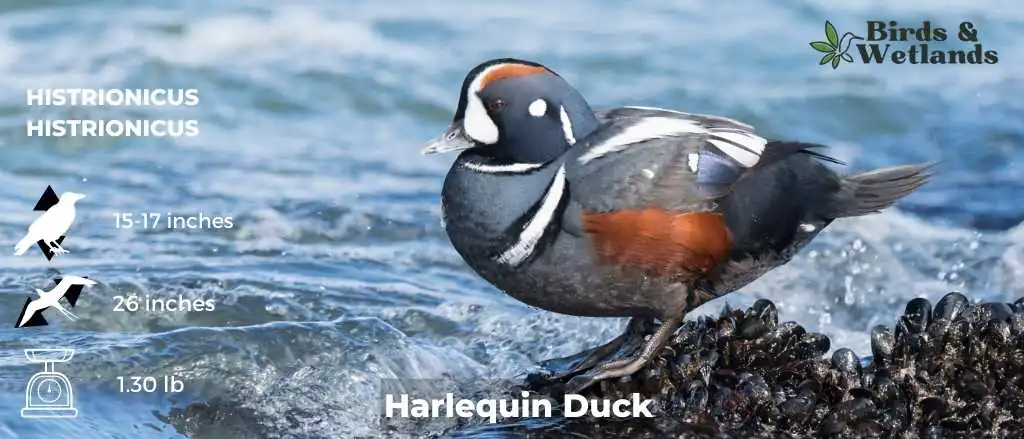

Harlequin Duck
Listen to Harlequin Duck
The Harlequin Duck is a beautiful small sea duck that is native to North America. It has a unique appearance. It has a black head, neck, and breast, with white cheeks and sides of the neck, and red eyes. The body is black with white spots on the wings.
In addition to being unique-looking birds, Harlequin Ducks are also very vocal animals who make sounds such as whistles and squeaks that can be heard from up to 100 yards away! These sounds are used primarily for communication between other ducks within a flock but can also be used to alert predators of danger if needed (such as when approaching land).
These birds feed on small fish and crustaceans such as shrimp and clams. They can dive up to 20 feet below the surface to catch their prey.
It can be found in coastal areas of North America, Europe, and Asia, where it lives in salt marshes. It lives in freshwater lakes, ponds, and rivers. The species is monogamous and breeds in April and May.
Unfortunately, these beautiful creatures are currently under threat from habitat loss due to human development as well as overfishing.
Scientific Name: Histrionicus histrionicus
Length: 15–17 in (380–430 mm)
Wingspan: 26 in (660 mm)
Weight: 600 g (1.3 lb)
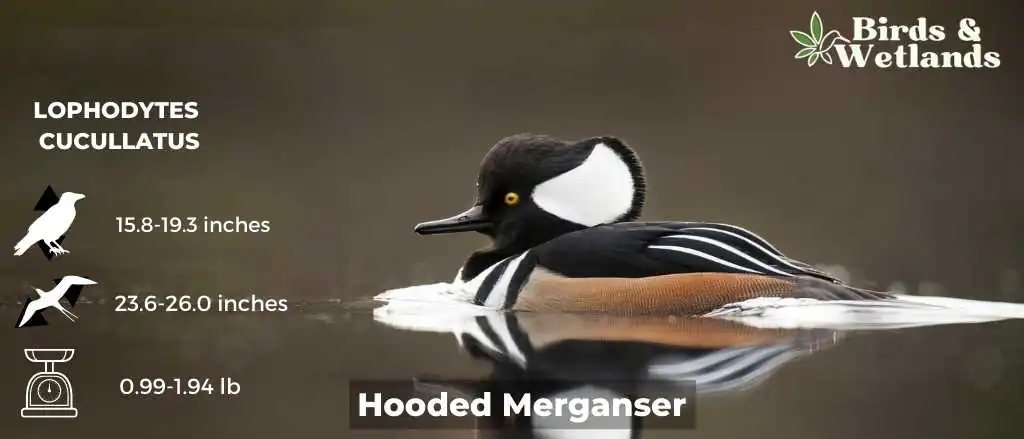

Listen to Hooded Mergansers
The Hooded Merganser is a relatively small duck with a slender body and a long tail.
Breeding males have a large black crest with a large white patch on each side. They also have golden yellow eyes.
Females have brown bodies with a slightly lighter colored crest which looks like a mohawk. They have dark eyes.
Non-breeding males look similar to females but with yellow eyes.
Hooded Mergansers eat mostly fish—they dive underwater to catch them! They also eat crayfish, crustaceans such as shrimp or krill, frogs, snails, and insects such as dragonflies or grasshoppers when they are unable to find enough food near the surface of water bodies.
The Hooded Mergansers live in North America and spend most of their time in freshwater ponds, lakes, and rivers during the spring season. It moves to saltwater marshes during the winter months to avoid freezing temperatures.
The Hooded Mergansers are currently listed as Least Concern by the IUCN Red List because its population is stable or increasing and it has a large range.
Scientific Name: Lophodytes cucullatus
Length: 15.8-19.3 in (40-49 cm)
Wingspan: 23.6-26.0 in (60-66 cm)
Weight: 16.0-31.0 oz (453-879 g)

King Eider
Listen to King Eider
The King Eider is a large sea duck that breeds in Arctic and sub-Arctic regions from Alaska to Greenland and along most of the northern Hudson Bay shoreline.
It is so named because of its magnificent crest, which it can raise or lower at will. It has a stocky body, a large head, and a short neck. Its plumage is brownish-gray on the back and sides, with a white belly and chest.
The King Eider prefers breeding grounds near the sea, where they can feed on mussels and other shellfish. They also eat small fish and crustaceans.
This species is found in coastal areas near water during the summer months, but it will migrate during winter months to coastal areas away from ice sheets where it can find food. They typically live about 15 years in the wild but have been known to live up to 35 years in captivity.
This bird can dive to depths of about 30 meters for over 30 seconds at a time in search of food such as small fish or mollusks.
The king eider is listed as Vulnerable by Birdlife International because its population has declined by more than 10% since 1980 due to overhunting in some parts of its range.
Scientific Name: Somateria spectabilis
Height: 52–57 cm (20–22 inches)
Wingspan: 86–102 cm (34–40 in)
Weight: 1.6 kg
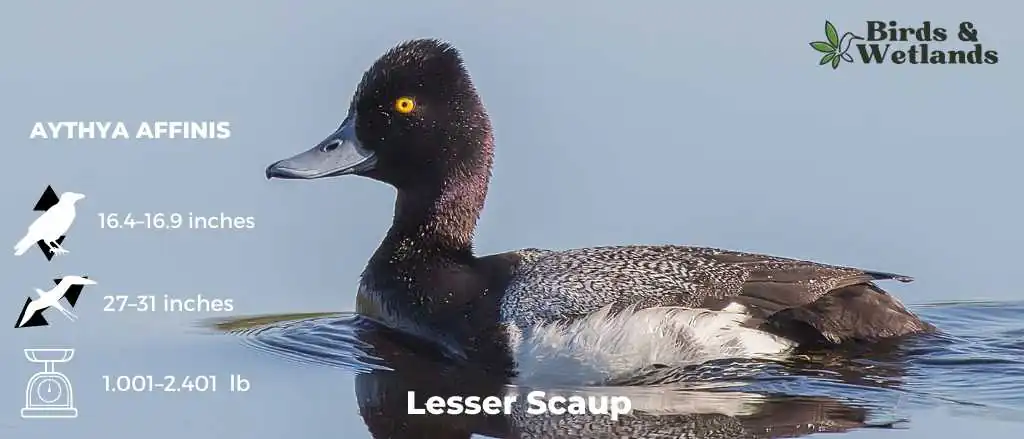

Listen to Lesser Scaups
The Lesser Scaup is a small diving duck native to North America and winter in Central America. Lesser Scaups are smaller than Greater Scaups.
Males have golden yellow eyes. Their chests and heads are black with a purple sheen. Their sides are white while their backs have an intricate pattern of gray and white feathers.
Females have darker heads than males. They have gray sides and brown bodies with a white patch around the base of their bills.
The Lesser Scaup’s habitat is typically freshwater lakes, rivers, and streams. They can also be found on large ponds and reservoirs with plenty of aquatic vegetation.
Lesser Scaups eat mostly fish but also insects and small crustaceans, which they find by diving beneath the surface of the water for up to 40 seconds at a time.
Lesser scaups breed in ponds and lakes across Canada and much of the northern United States from late April through May. They usually nest in colonies with other species such as Mallards and Common Goldeneyes.
The Lesser Scaups are not considered to be endangered or threatened and is currently listed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Scientific Name: Aythya affinis
Height: 41.7–43 cm (16.4–16.9 in)
Wingspan: 68–78 cm (27–31 in)
Weight: 454–1,089 g (1.001–2.401 lb)

Long-tailed Duck
Listen to Long-tailed Duck
Long-tailed Ducks are species of duck that are native to Australia and New Zealand. They are named for their long, narrow tails, which can be over 30% longer than the rest of their body. It has a black bill, brown eyes, and grayish-brown feathers on its back and wings. The underside of the bird is white in color.
The Long-tailed Duck eats aquatic plants, seeds, insects, snails, mollusks, crustaceans, fish eggs, and small fish. They can dive up to 60 feet below the surface.
These species of duck prefer to live in areas where there are plenty of lakes and ponds for them to feed on. They are also known for being very territorial so they tend not to share their space with other species unless they have no choice but to or if they’re trying to breed.
They can be found in Europe, Asia, and North America. They breed in freshwater lakes from May through July or August depending on where they live. They migrate to southern latitudes during the winter months to avoid freezing temperatures.
Long-tailed Ducks have a current population of roughly 2 million individuals worldwide—that’s down from an estimated 4 million during the 1980s.
Scientific Name: Clangula hyemalis
Length: 440–600 mm (17.5–23.5 in)
Wingspan: 710 mm (28 in)
Weight: 740 g (1.63 lb)

Mallard
Listen to Mallard
Mallards are native to the Northern Hemisphere. These ducks live in many parts of the United States and Canada.
The male mallard duck has a lustrous green head, with a white collar that sets off his dark chestnut breast. His back is a rich brown, and his tail is adorned with iridescent blue and green feathers.
The female mallard has mottled brown overalls with an orange and brown bill.
The Mallard’s diet consists mostly of seeds, fruit, and insects. They have been known to consume small rodents when available. They usually feed at night in shallow water or on land near water sources.
Most Mallards live in wetlands such as ponds, lakes, and rivers. They also inhabit saltwater environments close to lands such as bays and estuaries.
Mallards are also social birds that travel in flocks during the migration. Males and females form monogamous pairs during the winter months when they migrate southward to warmer climates.
Scientific Name: Anas platyrhynchos
Height: 50–65 cm (20–26 in)
Wingspan: 81–98 cm (32–39 in)
Weight: 0.7–1.6 kg (1.5–3.5 lb)
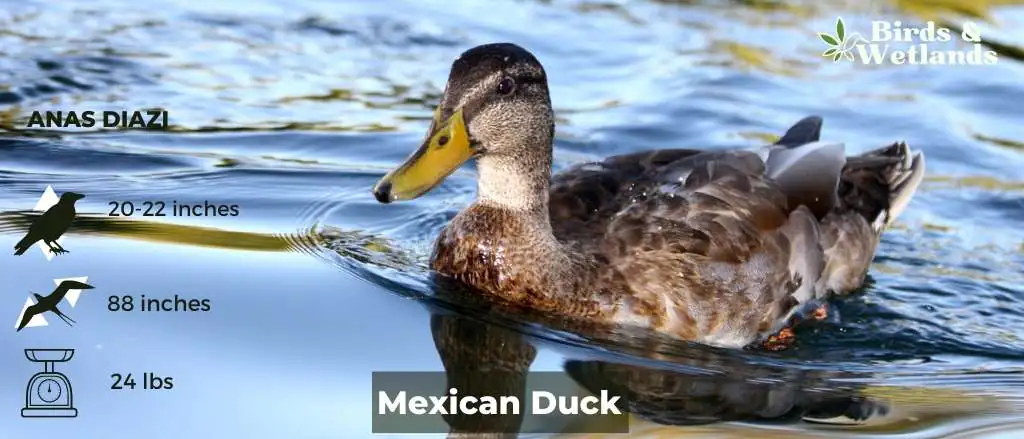

Mexican Duck
Listen to Mexican Duck
The Mexican Duck is a beautiful species that lives in Mexico and Central America. The Mexican Duck has a smaller head and neck than other ducks, and a brown body and tail. Its legs are also brown. These birds have long legs, short bill that curve upwards at the tips, and orange eyes.
Mexican ducks are omnivores that eat both plant matter and small animals such as insects or snails. They primarily eat aquatic vegetation like algae, water lilies or duckweed, and small fish, but will also eat small mammals, invertebrates such as snails or insects, and seeds from trees like oak or pine nuts.
Its habitat is mainly in the country’s mountain regions, but it is also found along the coastlines of Mexico and Central America, where it inhabits marshes, ponds, streams, rivers, lakes, and lagoons. They have adapted well to living near humans; they are often found around farms or even swimming pools.
The population of this bird has been declining in recent years, but they are still common enough to be spotted in the wild.
Scientific Name: Anas diazi
Height: 51–56 cm
Wingspan: 88 inches (2.24 meters).
Weight: 24 pounds (10.9 kg)
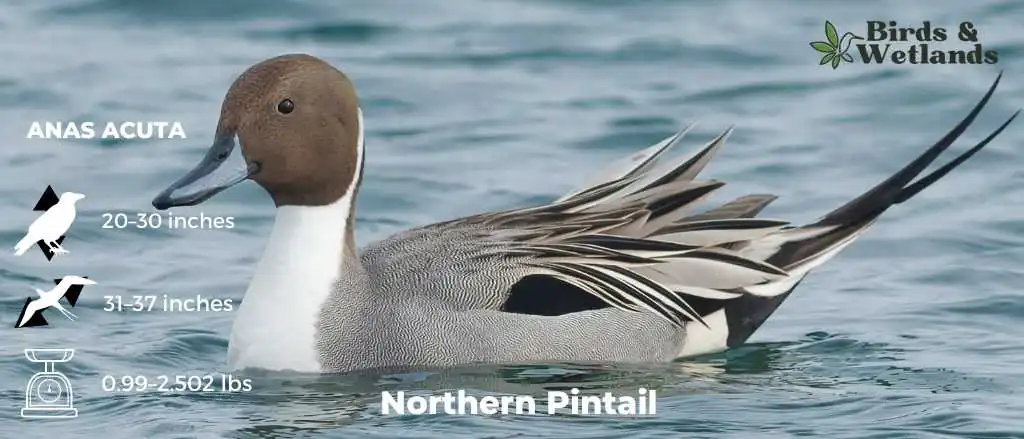

Northern Pintail
Listen to Northern Pintail
Northern Pintails are slender ducks with relatively long necks and tails. The male has a cinnamon-brown head, a white breast and throat. While males have gray bodies, females have rufous-brown plumage. Both sexes have a pale black-gray bill.
The Northern Pintail is a migratory bird that nests on or near open water with some vegetation nearby.
Northern Pintails feed on aquatic plants such as bulrush roots, pondweeds, and sedges. They also feed on seeds from different plants like grass, insects such as dragonflies, fish and other small animals worms and tadpoles.
There are approximately 1 million Northern Pintails left in the wild today.
Scientific Name: Anas acuta
Height:
Male: 59–76 cm (23–30 in)
Female: 51–64 cm (20–25 in)
Wingspan: 80–95 cm (31–37 in)
Weight:
Male: 450–1,360 g (0.99–3.00 lb)
Female: 454–1,135 g (1.001–2.502 lb)
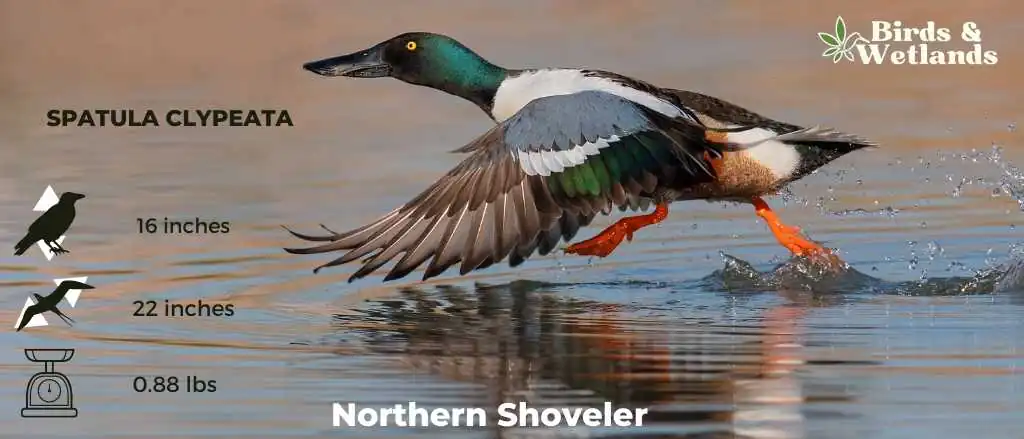

Northern Shovelers
credit https://xeno-canto.org/722967
The northern shoveler, often known as the shoveler in the United Kingdom, is a common and ubiquitous duck. With its brown head and neck and breast, greenish-yellow bill and wings, white breast and belly, and the dark greenback, and black tail feathers, it’s hard to mistake for any other duck species.
This duck lives in freshwater ponds, marshes, lakes, rivers, and streams but will also sometimes inhabit brackish water areas where the water has a high salt content. It breeds in North America from Canada to Mexico, migrating south for the winter months.
The Northern Shoveler’s diet consists primarily of aquatic plants like duckweed and water lettuce. It also eats insects, worms, crustaceans, and mollusks if they can find them in the water.
Wintering in southern Europe, the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Central and the Caribbean, it breeds in northern Europe, through the Palearctic, and across much of North America.
Scientific Name: Spatula clypeata
Height: 16 in (41 cm)
Wingspan: 22-inch (560 mm)
Weight: 14 oz (400 g)
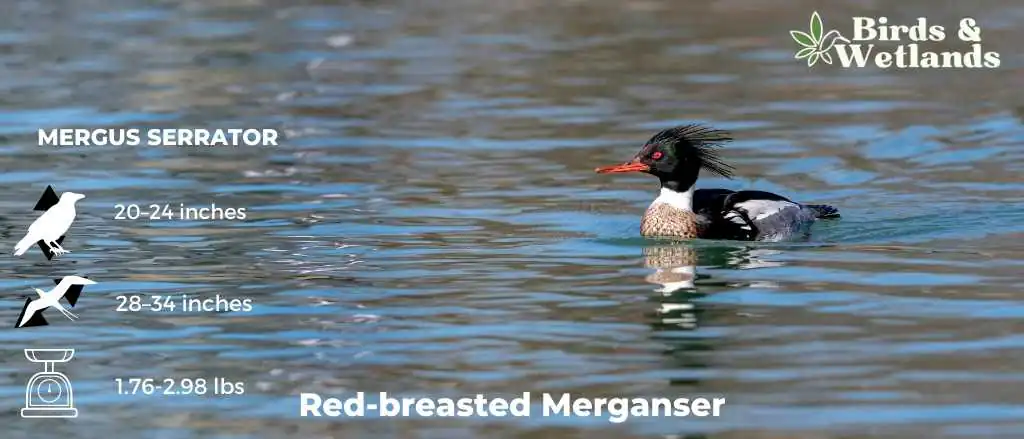

Listen to Red-breasted Merganser
Red-breasted Mergansers have long, slender bodies with equally long, thin bills and gray flanks.
Breeding males have cinnamon chests, red eyes, white neck bands and shaggy-looking green heads. The back and wings are dark brown, with some iridescent feathering on the wings.
Non-breeding males and females have mostly grayish bodies, spiky reddish-brown heads and brown eyes.
Red-breasted Mergansers feed on small fish by diving into the water. They use their wings to propel themselves forward like penguins do when swimming underwater.
Red-breasted Mergansers breed in boreal forests of North America. They inhabit lakes, rivers, and ponds where they can search for food and protect themselves against predators.
Red-breasted Mergansers are not endangered or threatened at this time because it has a very large population of over 8 million birds worldwide.
Scientific Name: Mergus serrator
Length: 51–62 cm (20–24 in)
Wingspan: 70–86 cm (28–34 in)
Weight: 28.2 to 47.6 oz (800 to 1,350 g)
Redhead (Aythya americana)
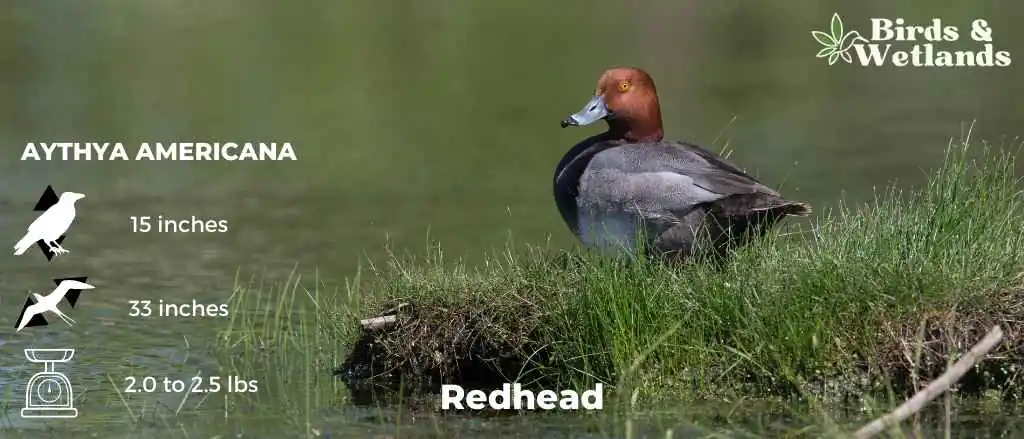

Redhead
The redhead duck is one of the most striking birds in North America. They are easily recognizable by their bright orange-red heads and chests, which contrast sharply with their pale grey bodies. Redheads are also known for their distinctive call, which sounds like a high-pitched whistle.
Scientific Name: Aythya americana
Length: 37 cm (15 in)
Wingspan: 84 cm (33 in)
Weight: 2.0 to 2.5 lbs
Redhead Description
Redhead Ducks are a common sight at the pond. They have a red head and white body, with some gray feathers on their wings. They are about the size of a mallard duck, but have shorter legs and a longer bill.
Redhead Sound
Redhead Habitat & Range
Redheads can be found throughout North America, with the exception of southern Mexico and parts of the southeastern United States. They are most common in coastal areas and large rivers. In fact, many people mistake them for musk ducks when they see them in freshwater habitats. Redheads tend to prefer shallow waters with plenty of vegetation near shorelines or riverbanks instead of deeper water where musk ducks tend to prefer staying put.
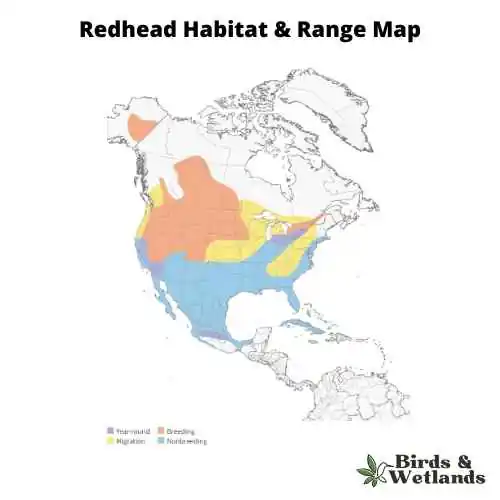
Redhead Range Map credit: https://www.allaboutbirds.org/
Redhead Diet
The redhead diet mainly consists of plant matter such as seeds, berries, shoots and buds from aquatic plants such as pondweed or cattails as well as insects such as dragonflies or small fish like minnows or smelt.
Redhead Nesting
The Redhead Duck lives on a diet of seeds and aquatic plants as well as insects and small fish. The female Redhead Duck lays between 8-12 eggs per clutch, which she then incubates for 28 days before they hatch. The male Redhead Duck will stay nearby while she is incubating her eggs and will care for them once they hatch by leading them to water where they can find food to eat.
Ring-necked Duck (Aythya collaris)

The Ring-necked Duck has a bright orange bill with a black tip and an olive-green head with a black mask across its eyes and down its beak. Its neck is white and speckled with gray, brown, or black patches. The rest of its body is grayish-brown to dark brown.
Scientific Name: Aythya collaris
Height: 15.3-18.1 in (39-46 cm)
Wingspan: 24.4-24.8 in (62-63 cm)
Weight: 17.3-32.1 oz (490-910 g)
Description
They are omnivorous so they also eat seeds and grains when they’re available too. They eat grasses, insects such as beetles and dragonflies when they’re available, seeds, and other types of plants like duckweed, water lilies, pondweeds, and grasses that grow along water edges or in open water areas.
Sound
Habitat & Range
It can be found throughout North America and Central America. It breeds in freshwater marshes, ponds, lakes, streams and the surrounding area. They’re also known to breed in saltwater marshes.
They use their bills to eat these things from the bottom of the lake or pond. They also swim underwater when they eat food. It prefers freshwater marshes, lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, and estuaries near forest edges where trees provide nesting sites for the ducklings.
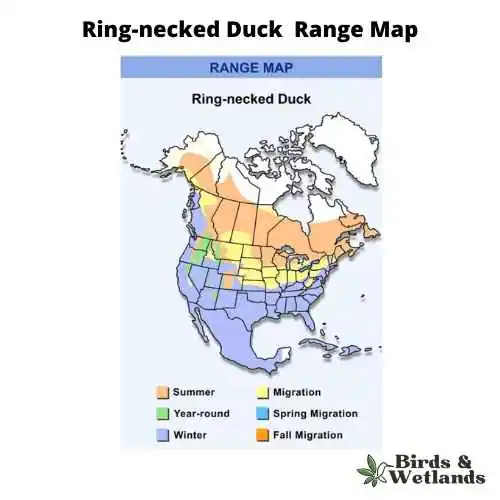
Ring-necked Duck Range Map credit: https://perceviaassets.azurewebsites.net/
Diet
They feed on aquatic plants like pondweed as well as insects and other invertebrates. They will also eat small crustaceans such as crabs or shrimp if they can find them in their habitat.
Nesting
During breeding season (which is usually in April or May), males will form flocks on the water while females lay eggs in nests made from grasses near shorelines or floating on debris near shorelines where there are no predators present to threaten their young hatchlings.

Ruddy Duck
Listen to Ruddy Duck
Ruddy Ducks, commonly referred to as Ruddies, are medium-sized ducks of North America.
Breeding males in their breeding plumage are unlike any other duck you’ve seen. They have thick necks, white cheeks and bright blue bills.
Females and non-breeding males are soft orange-brown with a dark, scoop-like bill.
Ruddy Ducks are omnivorous, eating plants and insects as well as fish and small animals. It eats insects, grains, seeds, and aquatic plants. They are monogamous animals; they mate for life and have one clutch per year of 4-6 eggs that hatch after 25 days.
Ruddy Ducks frequently move in small groups of 5–15 birds at night. They’re also very sociable animals.
Ruddy Ducks live in freshwater lakes, ponds, rivers, marshes, and swamps. They are migratory birds that spend the winter in South America. They are typically found in freshwater lakes and marshes during the mating season (April through August), but they can also be seen on rivers or coasts during migration or wintering months (October through February).
Scientific Name: Oxyura jamaicensis
Length: 13.8-16.9 in (35-43 cm)
Wingspan: 22.1-24.4 in (56-62 cm)
Weight: 10.6-30.0 oz (300-850 g)
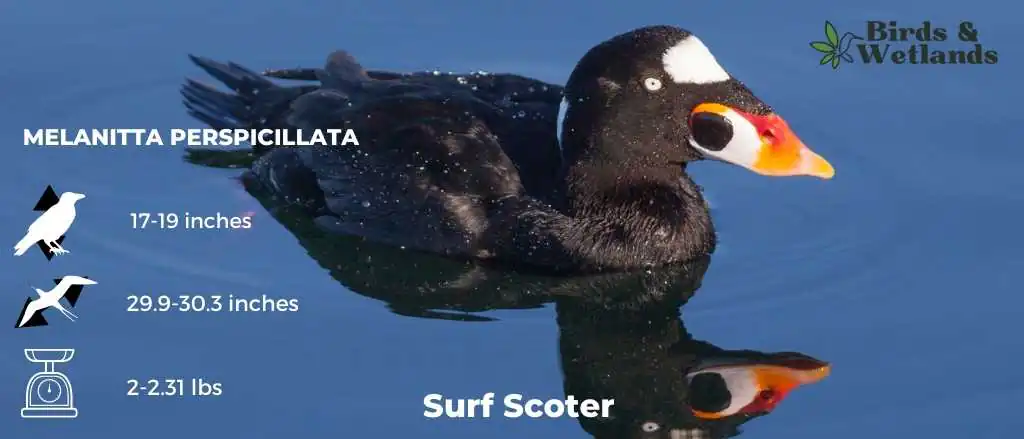

Surf Scoter
Listen to Surf Scoter
The Surf Scoter is a medium-sized sea duck black head, a colorful bill and white patches on the nape and forehead. They are “molt migrants,” meaning they migrate to an area where they may molt their flying feathers after nesting.
The Surf Scoter is an excellent swimmer, with webbed feet that allow it to dive after fish. They are able to dive deep into the ocean to find food, but they can only stay underwater for about 1 minute before having to come up for air.
The Surf Scoter’s diet consists of fish such as sand eels, anchovies, capelin, smelt, and herring. At times they can also feed on crustaceans such as krill or shrimp. It uses its bill to filter out small organisms from the water as it swims along the surface of the ocean.
The Surf Scoter breeds on Arctic coasts from Greenland to Alaska, but most populations migrate south to winter off California and Mexico. They can also be found along the coastlines of South America, Australia, New Zealand, and Japan.
Scientific Name: Melanitta perspicillata
Length:
Male: 48 cm (19 in)
Female: 44 cm (17 in)
Wingspan: 29.9-30.3 in (76-77 cm)
Weight:
Male: 1,050 g (2.31 lb)
Female: 900 g (2.0 lb)

White-winged Scoter
Listen to White-winged Scoter
The White-winged Scoter is classified as an “oceanic” bird because it spends most of its time in marine waters. They have white feathers on their wings and are named after the white patch on their back. It is a medium-sized duck that has a black head, neck, and upper body, with a white breast and belly. The rest of its plumage is dark brown.
They feed primarily on mollusks, crustaceans, and fish, which they find by sweeping their bills side to side through the water in search of prey. When this happens, you’ll hear them make a loud clacking noise with their bills—which is how they got their name “scoter”.
It prefers to make its home near the coastlines of North America, Europe, and Asia. They can be found in large groups of other waterfowl but prefer to keep themselves separate from them.
They are migratory birds that make seasonal journeys between northern Canada and Mexico each spring/summer season before returning south for the winter months (December through April).
Scientific Name: Melanitta deglandi
Length: 18.9-22.8 in (48-58 cm)
Wingspan: 31.5 in (80 cm).
Weight: 33.5-63.5 oz (950-1800 g)
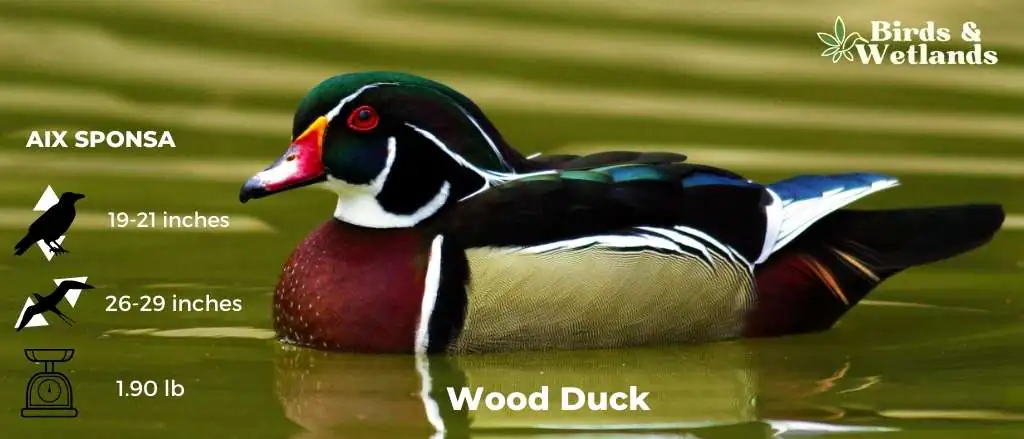

Wood Duck
Listen to Wood Duck
The Wood Duck is a medium-sized duck. It is a s a member of the Anatidae family and is native to North America. It ranges from southern Canada all the way down to Panama.
The male wood duck has a green crested head, red eyes, and chestnut breast with white flecks. The female has a brown body with a grayish head, which is also slightly crested, a white teardrop eye patch, and a blue patch on the wing.
They are omnivores meaning they eat both plants such as cherries and grapes, aquatic plants such as pondweeds and water lilies, and animals but are mainly insectivores feeding on small invertebrates such as insects and worms.
They live in wooded areas near water sources like ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, marshes, and swamps. They live in large flocks during the breeding season and then move to smaller groups during migration or winter.
The population of the wood duck was in serious decline in the late 19th century as a result of severe habitat loss and market hunting both for meat and plumage for the ladies’ hat market in Europe. By the beginning of the 20th century, wood ducks had virtually disappeared from much of their former range.
Scientific Name: Aix sponsa
Height: 47 to 54 cm (19 to 21 in) ( or 1.5 feet max.)
Wingspan: 66 to 73 cm (26 to 29 in)
Weight: 454-862 g (16.0-30.4 oz)
Where to Watch Ducks in Nevada?
Nevada, characterised by its arid landscapes, diverse wetlands, and unique habitats, is an intriguing destination for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts looking to observe a wide array of duck species. Notable birdwatching locations within the state include the Stillwater National Wildlife Refuge, the Ruby Lake National Wildlife Refuge, and the Anaho Island National Wildlife Refuge, all offering ample opportunities for exploration and admiration of these captivating ducks.
Conveniently located about 80 miles north of Las Vegas, Pahranagat National Wildlife Refuge offers plenty of bird-watching opportunities. The refuge is a stopover point for many birds travelling the Pacific Flyway during migration.
Floyd Lamb Park at Tule Springs is home to many different species of ducks. The 680-acre park has lakes surrounded by trees and vegetation.
Stillwater National Wildlife Refuge is another excellent spot for duck watching. The refuge consists of several lakes and marshes, which attract tens of thousands of waterfowl and shorebirds. Visitors can also see a variety of other birds, such as eagles and owls.
Neighbouring states offer even more fascinating birdlife can be discovered. To the north, you can explore the enchanting ducks in Oregon and marvel at the diverse species that inhabit the state’s wetlands.
Venturing eastward, you’ll encounter the picturesque landscapes of Utah, which host the intriguing duck populations in Utah, offering a fresh perspective on these delightful birds.
Go south, delve into the duck habitats in Arizona and immerse yourself in the state’s rich ecosystems, appreciating the beauty and variety of ducks found throughout the region.
Are There Any Resident Ducks in Nevada?
Aside from domestic ducks, Nevada has a few resident duck populations and the most common among them are wood ducks. Wood ducks are known for their striking plumage. Many flocks of wood ducks live in the western part of the state all year round while other flocks breed in the northeastern region of Nevada.
While they are not reliant on open water like some other ducks, wood ducks do need access to shallow ponds or streams in order to find food. As a result, they are often found near wetlands or other water sources. So don’t be surprised if you encounter these birds at your local pond.
Duck Hunting in Nevada
Nevada is home to a large number of ducks. So it’s not surprising that duck hunting is one of the most popular pastimes in many parts of the state.
Duck hunting season in Nevada typically runs from September (Elko and White Pine Counties) to January.
Waterfowl hunters are required to have a valid hunting license as well as a Federal Migratory Bird Hunting Stamp and a Nevada HIP (Harvest Information Program) number.
There are also a number of restrictions in place, such as a general daily bag of 7 and a possession limit of 21.
Can You Shoot Ducks in Nevada?
Yes, you can shoot ducks in the state of Nevada. However, lead shots are strictly prohibited. Instead, waterfowl hunters must use federally and state-approved non-toxic shots.
Where Can I Hunt Ducks in Nevada?
Nevada maintains several wildlife management areas, some of which provide many waterfowl hunting opportunities.
Some of the popular WMAs to hunt ducks include Mason Valley WMA which is located southeast of Reno and covers about 16,000 acres of land. Overton WMA which is located northeast of Las Vegas is popular for its controlled waterfowl hunts.
Ash Meadows and Pahranagat national wildlife refuges are two of the best waterfowl hunting spots in the southern part of the state.
Final Thoughts on Ducks in Nevada
Nevada has a vast amount of public land, including many protected areas and wildlife management refuges. These places provide suitable habitats for many birds including several species of ducks and other aquatic birds. The state also has a healthy domestic duck population.
Moreover, the state is located on the Pacific Flyway, a major migratory route for many birds from the north. Ducks passing through the state during migration often stop to rest and feed in Nevada’s wetlands, rivers, lakes, ponds, and marshes.

